HydroPol2D is an open-source, high-resolution 2D model built in MATLAB for simulating overland flow, infiltration, groundwater-surface water interactions, and pollutant transport. Developed with performance and flexibility in mind, it supports both CPU and GPU computations and can handle diverse forcing conditions such as spatially distributed rainfall, satellite-derived precipitation, design storms, and hydrograph inputs.
The model is particularly suited for urban, peri-urban, and rural catchments in both gauged and data-scarce regions.
- 2D overland flow using Cellular Automata or Local Inertial formulations (default)
- Fully distributed infiltration with Green-Ampt formulation and subgrid corrections
- Groundwater recharge and shallow aquifer flow via a 2D Boussinesq approach
- Flexible rainfall input: gauges, satellite, interpolated, synthetic hyetographs
- Snow accumulation and melt with mass balance tracking
- Dynamic reservoir and dam-break modeling
- Pollutant simulation: 1 pollutant per simulation with build-up/wash-off dynamics
- Digital twin & forecasting using real-time inputs (e.g., HADS, ANA)
- Mass-conserving adaptive time stepping (Courant-based)
- Output visualizations in
.tif,.mp4,.csv,.pdf, and.png
- MATLAB R2020a or newer
- Required Toolboxes:
- Mapping Toolbox
- Parallel Computing Toolbox (for GPU mode)
- NVIDIA GPU with at least 2 GB VRAM and compute capability > 3.5
- 8+ GB RAM for CPU mode
- Microsoft Excel (for parameter configuration)
- QGIS, Google Earth Engine, or R for raster preprocessing (DEM, LULC, soils, etc.)
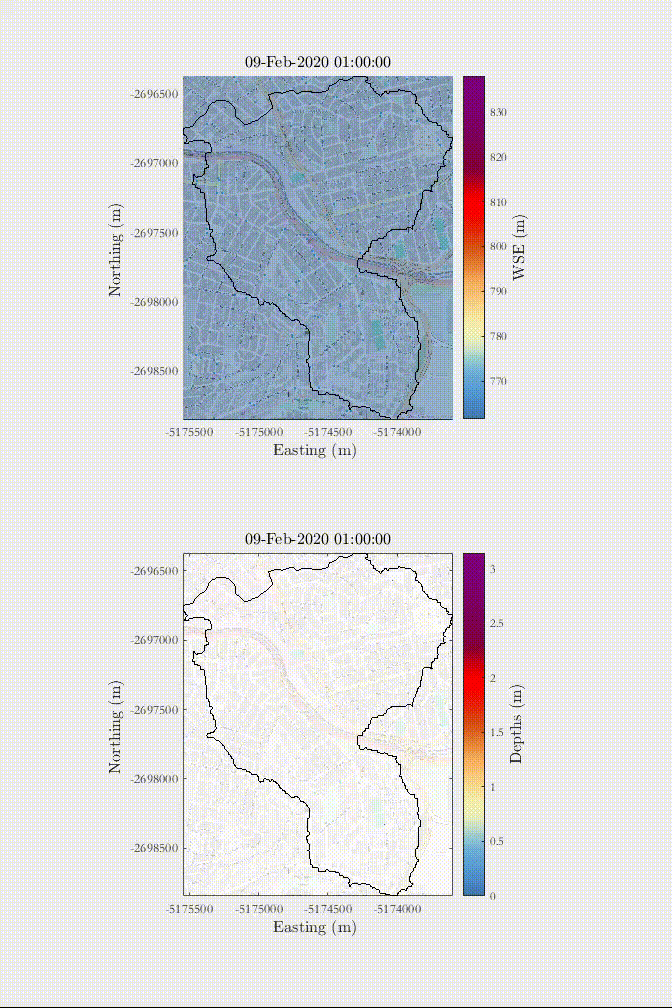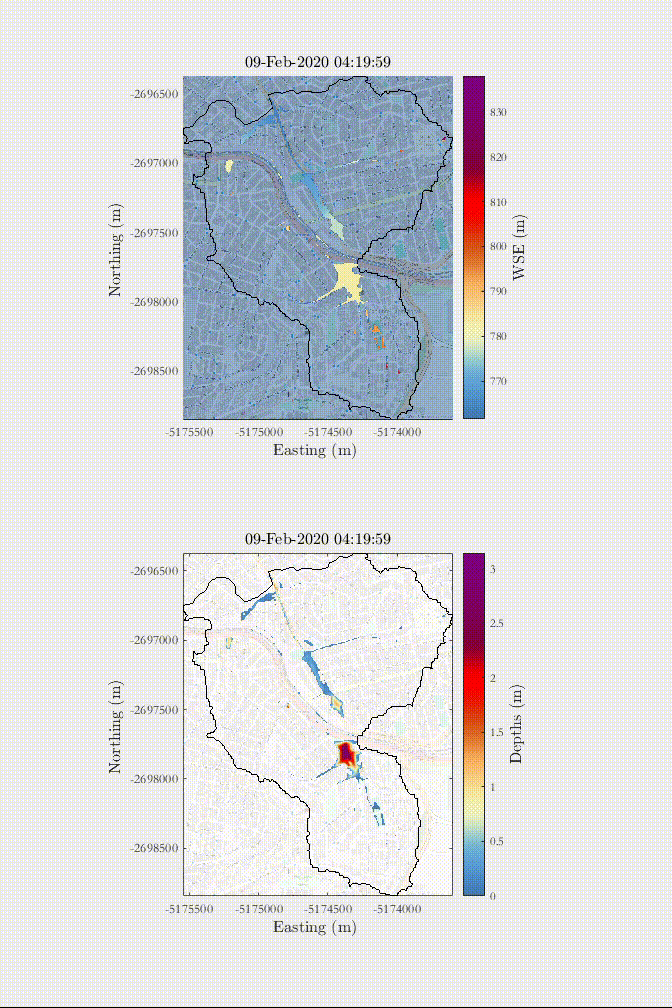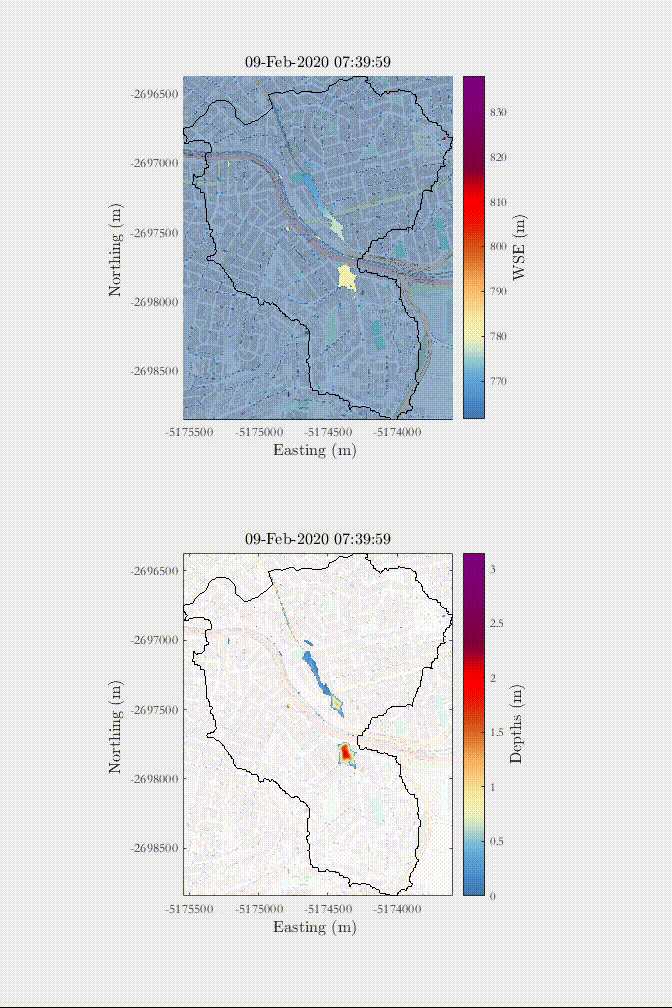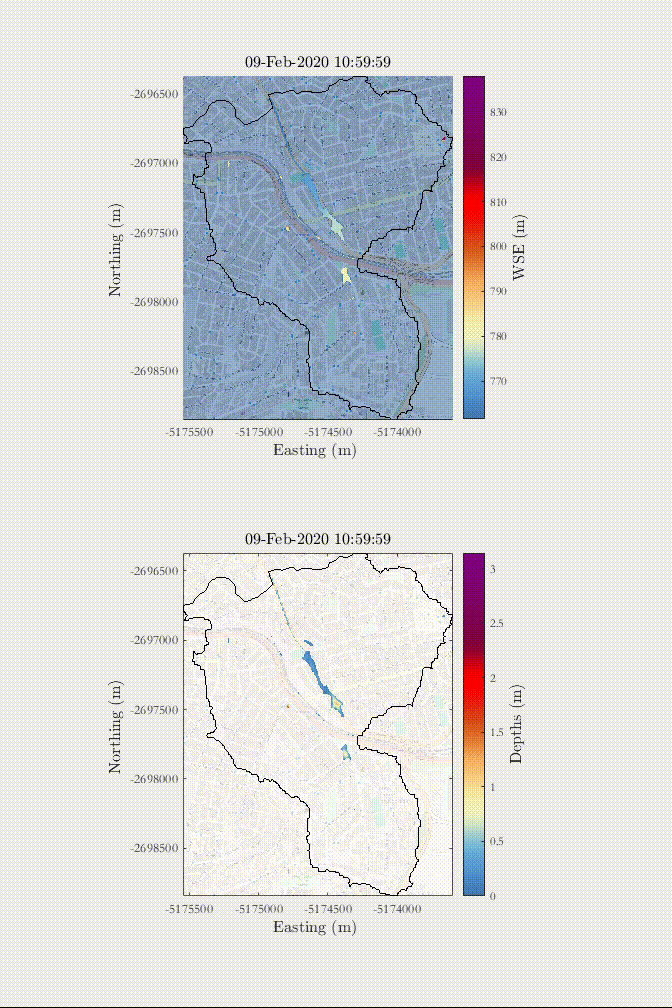
Example of a rain-on-the-grid simulation of a 1 in 50-year rainfall in an urban area with influence of urban drainage - Sao Paulo, Brazil.
Example of a total dam-break collapse scenario in a city in Pernambuco, Northeast - Brazil.
HydroPol2D requires the following input data files and parameters, which must be prepared and aligned before running the model:
- Digital Elevation Model (DEM): Defines terrain slope, flow direction, and is used for hydrologic routing and terrain preprocessing. Must be gap-filled and optionally smoothed. Elevation in meters.
- Land Use / Land Cover (LULC): Used to assign surface properties (e.g., roughness, imperviousness, pollutant loading). Each class must be indexed and named consistently with the LULC parameter table.
- Soil Map: Classifies soils spatially to define infiltration and water balance parameters. Must match indices in the soil parameter table.
- Optional Gridded Maps:
- Rainfall intensity maps (mm/hr)
- Potential Evapotranspiration (ETP)
- Actual Evapotranspiration (ETa)
- Snow Depth
- Groundwater Table Depth
- Subgrid river bathymetry and slope rasters
All rasters must be aligned spatially (same extent, resolution, and coordinate reference, preferably EPSG:3857).
-
LULC Parameter Table: Each land use class must include:
- Manning's
nroughness coefficient - Impervious index (0 or 1)
- Initial abstraction depth
h0 - Initial water depth
d0 - Pollutant loading coefficients:
C1(build-up rate),C2(capacity),C3(wash-off rate),C4(wash-off exponent)
- Manning's
-
Soil Parameter Table: Each soil class must include:
- Saturated hydraulic conductivity
Ksat(mm/hr) - Suction head
ψ(mm) - Initial soil water content
θi - Saturated water content
θsat - Water deficit (θsat - θi) for infiltration calculations
- Saturated hydraulic conductivity
Preprocessing must ensure that all rasters are aligned and projected (EPSG:3857 recommended).
HydroPol2D saves results in:
- Geospatial:
.tifrasters (depth, infiltration, pollutant, velocity, recharge, etc.) - Graphics:
.png,.pdf(hydrographs, profiles, maps) - Animation:
.mp4(dynamic maps) - Numerical:
.csv(time series, diagnostics)
Flags are configured via Excel and define:
- Simulation type (rainfall vs hydrograph)
- Processing mode (CPU vs GPU)
- Routing method (CA or Local Inertial)
- Hydrologic modules (baseflow, ET, GW, snow, pollutant)
- DEM preprocessing routines
Ensure consistency among flags (e.g., only one rainfall mode active).
| Mode | Grid Size | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| CPU | < 1 million cells | Single-core, slower |
| GPU | > 1 million cells | Faster, requires NVIDIA GPU |
- Adaptive time stepping based on Courant number (recommended: 0.3–0.7)
Cite HydroPol2D using:
- Gomes Jr, M. N., et al. (2023). HydroPol2D—Distributed hydrodynamic and water quality model: Challenges and opportunities in poorly-gauged catchments. Journal of Hydrology, 625, 129982.
- Gomes Jr, M. N., et al. (2024). Global optimization-based calibration algorithm for a 2D distributed hydrologic-hydrodynamic and water quality model. Environmental Modelling & Software, 179, 106128.
- Rápalo, L. M., Gomes Jr, M. N., & Mendiondo, E. M. (2024). Developing an open-source flood forecasting system... Journal of Hydrology, 644, 131929.
- [Full list in manual, section 1.0]
For issues, contact:
- Dr. Marcus N. Gomes Jr. – marcusnobrega.engcivil@gmail.com
- Dr. Luis Miguel Castillo Rápalo – luis.castillo@unah.hn
Repository: https://github.com/marcusnobrega-eng/HydroPol2D
- Multi-pollutant simulation capability
- Integration of SPI/SPEI climate indices from GEE
- Calibration and auto-setup interface
- Cloud deployment and Web dashboard
- Minimal reproducible examples
This project is licensed under the MIT License — you are free to use, modify, and distribute this software, provided proper credit is given.