Hi! This repository includes my project work done during my 7th semester major project "Practical Sign Language Recognition System using Deep Learning." This work is primarily focused on the deep learning model compression technique knowledge distillation. We achieve an overall accuracy of 89.667% and a maintained accuracy of 88.357% after compressing the model by a factor of 3.5 using knowledge distillation.
It is essentially a method of deploying high level deep learning models in devices with low specifications and power without hindering model performance. Model compression helps in increasing the lifetime of a deep learning model, by reducing its complexity and size so it can be easily implemented in several devices, making it more and more viable for years to come. Different types of model compression techniques are -
- Pruning: A method where connections between neurons or sometimes entire neurons, channels or filters are removed from trained models.
- Quantization: Achieves model compression by reducing the size of weights present.
- Low-Rank Approximation: It is a matrix decomposition technique done to evaluate useful parameters within a network. Similar to pruning in a way.
- Selective Attention: Only the layers and objects of interest and those which contribute towards the mode are considered, and rest of the elements are discarded.
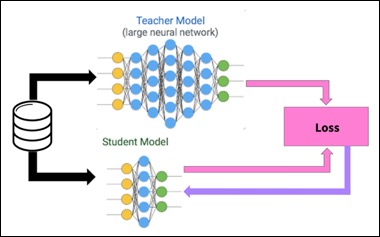
- Knowledge Distillation: Knowledge distillation is built on the idea that training and inference are two different tasks, and that the same model need not be used for each. (This is the technique used in the project)
Knowledge distillation is built on the idea that training and inference are two different tasks, and that the same model need not be used for each. Here a base expert model called the teacher model is trained, and its learning is then used to teach a much smaller student model with fewer parameters in comparison to mimic the base model’s performance. The goal is so that smaller student model has the same distribution as the larger teacher model and thus can be used for deployment. This is a model optimization technique. A student model is developed with much lesser parameters in comparison to the base model. The student model is then distilled over the teacher model i.e., trained using the base model. The outputs of the base model are replicated by the student model at each epoch, which enables the student model to mimic the exact behavior of the base model without actually having the same parameters as the base model but if there is a large enough difference in between the parameters and complexity of the teacher and student model, then the performance of the network can degrade while distilling it. Knowledge Distillation can substantially reduce the computational power of a Deep Learning Model without affecting it’s performance negatively. Therefore, it allows lower end devices such as mobile phones and embedded systems to compute the model without the cost of losing out on the accuracy. This is the motivation for Knowledge Distillation.
- Python (3.6 or higher)
- Pandas
- Keras
- Tensorflow
- Numpy
- Matplotlib
- Scipy
- Scikit-Learn
- Seaborn
- The dataset used in this study was acquired with the help of 5 volunteers. Different modalities were captured using Surface Electro-myogram or sEMG, tri-axis gyroscope and tri-axis accelerometer, and a multi-modal and multi-sensor database of signals for 50 commonly used signs from the Indian sign language (ISL), both static and dynamic. There are a total of 5,000 observations (50 signs, performed by 5 subjects, each sign performed 20 times by each subject), therefore making it 100 observations for each sign.
- Signals were recorded using six Delsys wireless sensors, consisting of one sEMG sensor and one IMU containing a tri-axis accelerometer and a tri-axis gyroscope each. The sampling period sEMG sensors was 900 μs and for accelerometer and gyroscopes, 6.7 ms and 16 bits per sample.
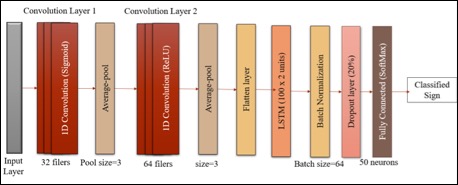
- 1D convolutional layer with 32 filters after the initial input layer with Sigmoid activation function.
- Average-pooling layer, with the pool size as 3
- Another 1D convolutional layer with 64 filters with ReLU activation function.
- Another average pool layer with the pool size as 3.
- Flatten layer which converts the data into one-dimension to make it appropriate for the next layer.
- 2 units of LSTM layer (Long Short-Term Memory), having 100 in each unit (200 total). These networks are a similar to an RNN, and are capable of learning order dependencies. Such a layer does data processing, while passing on information as it moves forward.
- A Batch normalization layer, with the batch size as 64.
- A Dropout layer with 20% dropout to avoid overfitting.
- A Dense or a fully connected layer with 50 neurons owing to the 50 target classes
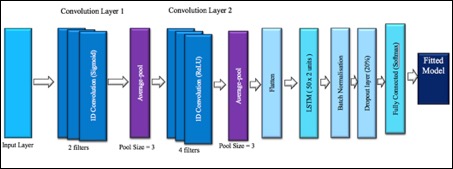
- 1D convolutional layer with 2 filters after the initial input layer with Sigmoid activation function.
- Average-pooling layer, with the pool size as 3
- Another 1D convolutional layer with 4 filters with ReLU activation function.
- Another average pool layer with the pool size as 3.
- Flatten layer which converts the data into one-dimension to make it appropriate for the next layer.
- 2 units of LSTM layer (Long Short-Term Memory), having 50 in each unit. (100 total). These networks are a similar to an RNN, and are capable of learning order dependencies. Such a layer does data processing, while passing on information as it moves forward.
- A Batch normalization layer, with the batch size as 64.
- A Dropout layer with 20% dropout to avoid overfitting.
- A Dense or a fully connected layer with 50 neurons owing to the 50 target classes
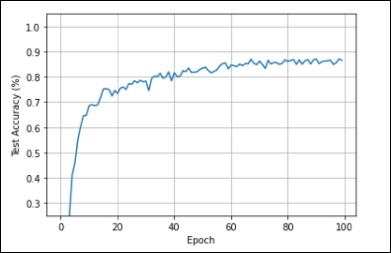
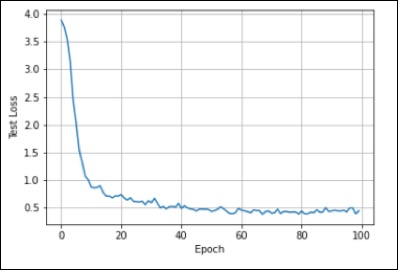
Accuracy: 89.667%
Size: 523,418 bytes
Accuracy: 88.357%
Size: 132,153 bytes
We would like to recognize the funding support provided by the Science & Engineering Research Board, a statutory body of the Department of Science & Technology (DST), Government of India, SERB file number ECR/2016/000637.