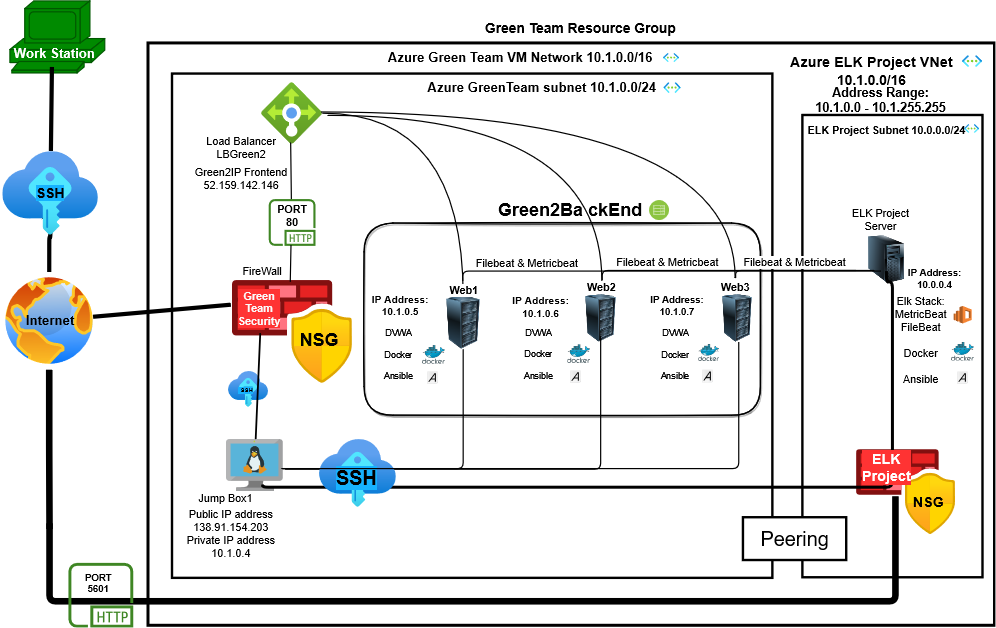
The files in this repository were used to configure the network depicted below.
(https://github.com/UCB-CyberSecurity-Cohort5/elk-stack-project-mdmd62378/blob/main/Diagram/Mission%20Green%20Team%20.drawio.png?raw=true)
These files have been tested and used to generate a live ELK deployment on Azure. They can be used to either recreate the entire deployment pictured above. Alternatively, select portions of the playbook file may be used to install only certain pieces of it, such as Filebeat.
https://github.com/UCB-CyberSecurity-Cohort5/elk-stack-project-mdmd62378/blob/main/PlayBook/Elk.yml
This document contains the following details:
- Description of the Topologu
- Access Policies
- ELK Configuration
- Beats in Use
- Machines Being Monitored
- How to Use the Ansible Build
The main purpose of this network is to expose a load-balanced and monitored instance of DVWA, the D*mn Vulnerable Web Application.
Load balancing ensures that the application will be highly available, in addition to restricting access to the network.
-
A Load balancer protects the network's integrity through the process of allocating incoming traffic over our network Webservers. The importance of such a feature on a Load Balancer is that we avert a shutdown so that our network constantly remains available.
-
A Jump Box allows remote access to only authorized users through a channel of preselected restrictions to preserve network security.
Integrating an ELK server allows users to easily monitor the vulnerable VMs for changes to the file system of the VMs on the network and system metrics.
-
Filebeat: Filebeat is a data shipper that I used for monitoring purposes on my webservers to detect any changes that occurred to the Filesystem of my Virtual Machines.
-
Metricbeat: Metricbeat is a data shipper that I used for monitoring purposes on my webservers to detect any changes that occurred to the system metrics.
The configuration details of each machine may be found below.
| Name | Function | IP Address | Operating System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jump Box | Gateway | 10.1.0.4 | Linux |
| Web1 | Webserver | 10.1.0.5 | Linux |
| Web2 | Webserver | 10.1.0.6 | Linux |
| Web3 | Webserver | 10.1.0.7 | Linux |
| Elk | Webserver | 10.0.0.4 | Linux |
The machines on the internal network are not exposed to the public Internet.
Only the Jump Box machine can accept connections from the Internet. Access to this machine is only allowed from the following IP addresses:
- Public IPv4 IP: 73.202.41.242
Machines within the network can only be accessed by the Jump Box.
- I only allowed SSH access to the Jump Box from my home network machine with an IP Address of 73.202.41.242. The Jump Box had authorization to SSH into the Elk Server via the private IP address of 10.1.0.4.
A summary of the access policies in place can be found in the table below.
| Name | Publicly Accessible | Allowed IP Addresses |
|---|---|---|
| Jump Box | Yes | 73.202.41.242 |
| Web1 | No | 10.0.0.4 |
| Web2 | No | 10.1.0.4 |
| Web3 | No | 10.1.0.4 |
| Elk | No | 10.1.0.4 |
Ansible was used to automate configuration of the ELK machine. No configuration was performed manually, which is advantageous because...
- The benefit of using an automation tool such as Ansible is that it excels in the efficiency and accuracy of software implementation by expediting the process to install multiple applications in mass deployment rather than individually installing applications.
The playbook implements the following tasks:
https://github.com/UCB-CyberSecurity-Cohort5/elk-stack-project-mdmd62378/blob/main/PlayBook/Elk.yml
- 1st: Install Docker containerization platform of choice for our project.
- 2nd: Install Python3 compatible programming language used for our project.
- 3rd: Install the Docker Python module, Installs remaining modules needed to allow docker to work efficiently using Python.
- 4th: Download and launch a Docker Elk container, download the Elk stack into our docker container so that we may use Kibana, Filebeat, Metricbeat.
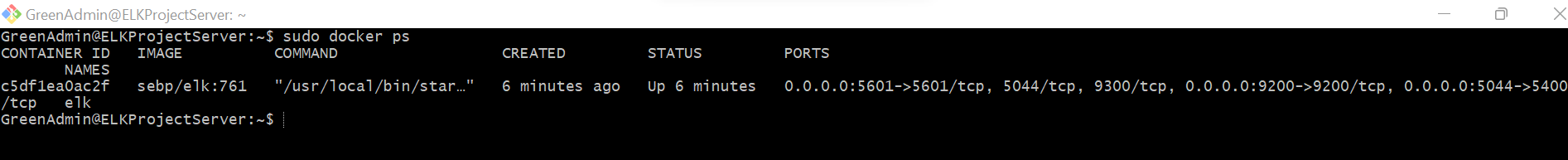
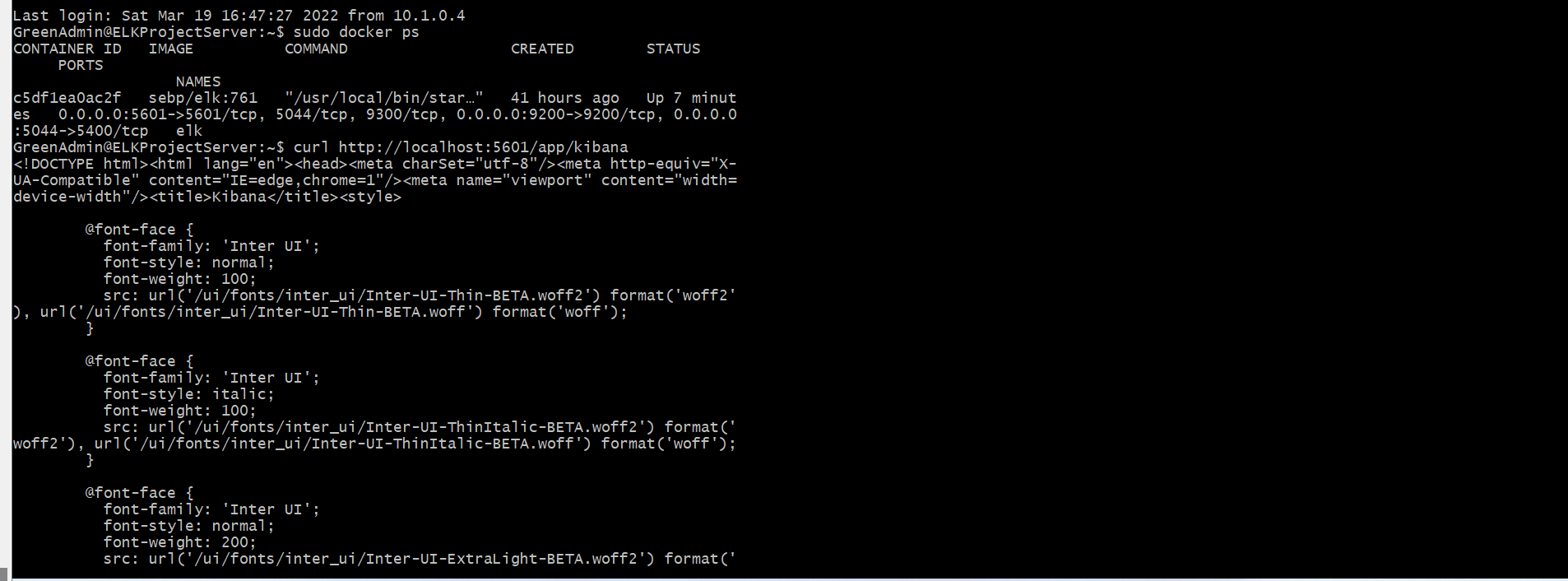
The following screenshot displays the result of running docker ps after successfully configuring the ELK instance.
This ELK server is configured to monitor the following machines:
| Name | IP Address |
|---|---|
| Web1 | 10.1.0.5 |
| Web2 | 10.1.0.6 |
| Web3 | 10.1.0.7 |
We have installed the following Beats on these machines:
| Name | Type of Beat Installed |
|---|---|
| Web1 | Filebeat & Metricbeat |
| Web2 | Filebeat & Metricbeat |
| Web3 | Filebeat & Metricbeat |
These Beats allow us to collect the following information from each machine:
-
Filebeat periodically monitor logs such as the Audit Logs, Server logs, and many others that are resourceful to us. The auth.log is particularly useful because it can monitor the SSH logs so that we can determine any unwanted users in our network.
-
Metricbeat monitors the system for changes to its OS metrics, such as CPU usage but most importantly it helps to watch our servers and collects data. Proactively monitoring our webservers is fundamentally important to prevent DDoS attacks.
In order to use the playbook, you will need to have an Ansible control node already configured. Assuming you have such a control node provisioned:
SSH into the control node and follow the steps below:
-
Copy the Elk.yml file to /etc/ansible/roles/
-
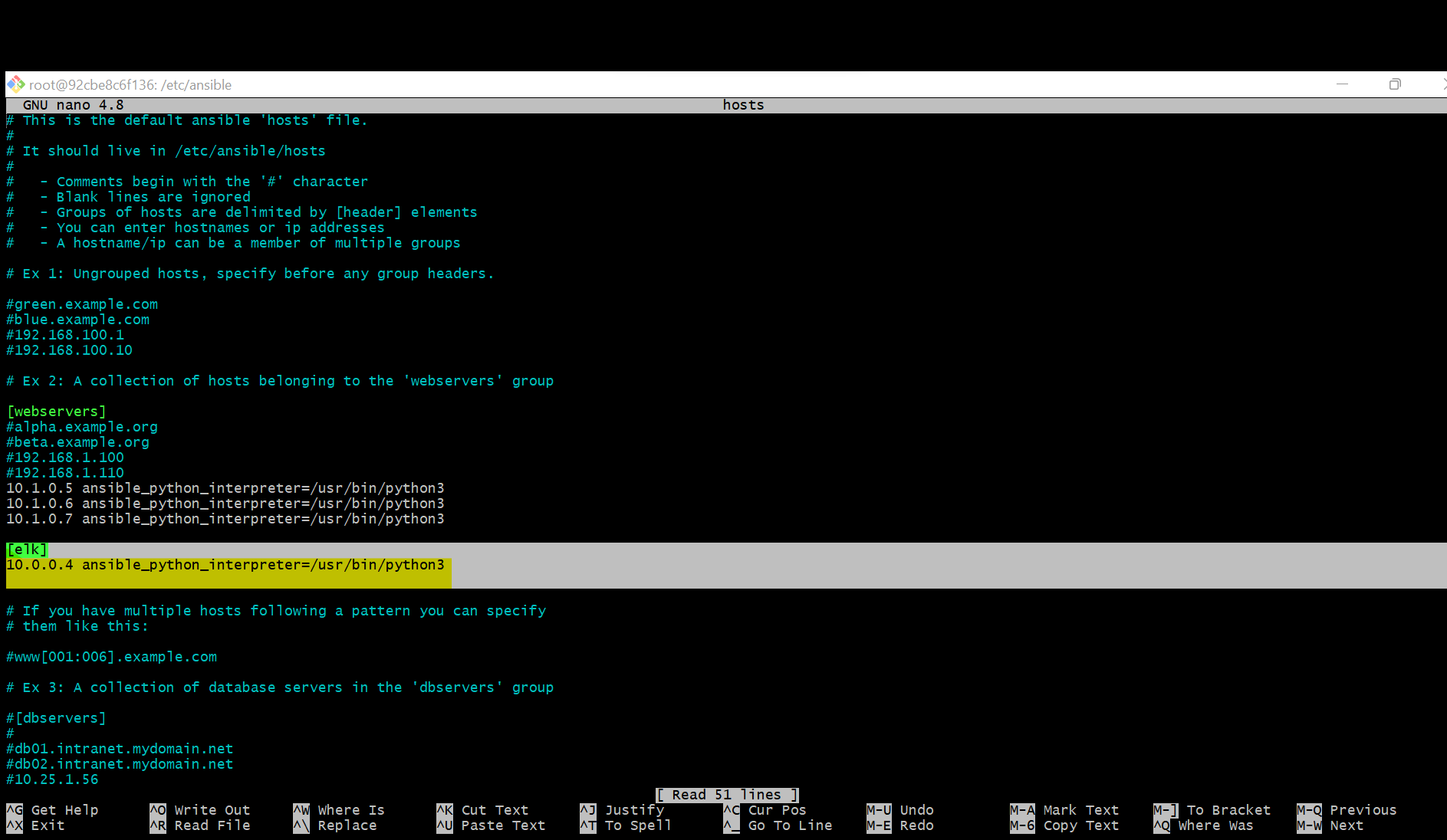
Update the Host file to include the Elk server and its IP Address 10.0.0.4 then specify what we want installed ansible_python_interpreter=/usr/bin/python3
-
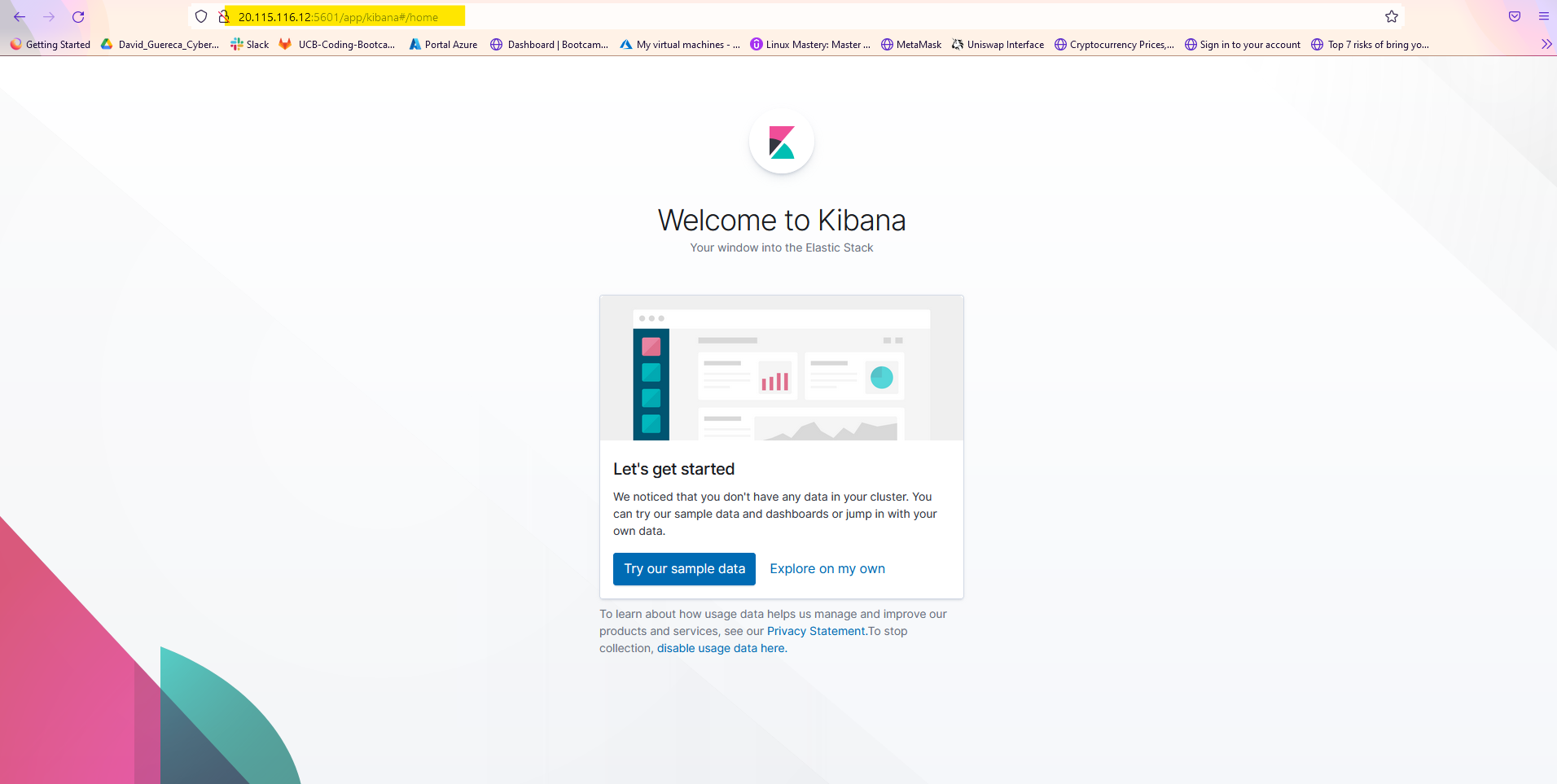
Run the playbook, and navigate to HTTP://20.115.11612:5601 to check that the installation worked as expected.
https://github.com/UCB-CyberSecurity-Cohort5/elk-stack-project-mdmd62378/blob/main/Images/Playbook_4/Kibana_http_Test_Success_of.png?raw=true
The PlayBook:Elk.yml
https://github.com/UCB-CyberSecurity-Cohort5/elk-stack-project-mdmd62378/blob/main/Images/Playbook_4/PlayBook_Nano_Elk.ymal_of.png?raw=true

https://github.com/UCB-CyberSecurity-Cohort5/elk-stack-project-mdmd62378/blob/main/PlayBook/Elk.yml
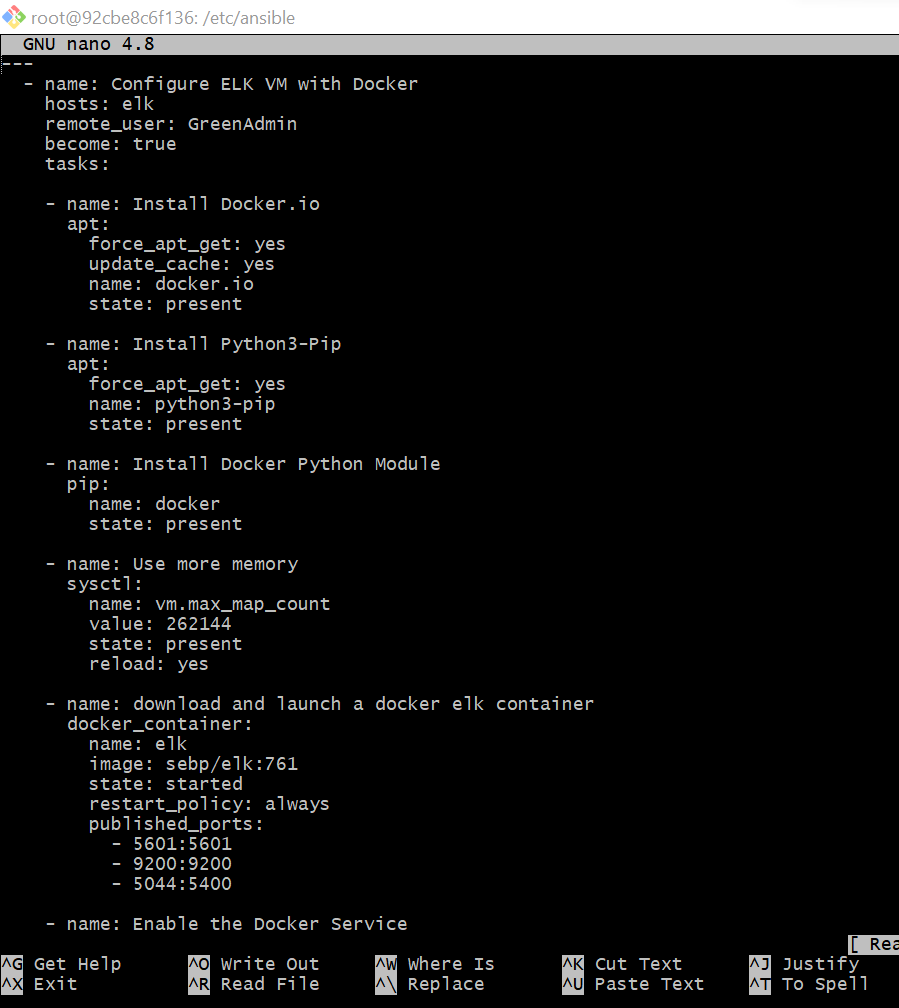
https://github.com/UCB-CyberSecurity-Cohort5/elk-stack-project-mdmd62378/blob/main/Images/Playbook_4/PlayBook_Install_of.png?raw=true

location: /etc/ansible Configuration file: Hosts is the configuration file that requires updating a new machine. We made the Elk server its own group with the specific IP address that we wanted to allow group install.
https://github.com/UCB-CyberSecurity-Cohort5/elk-stack-project-mdmd62378/blob/main/Images/Playbook_4/Configuration_Elk_Add_Server_of.png?raw=true
Url: curl HTTP://localhost:5601/app/kibana