sudo apt purge ubuntu-desktop
sudo systemctl disable --now gdm
systemctl set-default multi-user.target
To enable the GUI again:
systemctl set-default graphical.target
hostnamectl
hostnamectl set-hostname {name-here}
vi /etc/hosts #Replace the old name for the new one here
uptime
lscpu
Deb Version
wget https://github.com/cjbassi/gotop/releases/download/3.0.0/gotop_3.0.0_linux_amd64.deb
sudo dpkg -i gotop_3.0.0_linux_amd64.deb
or RPM Version
wget https://github.com/cjbassi/gotop/releases/download/3.0.0/gotop_3.0.0_linux_amd64.rpm
sudo rpm -ivh gotop_3.0.0_linux_amd64.rpm
lspci
# Look between those lines for the NIC. vm = Intel Corporation 82xxxx
sudo lshw
lsshow -html > systeminfo.html
systemctl list-unit-files --type service -all
systemctl list-unit-files --no-pager
systemctl | grep running
systemctl start service name
systemctl stop service name
systemctl restart service name
sudo systemctl disable name
sudo systemctl enable --now name
systemctl status name
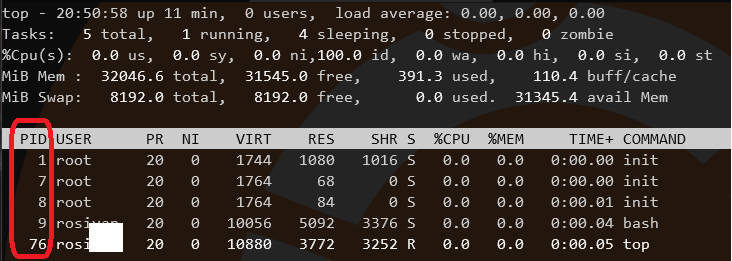
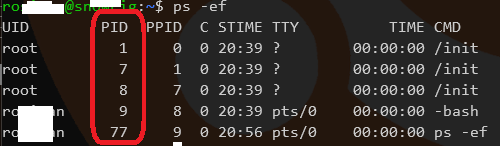
killall 9
where the next number is the PID, to close
or
kill 9
or
- If using GUI, then
xkillthen click over the app to close
amixer set Master muteclear
lsb_release -a
sudo -i
dmesg| grep sd
mount
to Reload Mounts
sudo mount -a
if Debian for how much space on HDD(s), even USB, (on the for line will tell you the Mount Drive name)
df -h --total
or
df -h --total | grep total
or
df -h --total | sed '4!d
or a better view with JSON output
wget https://github.com/muesli/duf/releases/download/v0.6.0/duf_0.6.0_linux_amd64.deb
dpkg -i duf_0.6.0_linux_amd64.deb
duf
last reboot
cal
or with current Time
date
w
or current
whoami
ps
#!/bin/sh
dpkg-query --show --showformat='${Package}\t${Installed-size}\t${Status}\n' |
awk '
{
# evaluate installed packages only
if($3 == "install"){
packages[$1] = $2
}
}
END {
# sort packages by size (change 'asc' to 'desc' to reverse the order)
PROCINFO["sorted_in"] = "@val_num_asc"
for (i in packages){
printf "%05.2fM | %s\n",
packages[i] / 1024, # convert from kilobytes to megabytes
i
}
}
'
vmstat -s
or
free -h
cat /proc/cpuinfo
hostname -I
sudo lsof -P -i:631
sudo ss -tulwnp
ip link show
OR
nmcli device status
OR
/sbin/ifconfig -a
Check for all the MAC address your device around the network, try to ping the device if stil doesn't show up
It works better on Windows
sudo apt install net-toolsc
arp -a
sudo dhclient -r
sudo dhclient
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
afterwards
sudo apt autoremove
pihole -v
tail -3 /var/log/cups/access_log
id
useradd -c "John Doe" -m john
userdel john
#Add the User to a group
usermod -aG sales john
ln -s /path/to/file linkname
apt install mlocate
locate file.txt
pstree
PS1="[ ${debian_chroot:+($debian_chroot)}\u is awesome: \w ]\\$ "
touch fileName
#Read a txt file
less file
history
mv fileA fileB
pihole -up
ip r
ip r | grep ^def
# SSH
ssh username@IpAddress
**yes** </br>
then type in the _password_ for the host </br>
Check for status </br>
sudo service ssh status
# Static IP Address
GUI Method
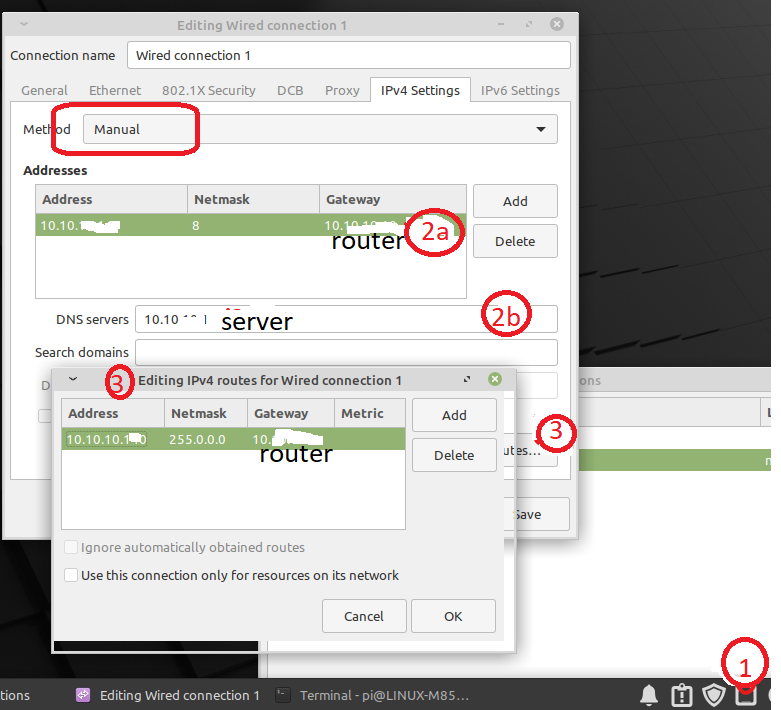
# Restart
systemctl reboot -i
# TracerRoute for Ubuntu
```RUBY
sudo apt install inetutils-traceroute
sudo apt install traceroute
ping -c 3 google.com
netstat -nutlp
Deb
systemctl restart network.service
or RPMs
systemctl restart networking.service
Back up your current network configuration:
sudo cp /etc/netplan/00-installer-config.yaml /etc/netplan/00-installer-config.yaml.bak
Find your Interface with ip a in this case is enp0s3 but it could be epns08...
then adjust the code below
network:
version: 2
renderer: networkd
ethernets:
enp0s3:
dhcp4: no
addresses: [192.168.1.2/24]
gateway4: 192.168.1.1
nameservers:
addresses: [8.8.8.8, 8.8.4.4]
save it with : press Ctrl + X while you could refresh it with sudo netplan apply is recommended to just restart hence you might be connected via SSH anyways
dig google.com
wget https://gdlp01.c-wss.com/gds/0/0300004730/02/eosrt3-eos1100d-im2-c-en.pdf
ls -all file.txt
ls -lh file.txt
ls -all folder
8 Permissions: r=Read ; w=Write ; x=Execute
sudo apt install samba -y
Create a folder destined to do the SHARE , 👉change your path
mkdir /home/USERNAME/Desktop/sambashare/
- Configure it
sudo nano /etc/samba/smb.conf
At the end of the file add this, 👉 But make your required changes to your path: , then save it
[sambashare]
comment = Samba on Ubuntu
path = /home/adam/Desktop/sambashare/
read only = no
browsable = yes
Restart and Allow the Firewall
sudo service smbd restart
sudo ufw allow samba
Create the Username and then it will ask you to add a password for the SAMBA
sudo smbpasswd -a USER-NAME-GOESHERE
To connect to it, if Linux/Mac smb://ipaddress/sambashare or Windows \\ipaddress\sambashare
sudo find / -size +5M -size -10M
find / -atime 2
find / -mmin -1
sudo apt install jshon -y
echo '{"name": "Kesk","surname":"norem"}' | jshon
echo '{"name": "Kesk","surname":"norem"}' | jshon > file.json
tar -czvf eosManual.tar.gz eosrt3-eos1100d-im2-c-en.pdf
Multiple folders & Files
tar -czvf file.tar.gz /home/user1/ /home/user2/
you can also exclude a folder ie.
tar -czvf archive.tar.gz /home/user1 --exclude=*.mp3
To Extract file in same directory
tar -xzvf eosManual.tar.gz
To Extract file in different directory
tar -xzvf eosManual.tar.gz -C folder2/
Prerequisites:
sudo apt install zip unzip
Name of the file that will be, then the actual filename, Example:
zip eosrt3-eos1100d-im2-c-en.zip eosrt3-eos1100d-im2-c-en.pdf
To Zip many Files & Folders
zip -r Manuals.zip eosrt3-eos1100d-im2-c-en.pdf folderWfiles
To Unzip
unzip Manuals.zip
scp file.pkg remote_username@10.10.0.2:/remote/directory
rm -rf folderWfiles/
nano Downloads/runner.sh
Content of a simple script:
#!/bin/bash
echo "Computer Name: " $(hostname) > Downloads/filelist.txt
echo " "
ls >> Downloads/filelist.txt
echo "Today's Date: " $(date) >> Downloads/filelist.txtMaking it Executable
sudo chmod 774 Downloads/runner.sh
Execution: ./Downloads/runner.sh
- Method 1: Via Line by Line:
ssh useradmin@10.10.10.10 'bash -s' <<'ENDSCRIPT' echo "Computer Name: " $(hostname) > Downloads/filelist.txt echo " " ls >> Downloads/filelist.txt echo "Today's Date: " $(date) >> Downloads/filelist.txt ENDSCRIPT
- Method 2: Via a script written in local:
ssh useradmin@10.10.10.10 'bash -s' < runner.sh
quotes.txt
The present is theirs; the future, for which I really worked, is mine.
Our virtues and our failings are inseparable, like force and matter. When they separate, man is no more.
The day science begins to study non-physical phenomena, it will make more progress in one decade than in all the previous centuries of its existence
-Nikola TeslaPicking and Highlighting specific word(s):
grep "virtues" quotes.txt
Picking and Highlighting specific word(s), while guessing char(s)
grep "virt[a-z][a-z]" quotes.txt
Replacing specific word(s)
sed -i 's/I really worked/I really did not worked/g' quotes.txt
Convert Lower Case
sed -e 's/\(.*\)/\L\1/' hello.txt > output.txt
Toast Notification
#!/bin/bash
sleep 10
notify-send "notify.sh" "Task complete successfully"
Text Styles
#!/bin/bash
bold=$(tput bold)
underline=$(tput smul)
italic=$(tput sitm)
info=$(tput setaf 2)
error=$(tput setaf 160)
warn=$(tput setaf 214)
reset=$(tput sgr0)
echo "${info}INFO${reset}: This is an ${bold}info${reset} message"
echo "${error}ERROR${reset}: This is an ${underline}error${reset} message"
echo "${warn}WARN${reset}: This is a ${italic}warning${reset} message"#!/bin/bash
function task1() {
echo "Running task1..."
sleep 5
}
function task2() {
echo "Running task2..."
sleep 5
}
task1 &
task2 &
wait
echo "All done!"While Loop
#!/bin/bash
while true;
do
# Frame #1
printf "\r< Loading..."
sleep 0.5
# Frame #2
printf "\r> Loading..."
sleep 0.5
doneExample 1
for i in 3 43 44 11 9; do echo $i; done
Example 2
#!/bin/bash
for i in {1..10}
do
echo "Thi is line: " $i
done
chmod +x looper.sh
./looper.sh
if [[ -f file ]]; then echo "exits"; else echo "doesn't exit"; fi
if [[ -d folder ]]; then echo "exits"; else echo "doesn't exit"; fi
sudo lvextend --resizefs -l +100%FREE ubuntu-vg/ubuntu-lv
sudo apt install nala
```Ruby
| Folder | Content |
|---|---|
| /. | Root Directory for every directory. Read/Write Only unlesss Sudo access |
| / | Everything on your Linux system is located under the / directory |
| /bin -> /usr/bin | Contains the essential user binaries (programs) that must be present when the system is mounted in single-user mode |
| /boot | The startup files and the kernel, vmlinuz. In some recent distributions also grub data. Grub is the GRand Unified Boot loader and is an attempt to get rid of the many different boot-loaders we know today. |
| /dev | directory contains a number of special files that represent devices. These are not actual files as we know them, but they appear as files — for example, /dev/sda represents the first SATA drive in the system. If you wanted to partition it, you could start a partition editor and tell it to edit /dev/sda, /dev/random produces random numbers. |
| /etc | Most important system configuration files are in /etc, this directory contains data similar to those in the Control Panel in Windows |
| /home | Home directories of the common users. |
| /lib -> /usr/lib | The /lib directory contains libraries needed by the essential binaries in the /bin and /sbin folder. Libraries needed by the binaries in the /usr/bin folder are located in /usr/lib |
| /lib64 -> /usr/lib64 | Directory containing 64-bit system libraries. |
| /media | contains subdirectories where removable media devices inserted into the computer are mounted |
| /mnt | Directory used for temporarily mounting remote filesystems and other media |
| /opt | contains subdirectories for optional software packages |
| /proc | /proc directory similar to the /dev directory because it doesn’t contain standard files. It contains special files that represent system and process information |
| /root | The root user's home directory. |
| /run | A runtime scratch directory (RAM-based). |
| /sbin -> /usr/sbin | The /sbin directory is similar to the /bin directory. It contains essential binaries that are generally intended to be run by the root user for system administration |
| /selinux | If your Linux distribution uses SELinux for security (Fedora and Red Hat, for example), the /selinux directory contains special files used by SELinux. It’s similar to /proc. Ubuntu doesn’t use SELinux, so the presence of this folder on Ubuntu appears to be a bug |
| /srv | Contains “data for services provided by the system.” If you were using the Apache HTTP server to serve a website, you’d likely store your website’s files in a directory inside the /srv directory |
| /sys | Directory containing devices, kernel modules, filesystems, and other kernel component info |
| /tmp | Temporary space for use by the system, cleaned upon reboot |
| /usr | Programs, libraries, documentation etc. for all user-related programs. |
| /var | Variable data files are stored here. This can include things like log files, MySQL, and other database files, web server data files, email inboxes, and much more. |
ie. The repository 'http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu kinetic Release' no longer has a Release file.
sudo nano /etc/apt/sources.list and add "old-", to the hyperlinks shown there. something like:
http://old-releases.ubuntu.com
then save the file and do do-release-upgrade this will revamp the next possible version and then run the progress
-
Back up you main repo file
sudo cp /etc/apt/sources.list /etc/apt/sources.bak -
findout what is the current version of Ubuntu Install
hostnamectlthen check in the ubuntu.com website what is the name codename -
Edit the same
sudo nano /etc/apt/sources.list -
Replace the prior version with the new version:
^ \in this example:kineticforlunar(check every entry) -
sudo apt update -y -
sudo apt upgrade -y -
If prompted to configure libc6 to restart services. Tab over to “yes” and hit ENTER.
-
Select all services (check with your other apps as this will be restarted, specially if this a PROD enviroment)
-
sudo apt dist-upgrade -y -
You might get prompted to select your language twice
-
sudo apt dist-upgrade -y -
you might need to remove all libraries
sudo apt autoremove -
sudo reboot -
check again and see if it is already upgraded
hostnamectl -
at this point the platform for that version now should be ready for the next
do-release-upgrade -
follow prompts., 🍵time and walk it off this part will take a while.
-
Enjoy! 😉