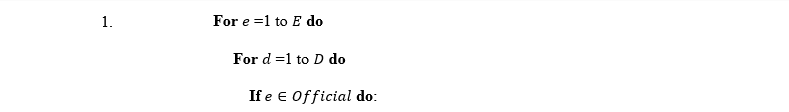- 👋 Hi, I’m Thuy Pham Tran Minh
- 👀 This is the thesis topic for the Degree of Bachelor of Engineering in Logistics and Supply Chain Management
- 📫 How to reach me: phamtranminhthuy@gmail.com
✨ METAHEURISTIC FOR STAFF SCHEDULING PROBLEM IN ORDER FULFILLMENT: A CASE STUDY OF LAZADA ELOGISTICS VIETNAM ✨
- Objectives of Study:
The solution of the scheduling model in this study will help not only Lazada E-Logistics Express but also other e-commerce platforms which have its order fulfillment service launch its outbound sales plan. When a vast majority of customer orders occurs, the outbound operation needs to work in full capacity. The rostering team needs some support tools to assign both temporary and official staff effectively in each area. Therefore, utilizing this rostering implementation in sales campaigns will help a company make the right decision at the right time to hire employees with affordable costs whilst satisfying worker preferences. These tools also can help managers reduce a bottleneck caused by improper assignment. Simultaneously, building a transparent contract including legal regulations, workplace policies, penalty, fixed labor cost, bonus cost, and other conditions not only ensure the rights and duties of employees but also help a warehouse avoid a sudden withdrawal.
- Scope:
The use of scheduling methods is crucial in building an effective real-world staff scheduling problem. This paper is aimed at solving a problem domain from order fulfillment industry, which plays a key vital to satisfy such a sudden increase of customer satisfactions, especially in Covid-19 pandemic by and large. There are two main objective functions including minimize the hiring cost and maximize the aspirations of workers.
In this research, Requirement-Based Staff Scheduling Algorithm (RSSA) is introduced to compare with a two-phase Mixed Integer Programming and Genetic Algorithm with two-dimensional array chromosome structure. Mathematical model of phase 1 is implemented to give a fesible solution for the first target. Besides, experimental results highlight that RSSA and mathematical model of phase 2 could be applied effectively in current scale for the second goal. Especially, this novel algorithm tends to save more time whilst the Mixed Integer Programming model seems to satisfy high percentage of staff preferences when a demand forecasting is fluctuated. On the other hand, Genetic Algorithm is recommended in case of a scale of data is immense.
------------- MODELLING FOR REQUIREMENT-BASED STAFF SCHEDULING ALGORITHM -------------
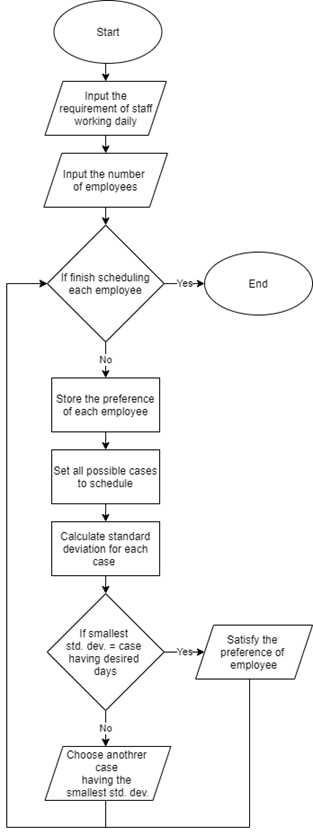
To follow closely the first phase, this thesis introduces the RSSA in this second phase to schedule working days based on the requirement of employees for each day. The highest priority is to minimize the standard deviation of demand after finishing rostering which tends to avoid the high fluctuation of employees between daily work. This algorithm helps reduce overstaffing and understaffing which leads to better control. Figure 4.1 shows a background implementation of RSSA.
First of all, the requirement of staff needed per day and the number of employees which should be scheduled is inputted. Each contract will have different preferences including day-off, five consecutive days, three consecutive days, and two consecutive days. Simultaneously, there are also different cases that could happen to schedule each type of staff. It is necessary to calculate all standard deviations between the requirement and each case to find out which case has the smallest standard deviation. In case that the preference and convenience of both official and temporary workforce do not affect the smallest standard deviation, the unique rule is set to satisfy their desire.
The pseudo-code of RSSA summarizes how this rule is applied.
- Notations:
E: The number of employees (e=1,…,E)
OffRegister: The request day-off of official employees
Official: Set of official employees
Twday: Set of two-day-contract employees
Thday: Set of three-day-contract employees
Fiday: Set of five-day-contract employees
D: The number of working days (d=1,…,D)
Schedule[e][d]: Binary variables; Schedule[e][d]=1 if employee ⅇ is assigned to day d, otherwise Schedule[e][d]=0
Requirement[d]: The number of employees required for day d
- Process: