-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
Cache
Triton's cache system accelerates kernel compilation by storing precompiled artifacts (PTX, CUBIN, HSACO etc.) and metadata. This document explains its structure, behavior and customization options.
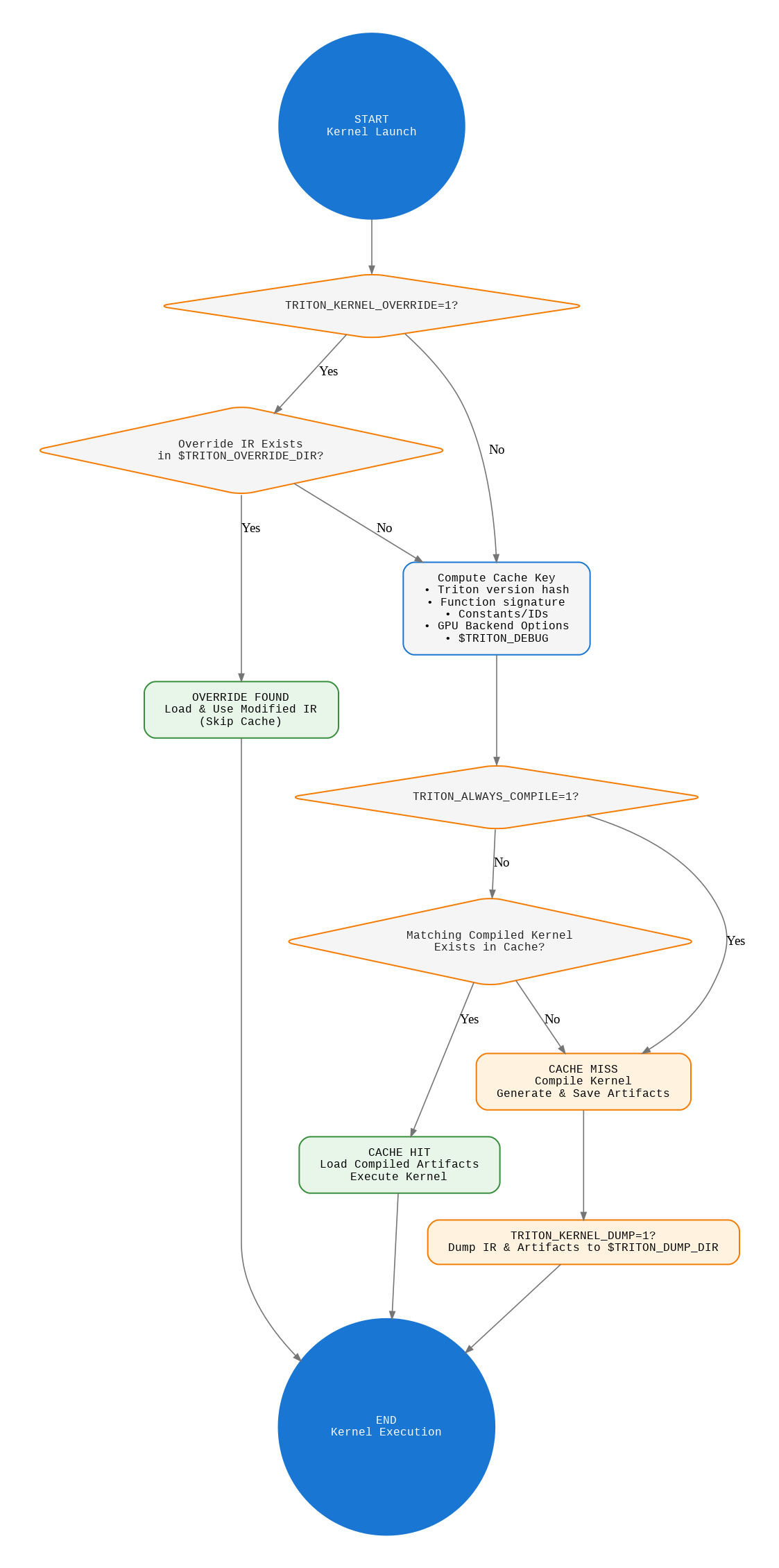
By default, Triton stores cached kernels in:~/.triton/cache/.
This can be customized using the TRITON_CACHE_DIR environment variable.
| Extension | Description |
|---|---|
.json |
Metadata, compilation parameters |
.cubin / .hsaco
|
Compiled binary kernel (CUDA, ROCm) |
.ptx / .amdgcn
|
PTX or AMDGCN intermediate representation |
.llir |
LLVM IR |
.ttir |
Triton IR |
.ttgir |
Triton GPU IR |
Example cache structure (NVIDIA):
$ tree ~/.triton/cache/QU0JRSfWJiAb9DadP-xn4vDFWO9yNo7Am32JeY1alLc
├── __grp__triton_poi_fused_threshold_backward_1.json
├── triton_poi_fused_threshold_backward_1.cubin
├── triton_poi_fused_threshold_backward_1.json
├── triton_poi_fused_threshold_backward_1.llir
├── triton_poi_fused_threshold_backward_1.ptx
├── triton_poi_fused_threshold_backward_1.ttgir
└── triton_poi_fused_threshold_backward_1.ttirThe cache key is generated from multiple inputs to ensure uniqueness:
-
Triton Environment
- Triton version (not stored in metadata but included in the hash)
-
Kernel Identity
- Function name
- Signature types (normalized, for example, pointer types become
"ptr") - Constant values
- Kernel attributes
-
Backend Configuration
- Backend (rocm/cuda)
- GPU architecture
- Warp size
- Compilation options (
num_warps,num_stages, etc.)
-
Environment Factors
-
TRITON_DEBUGvariable state (0 or 1)
-
import hashlib
import base64
def make_so_cache_key(version_hash, signature, constants, ids, **kwargs):
signature = {k: 'ptr' if v[0] == '*' else v for k, v in signature.items()}
key = f"{version_hash}-{''.join(signature.values())}-{constants}-{ids}"
for kw in kwargs:
key = f"{key}-{kwargs.get(kw)}"
key = hashlib.sha256(key.encode("utf-8")).hexdigest()
return _base32(key)Note: The Triton version is included in the cache key but is not stored in the metadata files. If you need to check the version, you must track it externally.
| Variable | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
TRITON_CACHE_DIR |
~/.triton/cache |
Custom cache directory |
TRITON_ALWAYS_COMPILE |
0 |
Bypass cache (force recompilation) when set to 1
|
TRITON_KERNEL_OVERRIDE |
0 |
Enable manual kernel IR overrides |
TRITON_OVERRIDE_DIR |
~/.triton/override/ |
Directory for manually overridden kernels |
TRITON_KERNEL_DUMP |
0 |
Enable kernel IR dumping |
TRITON_DUMP_DIR |
~/.triton/dump/ |
Directory for dumped compilation artifacts |
TRITON_STORE_BINARY_ONLY |
0 |
Store only essential binaries (saves ~77% space) |
TRITON_DEBUG |
0 |
Include debug info in cache key (affects hashing) |
To completely bypass the cache:
export TRITON_ALWAYS_COMPILE=1Enable binary-only storage to save space:
export TRITON_STORE_BINARY_ONLY=1This reduces stored files to:
-
.json(metadata) -
.cubin/.hsaco(compiled binaries)
Triton supports distributed caching via RemoteCacheManager. Example Redis setup:
import os
# Configure via environment variables
os.environ["TRITON_REMOTE_CACHE_BACKEND"] = "triton.backends.redis:RedisRemoteCacheBackend"
os.environ["TRITON_REDIS_HOST"] = "redis.example.com"
os.environ["TRITON_REDIS_PORT"] = "6379"| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| Stale Cache | Delete cache or use TRITON_ALWAYS_COMPILE=1
|
| Version Mismatch | Triton upgrades and different environment variable change the cache hash, invalidating old caches |