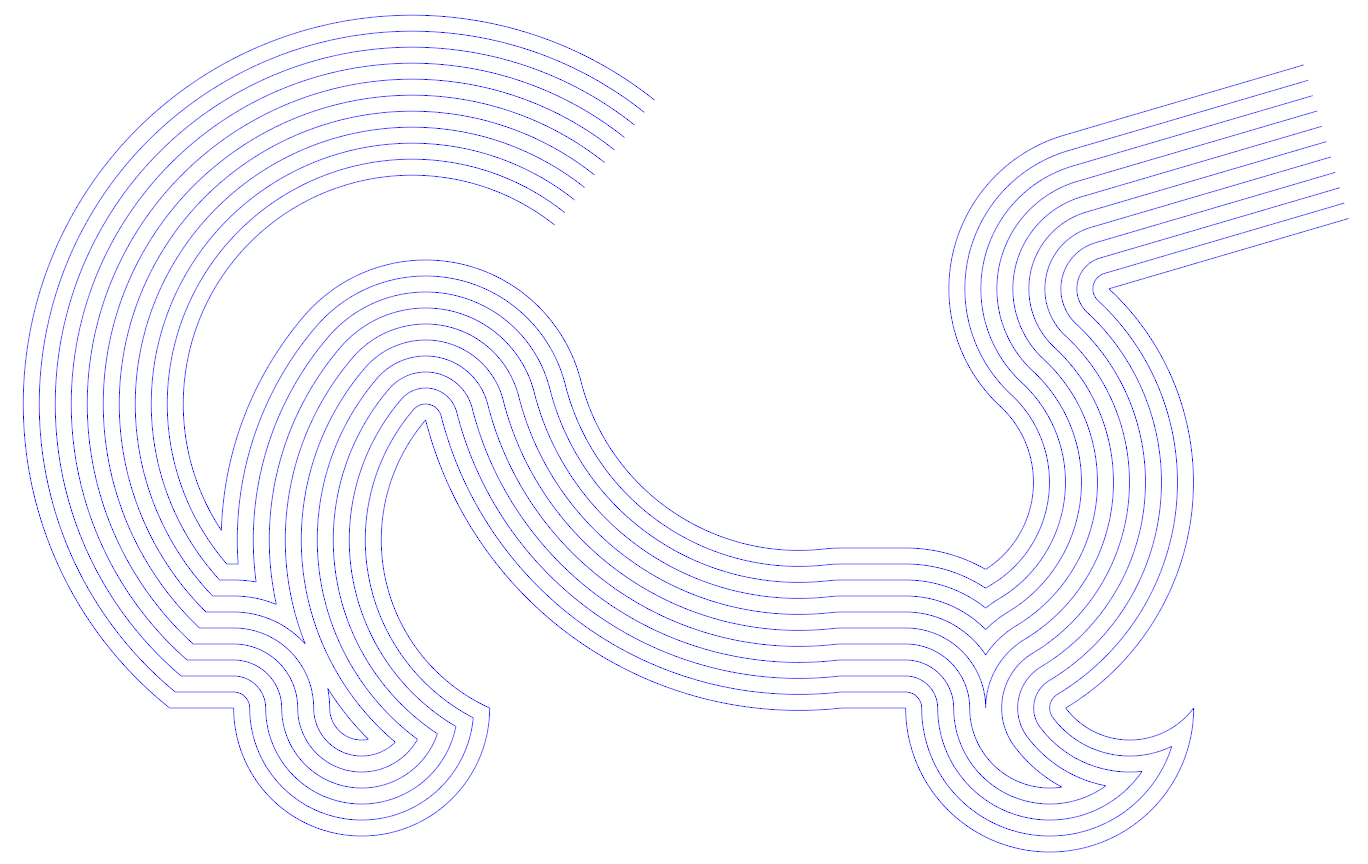
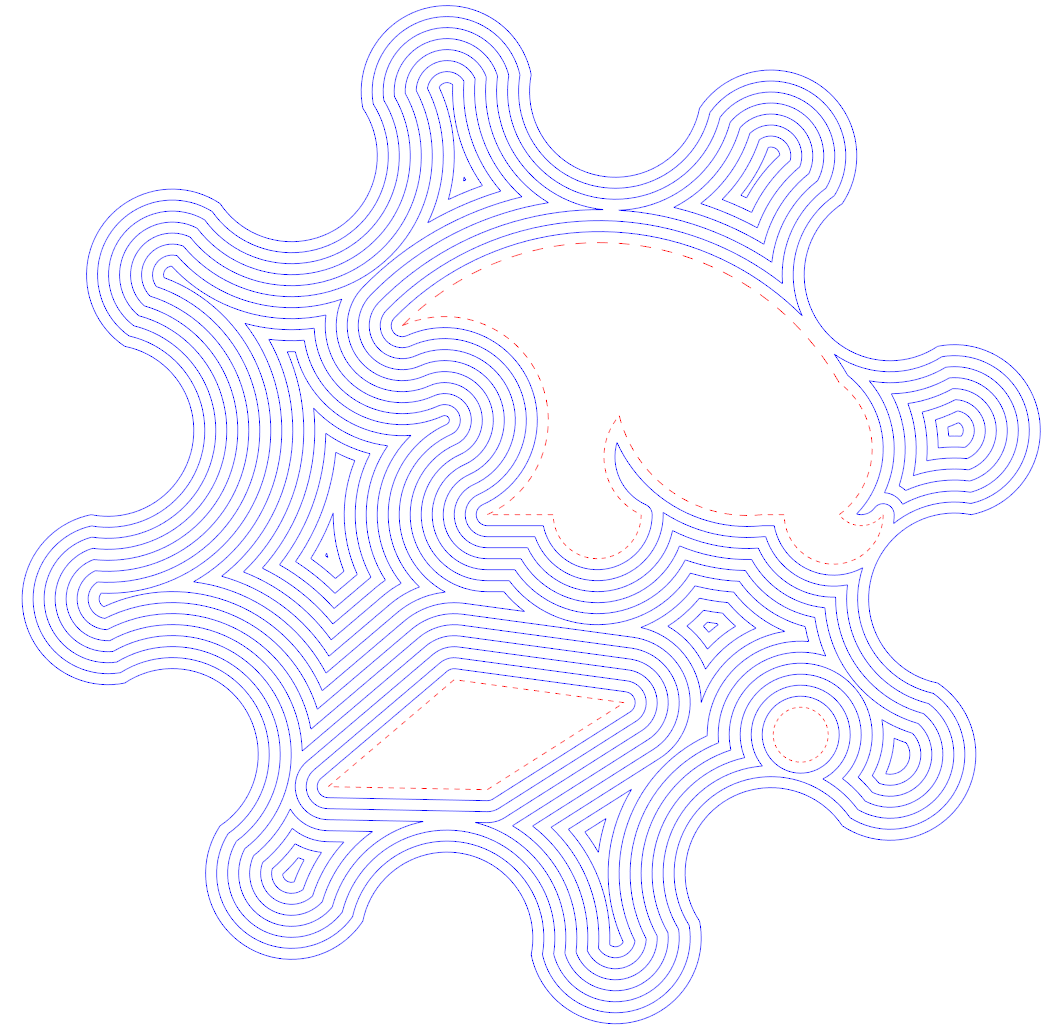
This project is a continuation of the C++
CavalierContours library rewritten in Rust with
the goal of building out more functionality, better documentation, and creating a stable C FFI.
This project has all of the functionality of the C++ repository with more code documentation, test
coverage, and some additional functions for working with polylines. For tracking progress and
contributing checkout the project GitHub issues. For more information about the parallel offset
algorithm and background information see the old C++ repository README.md
here.
use cavalier_contours::polyline::*;
use cavalier_contours::pline_closed;
// `pline` is a closed polyline representing a circle with radius 0.5 centered at (0.5, 0.0).
let pline = pline_closed![(0.0, 0.0, 1.0), (1.0, 0.0, 1.0)];
// Parallel offset inward 0.2 (positive value for counter-clockwise polyline).
let offset_plines = pline.parallel_offset(0.2);
// Just one resulting polyline.
assert_eq!(offset_plines.len(), 1);
let offset_pline = &offset_plines[0];
// Vertexes offset inward, bulge/curvature unchanged.
assert!(offset_pline[0].fuzzy_eq(PlineVertex::new(0.2, 0.0, 1.0)));
assert!(offset_pline[1].fuzzy_eq(PlineVertex::new(0.8, 0.0, 1.0)));See more examples here.
👉 Click to run the WASM web demo 👈
- Polylines defined with line and arc segments (fixed radius, arcs are not approximated as line segments)
- Polyline parallel offsetting (works on open, closed, and self-intersecting polylines)
- Boolean operations between two closed polylines (union, intersection, difference)
- Polyline containment and intersection tests
- Winding number (point in closed polyline) test
- Area, length, redundant vertex removal, and other geometric functions
- 2D spatial indexing to speed up alogorithms on high vertex count polylines
- Multi-polyline parallel offsetting ("shapes" defined with islands)
- No unsafe code in core crate
- C FFI for integration with other languages
- WebAssembly support and interactive web demo
- Bulge values for arcs only support values between -1.0 and 1.0 (up to half-circle) for arcs, workaround: use multiple arc segments to form larger arcs
- Only rounded joins are supported for parallel offsets (other join types are not implemented)
- Parallel offsets and boolean operations behave differently for resulting overlapping segments:
- Parallel offset result always retains overlapping segments (longest valid connection when joining slices)
- Boolean operation result always combines/merges/removes overlapping segments (based on boolean operation)
- Boolean operation algorithm operates on only two closed non-self-intersecting polylines
- Multi-polyline parallel offsetting was designed to support sets of polylines that are closed and not intersecting (areas with holes)
- May still work as desired for some intersecting or open polyline cases but algorithm does not implement configuration for such
- cavalier_contours: Core Rust library and API for polyline algorithms.
- cavalier_contours_ffi: C FFI bindings for use from C/C++ and other languages.
cavalier_contours_ffiREADME - cavalier_contours_ui: Web-based UI demo (WASM, using egui).
cavalier_contours_uiREADME (live page) - examples: examples demonstrating some of cavalier_contours functionality.
examplesREADME
- Rust 1.88+ (MSRV)
- Tested with CI on Linux, macOS, and Windows
- All the same benefits of using C or C++ (great performance/optimizations, native compile, no garbage collection, no run time) for creating fast portable libraries with a C FFI
- Great builtin tooling around builds and packages (cargo + crates)
- Great builtin tooling for writing and maintaining tests
- All of the great builtin tooling makes open source contribution and participation easier to facilitate
- Borrow checker + lifetimes allow for more advanced memory allocation optimizations without the risk of memory errors/corruption bugs
- Type system allows for leaning heavily on threads/concurrency without the risk of memory errors/corruption bugs
- Discriminated unions and pattern matching as first class language features
- Great tooling for targeting wasm
Licensed under either of
- Apache License, Version 2.0 (LICENSE-APACHE or http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0)
- MIT license (LICENSE-MIT or http://opensource.org/licenses/MIT)
at your option.
Unless you explicitly state otherwise, any contribution intentionally submitted for inclusion in the work by you, as defined in the Apache-2.0 license, shall be dual licensed as above, without any additional terms or conditions.