Try DocStrange Online → | No installation required - test all features instantly in your browser!
☁️ Free Cloud Processing upto 10000 docs per month !
Extract documents data instantly with the cloud processing - no setup or api key needed for getting started.
🔒 Local Processing Available!
Usecpuorgpumode for 100% local processing - no data sent anywhere, everything stays on your machine.
Extract and convert data from any document, images, pdfs, word doc, ppt or URL into multiple formats (Markdown, JSON, CSV, HTML) with intelligent content extraction and advanced OCR.
Test DocStrange instantly in your browser without installing anything:
Perfect for:
- Quick testing - Upload and convert documents instantly
- No setup - No installation, dependencies
- Live demo - See features in action before installing
- Share results - Easy to share converted outputs with team members
Once you're ready for automation, or local/private processing, install the Python library below.
- ☁️ Cloud Processing (Default): Instant free conversion with cloud API - no local setup needed
- 🔒 Local Processing: CPU/GPU options for complete privacy - no data sent anywhere
- Universal Input: PDFs, Word docs, Excel, PowerPoint, images, URLs, and raw text
- Smart Output: Markdown, JSON, CSV, HTML, and plain text formats
- LLM-Optimized: Clean, structured output perfect for AI processing
- Intelligent Extraction: Extract specific fields or structured data using AI
- Advanced OCR: Multiple OCR engines with automatic fallback
- Table Processing: Accurate table extraction and formatting
- Image Handling: Extract text from images and visual content
- 🤖 MCP Server: Integrate with Claude Desktop for intelligent document navigation
- URL Processing: Direct conversion from web pages
💡 Want a GUI? Run the local web interface for drag-and-drop document conversion with a beautiful UI!
DocStrange includes a built-in web interface that provides a user-friendly way to process documents locally. The interface automatically downloads required models on startup and supports both CPU and GPU processing modes.
- Install with web dependencies:
pip install "docstrange[web]"- Run the web interface:
# Method 1: Using the CLI command
docstrange web
# Method 2: Using Python module
python -m docstrange.web_app
# Method 3: Direct Python import
python -c "from docstrange.web_app import run_web_app; run_web_app()"- Open your browser:
Navigate to
http://localhost:8000(or the port shown in the terminal)
- 🖱️ Drag & Drop Interface: Simply drag files onto the upload area
- 📁 Multiple File Types: Supports PDF, Word, Excel, PowerPoint, images, and more
- ⚙️ Processing Modes: Choose between Local CPU and Local GPU processing
- 📊 Multiple Output Formats: Markdown, HTML, JSON, CSV, and Flat JSON
- 📥 Automatic Model Download: Models are downloaded automatically on startup
- 🔒 100% Local Processing: No data leaves your machine
- 📱 Responsive Design: Works on desktop, tablet, and mobile
- Documents: PDF, DOCX, DOC, PPTX, PPT
- Spreadsheets: XLSX, XLS, CSV
- Images: PNG, JPG, JPEG, TIFF, BMP
- Web: HTML, HTM
- Text: TXT
- Local CPU: Works offline, slower but private (default)
- Local GPU: Fastest local processing, requires CUDA support
- Markdown: Clean, structured text perfect for documentation
- HTML: Formatted output with styling and layout
- JSON: Structured data with metadata
- CSV: Table data in spreadsheet format
- Flat JSON: Simplified JSON structure
Custom Port:
# Run on a different port
docstrange web --port 8080
python -c "from docstrange.web_app import run_web_app; run_web_app(port=8080)"Development Mode:
# Run with debug mode for development
python -c "from docstrange.web_app import run_web_app; run_web_app(debug=True)"Custom Host:
# Make accessible from other devices on the network
python -c "from docstrange.web_app import run_web_app; run_web_app(host='0.0.0.0')"Port Already in Use:
# Use a different port
docstrange web --port 8001GPU Not Available:
- The interface automatically detects GPU availability
- GPU option will be disabled if CUDA is not available
- CPU mode will be selected automatically
Model Download Issues:
- Models are downloaded automatically on first startup
- Check your internet connection during initial setup
- Download progress is shown in the terminal
Installation Issues:
# Install with all dependencies
pip install -e ".[web]"
# Or install Flask separately
pip install FlaskNeed cloud processing? Use the official DocStrange Cloud service: 🔗 docstrange.nanonets.com
pip install docstrange💡 New to DocStrange? Try the online demo first - no installation needed!
from docstrange import DocumentExtractor
# Initialize extractor (cloud mode by default)
extractor = DocumentExtractor()
# Convert any document to clean markdown
result = extractor.extract("document.pdf")
markdown = result.extract_markdown()
print(markdown)from docstrange import DocumentExtractor
# Extract document as structured JSON
extractor = DocumentExtractor()
result = extractor.extract("document.pdf")
# Get all important data as flat JSON
json_data = result.extract_data()
print(json_data)from docstrange import DocumentExtractor
# Extract only the fields you need
extractor = DocumentExtractor()
result = extractor.extract("invoice.pdf")
# Specify exactly which fields to extract
fields = result.extract_data(specified_fields=[
"invoice_number", "total_amount", "vendor_name", "due_date"
])
print(fields)from docstrange import DocumentExtractor
# Extract data conforming to your schema
extractor = DocumentExtractor()
result = extractor.extract("contract.pdf")
# Define your required structure
schema = {
"contract_number": "string",
"parties": ["string"],
"total_value": "number",
"start_date": "string",
"terms": ["string"]
}
structured_data = result.extract_data(json_schema=schema)
print(structured_data)# Force local CPU processing
extractor = DocumentExtractor(cpu=True)
# Force local GPU processing (requires CUDA)
extractor = DocumentExtractor(gpu=True)- Markdown: Clean, LLM-friendly format with preserved structure
- JSON: Structured data with metadata and intelligent parsing
- HTML: Formatted output with styling and layout
- CSV: Extract tables and data in spreadsheet format
- Text: Plain text with smart formatting
from docstrange import DocumentExtractor
extractor = DocumentExtractor()
# PDF document
pdf_result = extractor.extract("report.pdf")
print(pdf_result.extract_markdown())
# Word document
docx_result = extractor.extract("document.docx")
print(docx_result.extract_data())
# Excel spreadsheet
excel_result = extractor.extract("data.xlsx")
print(excel_result.extract_csv())
# PowerPoint presentation
pptx_result = extractor.extract("slides.pptx")
print(pptx_result.extract_html())
# Image with text
image_result = extractor.extract("screenshot.png")
print(image_result.extract_text())
# Web page
url_result = extractor.extract("https://example.com")
print(url_result.extract_markdown())# Extract all tables from a document
result = extractor.extract("financial_report.pdf")
csv_data = result.extract_csv()
print(csv_data)Requirements for enhanced JSON (if using cpu=True):
- Install:
pip install 'docstrange[local-llm]' - Install Ollama and run:
ollama serve - Pull a model:
ollama pull llama3.2
If Ollama is not available, the library automatically falls back to the standard JSON parser.
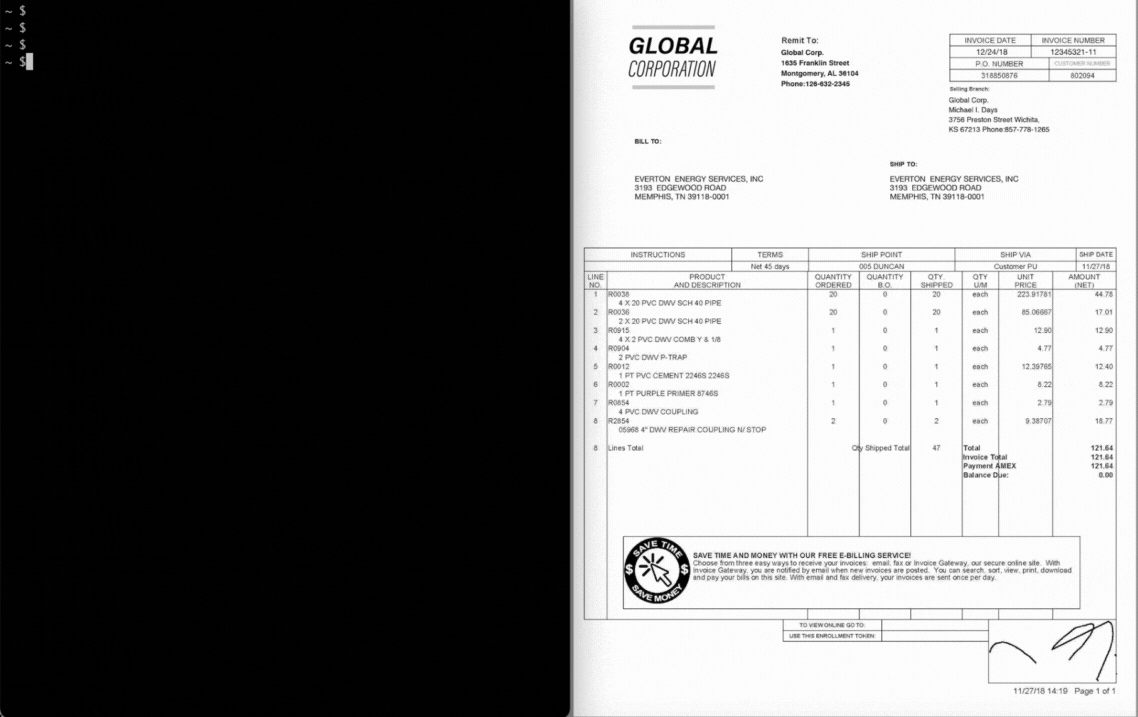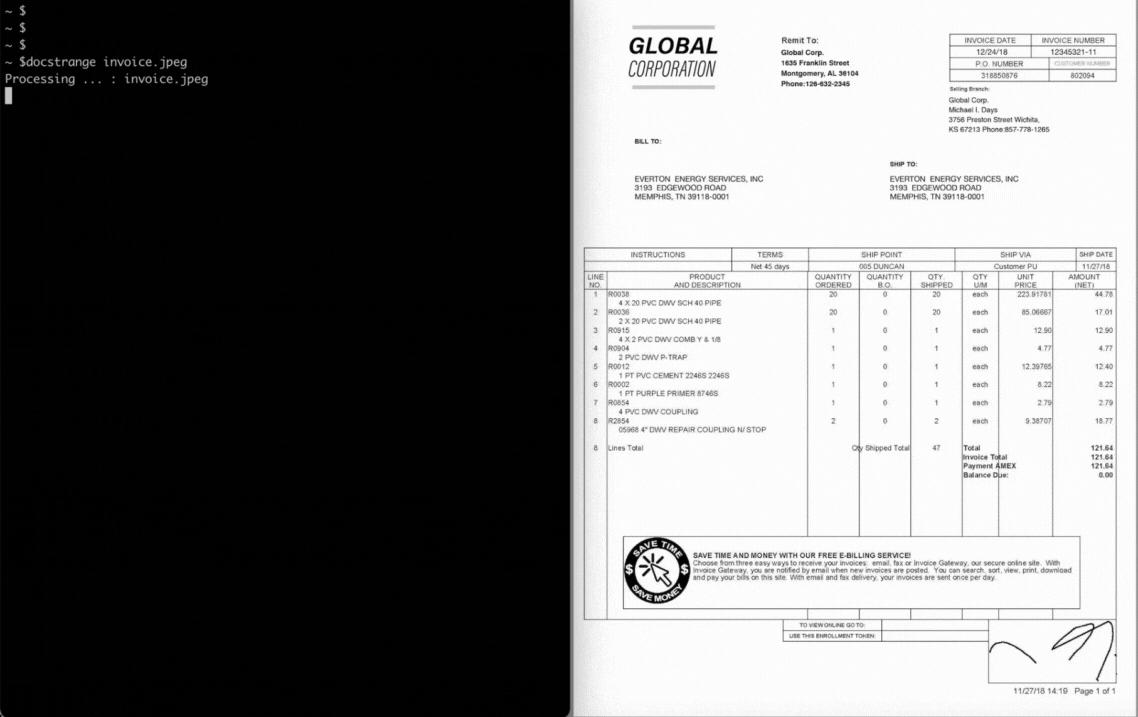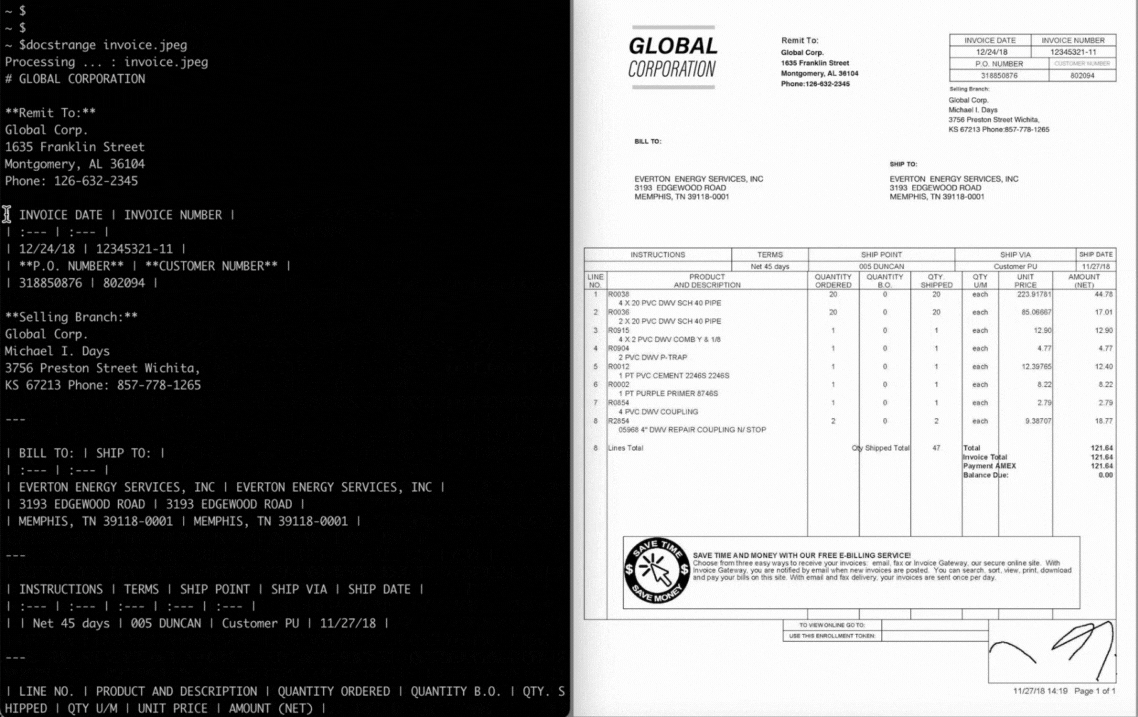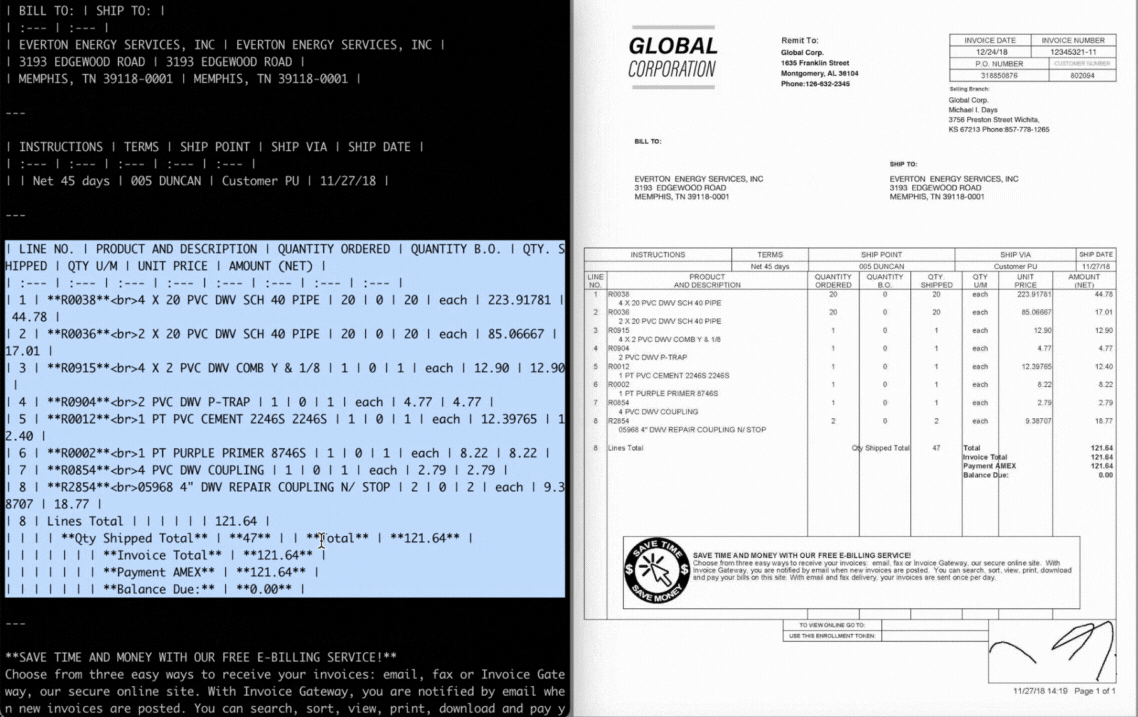
# Extract specific fields from any document
result = extractor.extract("invoice.pdf")
# Method 1: Extract specific fields
extracted = result.extract_data(specified_fields=[
"invoice_number",
"total_amount",
"vendor_name",
"due_date"
])
# Method 2: Extract using JSON schema
schema = {
"invoice_number": "string",
"total_amount": "number",
"vendor_name": "string",
"line_items": [{
"description": "string",
"amount": "number"
}]
}
structured = result.extract_data(json_schema=schema)Cloud Mode Usage Examples:
from docstrange import DocumentExtractor
# Default cloud mode (rate-limited without API key)
extractor = DocumentExtractor()
# Authenticated mode (10k docs/month) - run 'docstrange login' first
extractor = DocumentExtractor() # Auto-uses cached credentials
# With API key for 10k docs/month (alternative to login)
extractor = DocumentExtractor(api_key="your_api_key_here")
# Extract specific fields from invoice
result = extractor.extract("invoice.pdf")
# Extract key invoice information
invoice_fields = result.extract_data(specified_fields=[
"invoice_number",
"total_amount",
"vendor_name",
"due_date",
"items_count"
])
print("Extracted Invoice Fields:")
print(invoice_fields)
# Output: {"extracted_fields": {"invoice_number": "INV-001", ...}, "format": "specified_fields"}
# Extract structured data using schema
invoice_schema = {
"invoice_number": "string",
"total_amount": "number",
"vendor_name": "string",
"billing_address": {
"street": "string",
"city": "string",
"zip_code": "string"
},
"line_items": [{
"description": "string",
"quantity": "number",
"unit_price": "number",
"total": "number"
}],
"taxes": {
"tax_rate": "number",
"tax_amount": "number"
}
}
structured_invoice = result.extract_data(json_schema=invoice_schema)
print("Structured Invoice Data:")
print(structured_invoice)
# Output: {"structured_data": {...}, "schema": {...}, "format": "structured_json"}
# Extract from different document types
receipt = extractor.extract("receipt.jpg")
receipt_data = receipt.extract_data(specified_fields=[
"merchant_name", "total_amount", "date", "payment_method"
])
contract = extractor.extract("contract.pdf")
contract_schema = {
"parties": [{
"name": "string",
"role": "string"
}],
"contract_value": "number",
"start_date": "string",
"end_date": "string",
"key_terms": ["string"]
}
contract_data = contract.extract_data(json_schema=contract_schema)Local extraction requirements (if using cpu=True):
- Install ollama package:
pip install 'docstrange[local-llm]' - Install Ollama and run:
ollama serve - Pull a model:
ollama pull llama3.2
# Perfect for LLM workflows
document_text = extractor.extract("research_paper.pdf").extract_markdown()
# Use with any LLM
response = your_llm_client.chat(
messages=[{
"role": "user",
"content": f"Summarize this research paper:\n\n{document_text}"
}]
)DocStrange offers free cloud processing with rate limits to ensure fair usage:
- Rate Limit: limited calls
- Access: All output formats (Markdown, JSON, CSV, HTML)
- Setup: Zero configuration - works immediately
- Rate Limit: 10,000 documents/month
- Setup: One command:
docstrange login - Benefits: Same Google account as docstrange.nanonets.com
- Rate Limit: 10,000 documents/month
- Setup: Get your free API key from app.nanonets.com
- Usage: Pass API key during initialization
# Free tier usage (limited calls daily)
extractor = DocumentExtractor()
# Authenticated access (10k docs/month) - run 'docstrange login' first
extractor = DocumentExtractor() # Auto-uses cached credentials
# API key access (10k docs/month)
extractor = DocumentExtractor(api_key="your_api_key_here")💡 Tip: Start with the free tier (limited calls) to test functionality, then authenticate with
docstrange loginfor free 10,000 docs/month, or get an API key for the same enhanced limits.
💡 Prefer a GUI? Try the web interface for drag-and-drop document conversion!
# One-time login for free 10k docs/month (alternative to api key)
docstrange login
# Alternatively
docstrange --login
# Re-authenticate if needed
docstrange login --reauth
# Logout and clear cached credentials
docstrange --logout# Basic conversion (cloud mode default - limited calls free!)
docstrange document.pdf
# Authenticated processing (10k docs/month for free after login)
docstrange document.pdf
# With API key for 10k docs/month access (alternative to login)
docstrange document.pdf --api-key YOUR_API_KEY
# Local processing modes
docstrange document.pdf --cpu-mode
docstrange document.pdf --gpu-mode
# Different output formats
docstrange document.pdf --output json
docstrange document.pdf --output html
docstrange document.pdf --output csv
# Extract specific fields
docstrange invoice.pdf --output json --extract-fields invoice_number total_amount
# Extract with JSON schema
docstrange document.pdf --output json --json-schema schema.json
# Multiple files
docstrange *.pdf --output markdown
# Save to file
docstrange document.pdf --output-file result.md
# Comprehensive field extraction examples
docstrange invoice.pdf --output json --extract-fields invoice_number vendor_name total_amount due_date line_items
# Extract from different document types with specific fields
docstrange receipt.jpg --output json --extract-fields merchant_name total_amount date payment_method
docstrange contract.pdf --output json --extract-fields parties contract_value start_date end_date
# Using JSON schema files for structured extraction
docstrange invoice.pdf --output json --json-schema invoice_schema.json
docstrange contract.pdf --output json --json-schema contract_schema.json
# Combine with authentication for 10k docs/month access (after 'docstrange login')
docstrange document.pdf --output json --extract-fields title author date summary
# Or use API key for 10k docs/month access (alternative to login)
docstrange document.pdf --api-key YOUR_API_KEY --output json --extract-fields title author date summary
# Force local processing with field extraction (requires Ollama)
docstrange document.pdf --cpu-mode --output json --extract-fields key_points conclusions recommendationsExample schema.json file:
{
"invoice_number": "string",
"total_amount": "number",
"vendor_name": "string",
"billing_address": {
"street": "string",
"city": "string",
"zip_code": "string"
},
"line_items": [{
"description": "string",
"quantity": "number",
"unit_price": "number"
}]
}DocumentExtractor(
api_key: str = None, # API key for 10k docs/month (or use 'docstrange login' for same limits)
model: str = None, # Model for cloud processing ("gemini", "openapi", "nanonets")
cpu: bool = False, # Force local CPU processing
gpu: bool = False # Force local GPU processing
)result.extract_markdown() -> str # Clean markdown output
result.extract_data( # Structured JSON
specified_fields: List[str] = None, # Extract specific fields
json_schema: Dict = None # Extract with schema
) -> Dict
result.extract_html() -> str # Formatted HTML
result.extract_csv() -> str # CSV format for tables
result.extract_text() -> str # Plain textThe docstrange repository includes an optional MCP (Model Context Protocol) server for local development that enables intelligent document processing in Claude Desktop with token-aware navigation.
Note: The MCP server is designed for local development and is not included in the PyPI package. Clone the repository to use it locally.
- Smart Token Counting: Automatically counts tokens and recommends processing strategy
- Hierarchical Navigation: Navigate documents by structure when they exceed context limits
- Intelligent Chunking: Automatically splits large documents into token-limited chunks
- Advanced Search: Search within documents and get contextual results
- Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/nanonets/docstrange.git
cd docstrange- Install in development mode:
pip install -e ".[dev]"- Add to your Claude Desktop config (
~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json):
{
"mcpServers": {
"docstrange": {
"command": "python3",
"args": ["/path/to/docstrange/mcp_server_module/server.py"]
}
}
}- Restart Claude Desktop
For detailed setup and usage, see mcp_server_module/README.md
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details.
- 🌐 Online Demo: docstrange.nanonets.com - Test features instantly
- Email: support@nanonets.com
- Issues: GitHub Issues
- Discussions: GitHub Discussions
Star this repo if you find it helpful! Your support helps us improve the library.