It is a code that uses geometry measers to evaluate Feature subsets and to select optimal Feature subsets based on them.
Feature subset's evaluation implements the 'Feature selection based on geometric distance for high-dimensional data.' introduced in the paper.
This is a hybrid feature selection that combines filter and wrapper.
Therefore, even if this technique is not applied as it is, it would be a good reference for those who want to implement the hybrid method.
It can be used through 'pip install gdbfs'.
Please refer to the Repository 'https://github.com/seo-young-kim/GDBFS_deploy' for details.
This page provides a brief description of the techniques.
Reference 'Lee, J. H., & Oh, S. Y. (2016). Feature selection based on geometric distance for high-dimensional data. Electronics Letters, 52(6), 473-475.'.
This technique uses the distance between classification classes. So it can only be applied to classification problems.
The measurement for Feature subsets is multiplied by two geometric distances.
First, the distance between classes from the corresponding Feature subspace is achieved.
When referenced in the figure1, the further the distance between the center of the class and the smaller the intracranial partiality, the easier it will be classified.
Therefore, (the distance between the center of the class) - (class Internal Variance) is used as measurement.
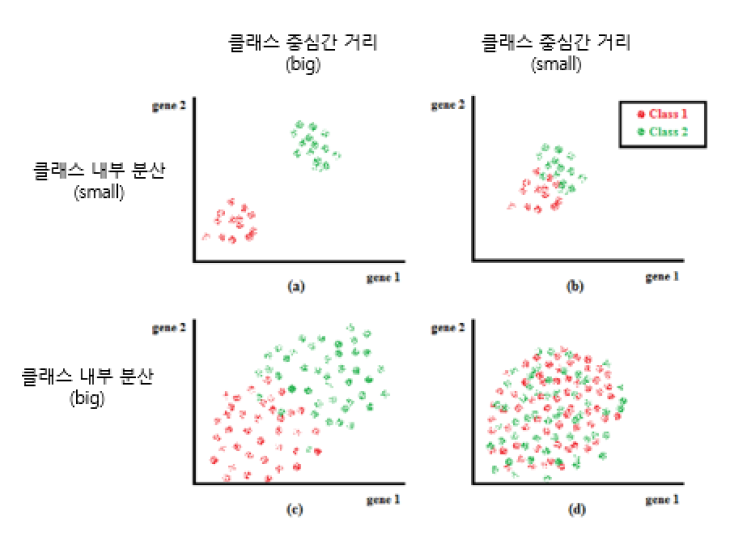
The more equal the distance between classes in the Feature subspace, the easier it can be expected to be classified.
Therefore, it is used as a second measurement.
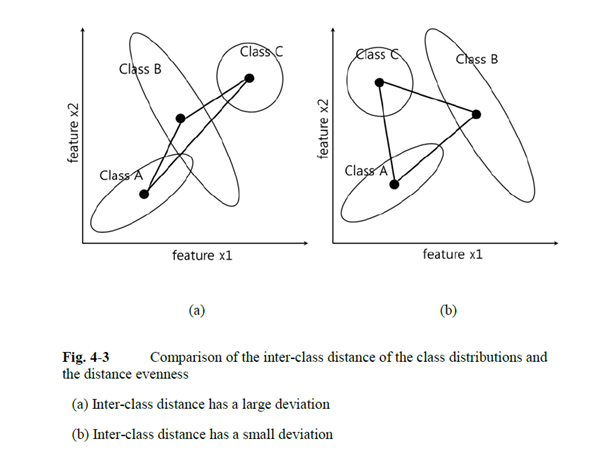
Figure 2. Comparision of the inter-class distance of the class distributions and the distance evenness from : Feature selection based on geometric distance for high-dimensional data. Electronics Letters, 52(6), 473-475.
Through Sequential Forward selection, we can selects feature subsets with maximum gdbfs value.
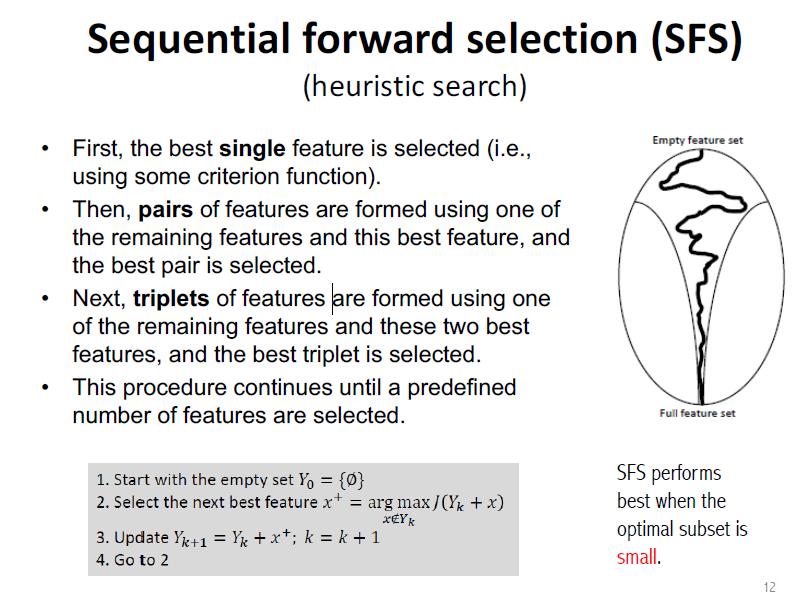
Figure 3. Sequential forward selection from : https://www.cc.gatech.edu/~bboots3/CS4641-Fall2018/Lecture16/16_FeatureSelection.pdf