⚠️ Alert: If you are using this code with Keras v3, make sure you are using Keras ≥ 3.6.0. Earlier versions of Keras v3 do not honortrainable=False, which will result in training hand-crafted filters in LITEMV unexpectedly.
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| CI/CD | |
| Code |     |
| Community |  |
Authors: Ali Ismail-Fawaz1, Maxime Devanne1, Stefano Berreti2, Jonathan Weber1 and Germain Forestier1,3
1 IRIMAS, Universite de Haute-Alsace, France
2 MICC, University of Florence, Italy
3 DSAI, Monash University, Australia
This repository is the source code of the article titled "Re-framing Time Series Augmentation Through the Lens of Generative Models" accepted in the 10th Workshop on Advanced Analytics and Learning on Temporal Data (AALTD 2025) in conjunction with the 2025 European Conference on Machine Learning and Principles and Practice of Knowledge Discovery in Databases (ECML-PKDD 2025). In this article, we present a benchmark comparison between 22 data augmentation techniques on 131 time series classification datasets of the UCR archive.
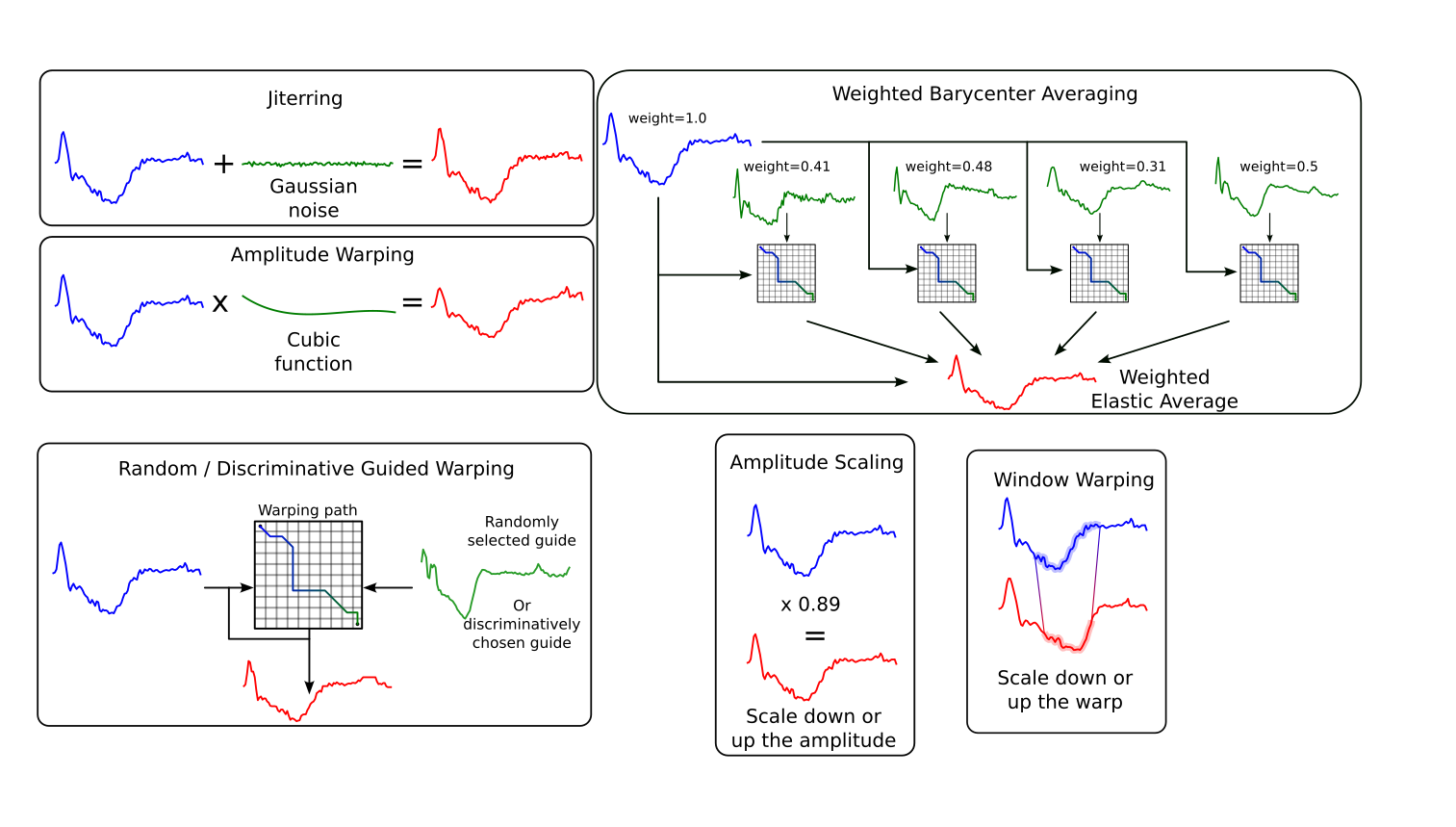
Time series classification is widely used in many fields, but it often suffers from a lack of labeled data. To address this, researchers commonly apply data augmentation techniques that generate synthetic samples through transformations such as jittering, warping, or resampling. However, with an increasing number of available augmentation methods, it becomes difficult to choose the most suitable one for a given task. In many cases, this choice is based on intuition or visual inspection. Assessing the impact of this choice on classification accuracy requires training models, which is time-consuming and depends on the dataset. In this work, we adopt a generative model perspective and evaluate augmentation methods prior to training any classifier, using metrics that quantify both fidelity and diversity of the generated samples. We benchmark 22 augmentation techniques on 131 public datasets using eight metrics. Our results provide a practical and efficient way to compare augmentation methods without relying solely on classifier performance.
In this work we utilize 131 datasets of the UCR archive taken from the original repository and the new added datasets.
However you are not obligated to download them as our code loads the datasets through the Time Series Classification webpage using aeon-toolkit.
This repository supports the usage of docker. In order to create the docker image using the dockerfile, simply run the following command (assuming you have docker installed and nvidia cuda container as well):
docker build --build-arg USER_ID=$(id -u) --build-arg GROUP_ID=$(id -g) -t data-augmentation-review-image .After the image has been successfully built, you can create the docker container using the following command:
docker run --gpus all -it --name data-augmentation-review-container -v "$(pwd):/home/myuser/code" --user $(id -u):$(id -g) data-augmentation-review-image bashThe code will be stored under the directory /home/myuser/code/ inside the docker container. This will allow you to use GPU acceleration.
If you do not want to use docker, simply install the project using the following command:
python3 -m venv ./data-augmentation-review-venv
source ./data-augmentation-review-venv/bin/activate
pip install --upgrade pip
pip install -e .[dev]Make sure you have jq installed on your system. This project supports python>=3.10 only.
You can see the list of dependencies and their required version in the pyptoject.toml file.
If you wish to run a single experiment on a single dataset, using a single augmentation method, using a single model then first you have to execute your docker container to open a terminal inside if you're not inside the container:
docker exec -it data-augmentation-review-container bashThen you can run the following command for example to run Amplitude Warping on the Adiac dataset:
python3 main.py task=generate_data dataset_name=Adiac generate_data.method=AWThe code uses hydra for the parameter configuration, simply see the hydra configuration file for a detailed view on the parameters of our experiments.
If you wish to run all the experiments to reproduce the results of our article simply run the following for data generation experiments:
chmod +x run_generate_data.sh
nohup ./run_generate_data.sh &and the following for training the feature extractor:
chmod +x run_train_feature_extractor.sh
nohup ./run_train_feature_extractor.sh &and the following for evaluation of the generations:
chmod +x run_evaluate_generation.sh
nohup ./run_evaluate_generation.sh &If you use this work please cite the following:
@inproceedings{ismail-fawaz2025Data-Aug-4-TSC,
author = {Ismail-Fawaz, Ali and Devanne, Maxime and Berretti, Sefano and Weber, Jonathan and Forestier, Germain},
title = {Re-framing Time Series Augmentation Through the Lens of Generative Models},
booktitle = {ECML/PKDD Workshop on Advanced Analytics and Learning on Temporal Data},
city = {Porto},
country = {Portugal},
year = {2025}
}This work was supported by the ANR DELEGATION project (grant ANR-21-CE23-0014) of the French Agence Nationale de la Recherche. The authors would like to acknowledge the High Performance Computing Center of the University of Strasbourg for supporting this work by providing scientific sup- port and access to computing resources. Part of the computing resources were funded by the Equipex Equip@Meso project (Programme Investissements d’Avenir) and the CPER Alsacalcul/Big Data. The authors would also like to thank the creators and providers of the UCR Archive