Name of vulnerable machine: De-COW.
De-COW is a vulnerable machine made for a CTF. In this vulnerable machine Dirty COW vulnerability is established. Dirty COW vulnerability is a type of privilege escalation exploit, which essentially means that it can be used to gain root-user access on any Linux-based system. While security experts claim that such kinds of exploits are not uncommon, its easy-to-exploit nature and the fact that it has been around for more than 11 years is pretty worrisome. Dirty COW gets its name from the copy-on-write (COW) mechanism in the kernel's memory management system. Malicious programs can potentially set up a race condition to turn a read-only mapping of a file into a writable mapping. Thus, an underprivileged user could utilize this flaw to elevate their privileges on the system. By gaining root privileges, malicious programs obtain unrestricted access to the system. From there on, it can modify system files, deploy keyloggers, access personal data stored on your device, etc.
Dirty COW vulnerability affects all versions of the Linux Kernel since version 2.6.22, which was released in 2007. According to Wikipedia, the vulnerability has been patched in kernel versions 4.8.3, 4.7.9, 4.4.26 and newer. A patch was released in 2016 initially, but it didn't address the issue fully, so a subsequent patch was released in November 2017. Major Linux distros like Ubuntu, Debian and ArchLinux have all released the appropriate fixes. So if you haven't already, make sure to update your Linux kernel.
Since most of the systems are now patched, the risk is mitigated, right? Well, not exactly.
While most of the mainstream systems have been patched, there are several other Linux-based embedded devices like IoT devices that are still vulnerable. Since Android is based on the Linux kernel, a majority of Android devices are also affected.
ZNIU is the first malware for Android based on the Dirty COW vulnerability. It can be utilized to root any Android devices up to Android 7.0 Nougat. While the vulnerability itself affects all versions of Android, ZNIU specifically affects Android devices with the ARM/X86 64-bit architecture. The ZNIU-affected app often appears as a soft-porn app on malicious websites, where users are tricked into downloading it. Since Android makes it easy to sideload apps, a lot of novice users fall into this trap and download it. If your device is running Android 4.4 KitKat and above, make sure that you have the latest security patch installed. To check this, open Settings > About phone. Scroll to the bottom and check Android security patch level. If the installed security patch is newer than December 2016, you should be protected from this vulnerability. While Android antivirus apps can detect such elevated-permission attacks, they cannot prevent it. Anti-virus apps may be useful for other features such as anti-theft, but they certainly aren't much use in this case. As a final precaution, you should be mindful when it comes to installing apps from unknown sources. Android 8.0 Oreo makes installing apps from unknown sources a little bit safer, but you should still proceed with caution.
Step 1: Download old releases of Ubuntu.
Visit http://old-releases.ubuntu.com/releases/ if you want to download old releases of ubuntu.
I have downloaded 16.04.1/ version for making this vulnerable machine.
Step 2: Use virtual box to install this as it is easy to export the OVA file that you later will upload on some CTF platforms.
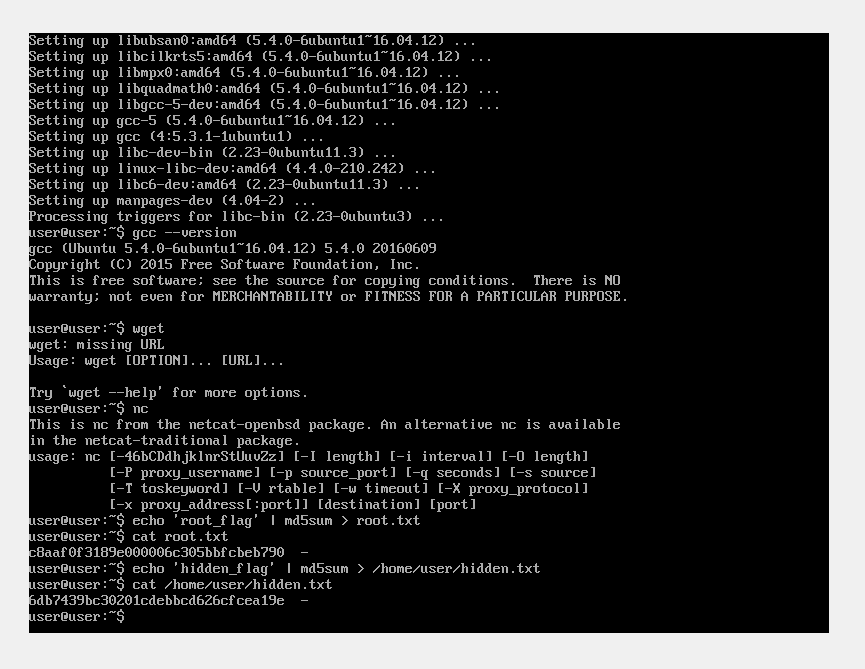
Step 3: We have to exploit this box through Dirty Cow and it is written in C language so we need a compiler. For this is gcc so we check the version of gcc by running the command:
gcc --version
If it is not installed before then run the following command to install it:
apt install gcc
Step 4: In order to add root and hidden flags just type any text and pipe into md5sum to get a md5 hash and store it in files and make sure to give it permissions that only specific user can read those flags.

Step 5: In order to configure FTP server on this box run the following command:
vsftpd
Step 6: To make a backup of configuration file, run the following command:
cp /etc/vsftpd.conf /etc/vsftpd.conf.orig
Step 7: To enable ftp service run the following command:
service vsftp start
Step 8: To connet ftp service run the following command:
ftp localhost
Step 9: To configure HTTP server we have to allow ufw (Uncomplicated Firewall) to enable traffic for http or port 80 by running the following command:
ufw allow http
Step 10: Run php on web pages
Step 11: Inorder to create page vulnerable to RCE we need to do something like this:
Step 12: To export this vulnerable machine into OVA format, go to File > Export Appliance then select your virtual machine.
Export is completed!!!
NOTE: If any command doesn't run then prefix sudo before the command which will give administrative privileges to the user.
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1Wr4Q3rI9elqvRNQpk32TDMVlKtSxAxqN/view?usp=sharing