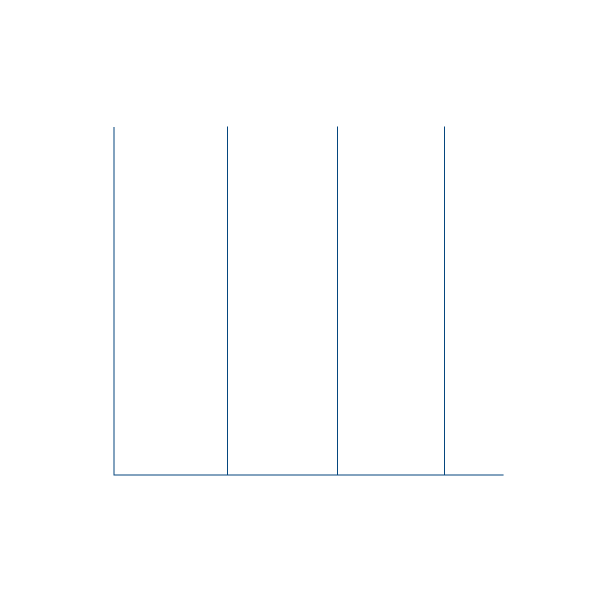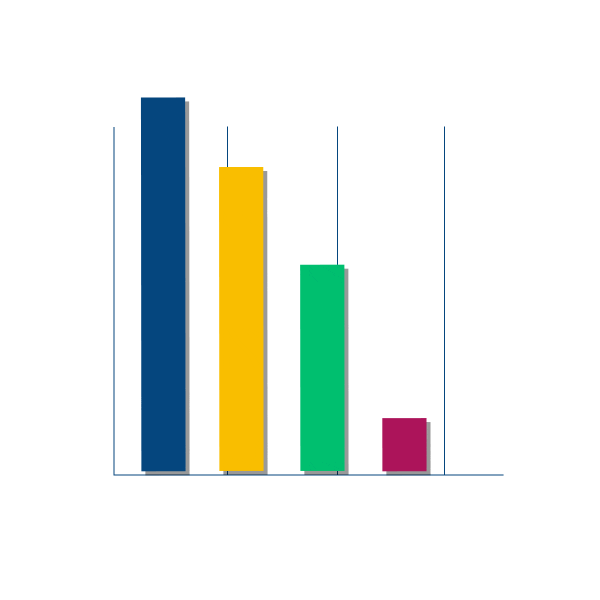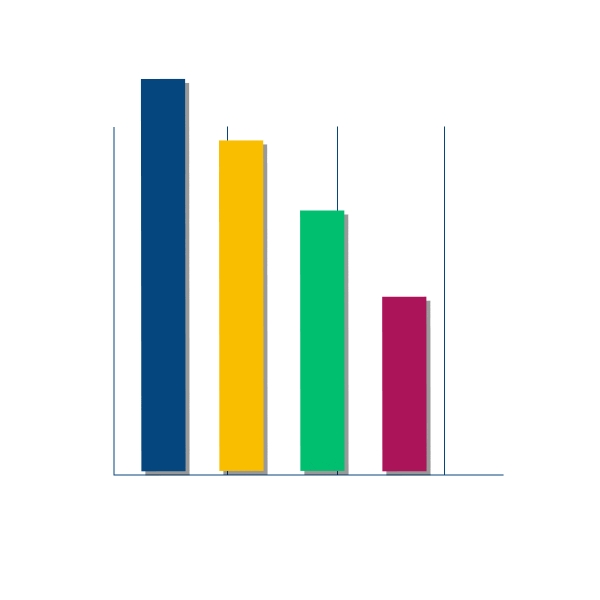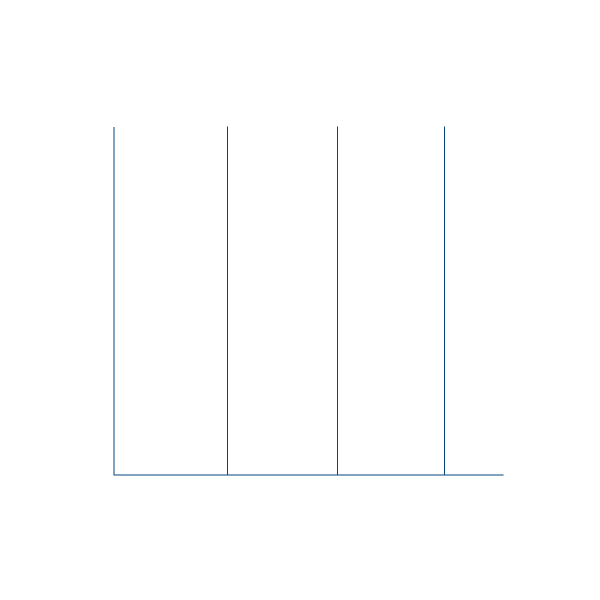
Hospitalization and readmission rates for patients with Diabetes Mellitus (DM) are increasing, posing significant financial and mental burdens. Traditional treatment guidelines recommend that patients with diabetes undergo regular HbA1C testing and check-ups every three months. Unfortunately, many patients find it increasingly challenging and inconvenient to adhere to these recommendations due to limited accessibility to healthcare services. This difficulty leads to missed appointments and exacerbates the problem of preventable hospitalizations. Analysis of data spanning from 1999 to 2008 reveals that 46% of patients admitted to hospitals for diabetes-related issues experience readmissions. This trend prompts further investigation into the rates of preventable hospitalizations from 2005 to 2021, which consistently show that nearly 30% of all cases are diabetes-related.
Dependencies:
- jupyter
- ipykernel
- pandas
- seaborn
- dash
- plotly
To find relation between Diabetes Melitus (DM) and hospitalization rates. Possible ways to prevent quarter checkup's being held in a hospital.
Commonly used data=cleaning tecniques :
- Remove irrelevant data.
- Deduplicate your data, which in this case was not applicable.
- Fix structural errors.
- Deal with missing data.
- Filter out data outliers.
- Validate your data.
- Visualise it using EDA.
Graphs presenting :
- Different genders affected by readmittions.
- Different age groups affected by readmittions.
- Most common hospitalisation statistics.
Authors
Deimante PiraityteData No 1 :
Beata Strack, Jonathan P. DeShazo, Chris Gennings, Juan L. Olmo, Sebastian Ventura, Krzysztof J. Cios, and John N. Clore, “Impact of HbA1c Measurement on Hospital Readmission Rates: Analysis of 70,000 Clinical Database Patient Records,” BioMed Research International, vol. 2014, Article ID 781670, 11 pages, 2014.
https://archive.ics.uci.edu/dataset/296/diabetes+130-us+hospitals+for+years+1999-2008
Data No 2 :
California Health and Human Services Agency (CalHHS) Open Data Portal