- Create a flutter project named flutter_calculator as explained earlier
- A simple counter project is created as default.
- Since our aim does not involve any functoinality of this we will remove this code.
- So, in main.dart file of lib directory, we remove the code which is of no use to us i.e. from Line 32(remove the following code).
class MyHomePage extends StatefulWidget {
const MyHomePage({super.key, required this.title});
// This widget is the home page of your application. It is stateful, meaning
// that it has a State object (defined below) that contains fields that affect
// how it looks.
// This class is the configuration for the state. It holds the values (in this
// case the title) provided by the parent (in this case the App widget) and
// used by the build method of the State. Fields in a Widget subclass are
// always marked "final".
final String title;
@override
State<MyHomePage> createState() => _MyHomePageState();
}
class _MyHomePageState extends State<MyHomePage> {
int _counter = 0;
void _incrementCounter() {
setState(() {
// This call to setState tells the Flutter framework that something has
// changed in this State, which causes it to rerun the build method below
// so that the display can reflect the updated values. If we changed
// _counter without calling setState(), then the build method would not be
// called again, and so nothing would appear to happen.
_counter++;
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
// This method is rerun every time setState is called, for instance as done
// by the _incrementCounter method above.
//
// The Flutter framework has been optimized to make rerunning build methods
// fast, so that you can just rebuild anything that needs updating rather
// than having to individually change instances of widgets.
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
// Here we take the value from the MyHomePage object that was created by
// the App.build method, and use it to set our appbar title.
title: Text(widget.title),
),
body: Center(
// Center is a layout widget. It takes a single child and positions it
// in the middle of the parent.
child: Column(
// Column is also a layout widget. It takes a list of children and
// arranges them vertically. By default, it sizes itself to fit its
// children horizontally, and tries to be as tall as its parent.
//
// Invoke "debug painting" (press "p" in the console, choose the
// "Toggle Debug Paint" action from the Flutter Inspector in Android
// Studio, or the "Toggle Debug Paint" command in Visual Studio Code)
// to see the wireframe for each widget.
//
// Column has various properties to control how it sizes itself and
// how it positions its children. Here we use mainAxisAlignment to
// center the children vertically; the main axis here is the vertical
// axis because Columns are vertical (the cross axis would be
// horizontal).
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
const Text(
'You have pushed the button this many times:',
),
Text(
'$_counter',
style: Theme.of(context).textTheme.headlineMedium,
),
],
),
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: _incrementCounter,
tooltip: 'Increment',
child: const Icon(Icons.add),
), // This trailing comma makes auto-formatting nicer for build methods.
);
}
}
- Now we will create the file for our calculator screen, for which we will create a new file in lib folder named calc.dart.
- In the new file, we will create a stateful widget as our screen will have values that change.
- For that just type stf and from the options available choose flutter stateful widget.

- Name this widget CalcPage, we are left with the following code in calc.dart
import 'package:flutter/src/widgets/framework.dart';
import 'package:flutter/src/widgets/placeholder.dart';
class CalcPage extends StatefulWidget {
const CalcPage({super.key});
@override
State<CalcPage> createState() => _CalcPageState();
}
class _CalcPageState extends State<CalcPage> {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return const Placeholder();
}
}
- Now we change the page loaded when our app opens with changing Line 27 in main.dart.
home: const CalcPage(),
- Now we will create the front end part(UI) of our app.
- For that we use Scaffold widget wrapped with SafeArea to be returned from CalcPage at Line 14
return SafeArea();
- Adding Scaffold widget as a child of SafeArea:
return SafeArea(
child: Scaffold(),
);
The Scaffold() widget has properties like appBar, body, floating action button etc. So here we will be making use of the appBar and body properties. The appBar property is where we provide the title and other actions in our app. The app bar is quite simple with a background colour and a text
- Now we will create an app bar for our application by adding appBar attribute to our Scaffold .
child: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(),
),
- In the AppBar widget, we give the title attribute a Text widget widget with name Calculator.
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text("Calculator"),
),
In AppBar() widget we can provide the background color, title and center title properties as below:
appBar: AppBar(
backgroundColor: Colors.lightGreen,
title: Text("Calculator"),
centerTitle: true,
),
- Next we come to the body property of Scaffold(). The body consists of 20 buttons to calculate and clear the result and an area to display the answer.
- body part of scaffold will contain a container at Line 22.
body: Container(),
- As we have buttons below the output bar, we will need a Column with 3 parts.
body: Container(
child: Column(children: []),
),
- We will add two containers, one for output part, other for the buttons.
child: Column(
children: [
Container(),
Container(),
Container(),
],
),
- The first container has a text widget which contains the expression.
child: Column(
children: [
Container(
child: Text('0 + 0'),
),
Container(),
Container(),
],
),
- Since the calculator are generally right alligned.
child: Column(
children: [
Container(
alignment: Alignment.centerRight,
child: Text('0 + 0'),
),
Container(),
Container(),
],
),
- Second Container will contain the output.
child: Column(
children: [
Container(
alignment: Alignment.centerRight,
child: Text('0 + 0'),
),
Container(
alignment: Alignment.centerRight,
child: Text('0'),
),
Container(),
],
),
- Since the buttons are in a grid, we will create a column widget first.
Container(
child: Column(),
),
- Now, we will create 5 rows to form the grid.
Container(
child: Column(
children: [
Row(),
Row(),
Row(),
Row(),
Row(),
],
),
),
- Each Row contains 4 buttons.
- Since all the buttons look the same, we will create a new widget so that we dont have to write same code again and again.
- Create a new file my_button.dart
- In that file we will create a stateless widget as no changes are required in the buttons. For the same we will type stl and choose the first option.

- Name that class created as MyButton.
- The file will be as follows:
import 'package:flutter/src/widgets/framework.dart';
import 'package:flutter/src/widgets/placeholder.dart';
class MyButton extends StatelessWidget {
const MyButton({super.key});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return const Placeholder();
}
}
- Now we will change the return widget of the MyButton class and return a GestureDetetor.
return GestureDetector();
- Now we will assign the child attribute of the gestureDetector with Container.
return GestureDetector(
child: Container(),
);
- Since we need to show a digit/operator in this button.
return GestureDetector(
child: Container(
child: Center(
child: Text('0'),
),
),
);
- Since every button will show different text, we need to give this class an attribute buttonText which changes with every button. We can also add a diff color with operators and digits. Thus, we add the following at Line 6
String buttonText;
Color buttonColor;
- Now we need to change the constructor of the class with new variables.
MyButton({super.key, required this.buttonColor, required this.buttonText});
- Now, we give the color passed as attribute to the container and buttonText as the displayed text, after which the file my_button.dart.
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:flutter/src/widgets/framework.dart';
import 'package:flutter/src/widgets/placeholder.dart';
class MyButton extends StatelessWidget {
final String buttonText;
final Color buttonColor;
MyButton({super.key, required this.buttonColor, required this.buttonText});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return GestureDetector(
child: Container(
color: buttonColor,
child: Center(
child: Text(buttonText),
),
),
);
}
}
- Now we add buttons to the grid we created. For that we need to import the my_button.dart at Line 5 in calc.dart.
import 'my_button.dart';
- Adding the buttons to the grid. The code to the grid at Line 35 and we will give light blue color to the digits and orange color to the operators.
Container(
child: Column(
children: [
Row(
children: [
MyButton(
buttonColor: Colors.orange,
buttonText: 'C',
),
MyButton(
buttonColor: Colors.orange,
buttonText: 'Del',
),
MyButton(
buttonColor: Colors.orange,
buttonText: '%',
),
MyButton(
buttonColor: Colors.orange,
buttonText: '/',
),
],
),
Row(
children: [
MyButton(
buttonColor: Colors.lightBlue,
buttonText: '7',
),
MyButton(
buttonColor: Colors.lightBlue,
buttonText: '8',
),
MyButton(
buttonColor: Colors.lightBlue,
buttonText: '9',
),
MyButton(
buttonColor: Colors.orange,
buttonText: 'x',
),
],
),
Row(
children: [
MyButton(
buttonColor: Colors.lightBlue,
buttonText: '4',
),
MyButton(
buttonColor: Colors.lightBlue,
buttonText: '5',
),
MyButton(
buttonColor: Colors.lightBlue,
buttonText: '6',
),
MyButton(
buttonColor: Colors.orange,
buttonText: '-',
),
],
),
Row(
children: [
MyButton(
buttonColor: Colors.lightBlue,
buttonText: '1',
),
MyButton(
buttonColor: Colors.lightBlue,
buttonText: '2',
),
MyButton(
buttonColor: Colors.lightBlue,
buttonText: '3',
),
MyButton(
buttonColor: Colors.orange,
buttonText: '+',
),
],
),
Row(
children: [
MyButton(
buttonColor: Colors.lightBlue,
buttonText: '.',
),
MyButton(
buttonColor: Colors.lightBlue,
buttonText: '0',
),
MyButton(
buttonColor: Colors.lightBlue,
buttonText: '00',
),
MyButton(
buttonColor: Colors.orange,
buttonText: '=',
),
],
),
],
),
),
-Now that our basic structure is ready we will make it visually appealing. For that we will change the height and width of the containers.
- We can use simple numbers like 50,100, etc. or we can use the screen's width and height for giving size to the widgets. For that we use :
MediaQuery.of(context).size.width;
MediaQuery.of(context).size.height;
- Now we will give height and width to the first container i.e. expression display box. Add the following lines at Line 28
width: MediaQuery.of(context).size.width * 0.9,
height: MediaQuery.of(context).size.height * 0.2,
- Similarly add height and width to the second container at Line 34
width: MediaQuery.of(context).size.width * 0.9,
height: MediaQuery.of(context).size.height * 0.2,
- Now we will change the height and width of the buttons. Add the following lines at Line 14 of my_button.dart.
width: MediaQuery.of(context).size.width * 0.2,
height: MediaQuery.of(context).size.height * 0.1,
- Now we will give spacing to the grid. Add following line at Line 26 in calc.dart.
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceEvenly,
-
Similarly add same line after every Row and Column. The app appears as follows so far.
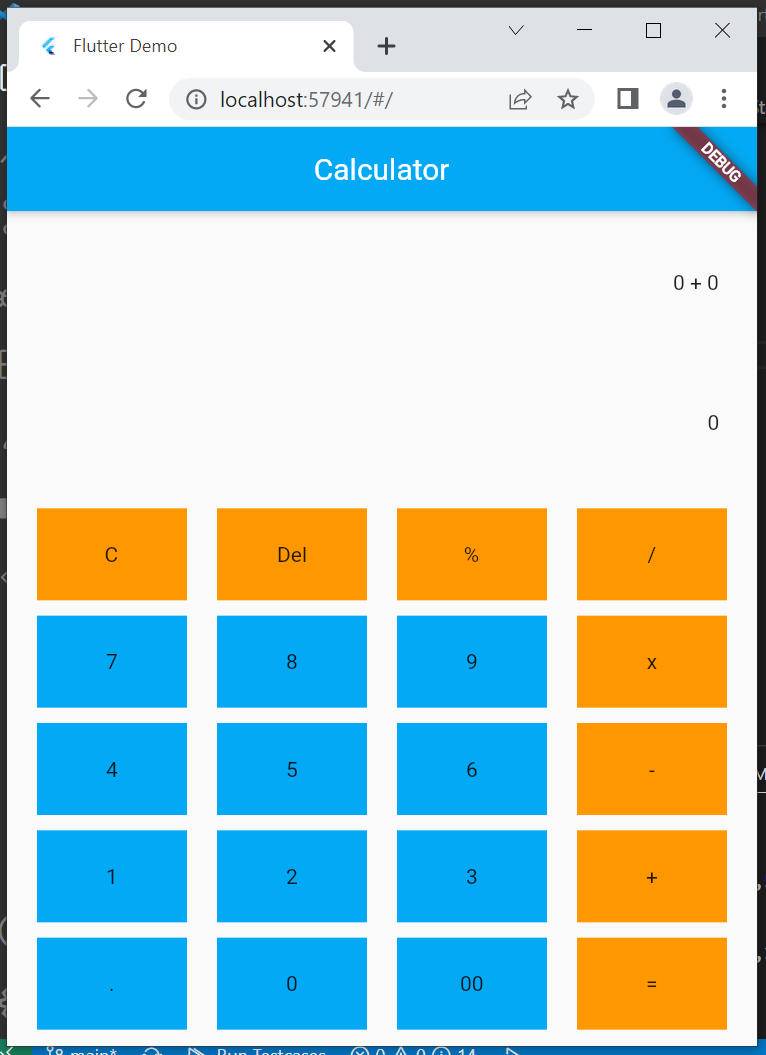
-
Since the text appears small, let us increase the size of text. Add the textScaleFactor to every text widget.
textScaleFactor: 1.5,
- Adding padding and color to the display containers will make it more pretty.
padding: EdgeInsets.all(10),
To make it look more eye pleasing, you can explore more using the links given with the resources of the first lecture.