Wildfire occurrence, frequency, and behavior have altered dramatically across time and location, owing primarily to the complex factors of climate change and variation. The annual amount of forest area burned by wildland fires in Canada's northwestern boreal regions increased steadily throughout the second half of the 20th century. “Climate change during the 21st century is expected to result in more frequent fires in many boreal forests, with severe environmental and economic consequences” [1]. Understanding the future activity of wildfires is a prevalent research topic in academia. To that end, we present an exploratory analysis of historical wildfire activity seen in Canada from 1930 to 2020 using Google’s BigQuery platform and Data Studio. In addition, we apply various Machine Learning approaches to estimate the approximate amount of damage caused by fire based on key indices.
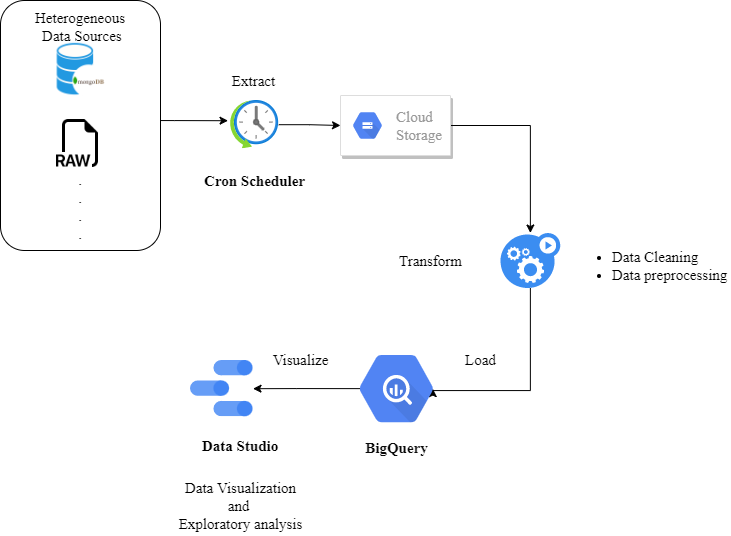
Following demonstration displays the Extract Transform and Load datapipeline to feed data from various databases to Google's BigQuery Data Platform
ETL.Demo.mp4
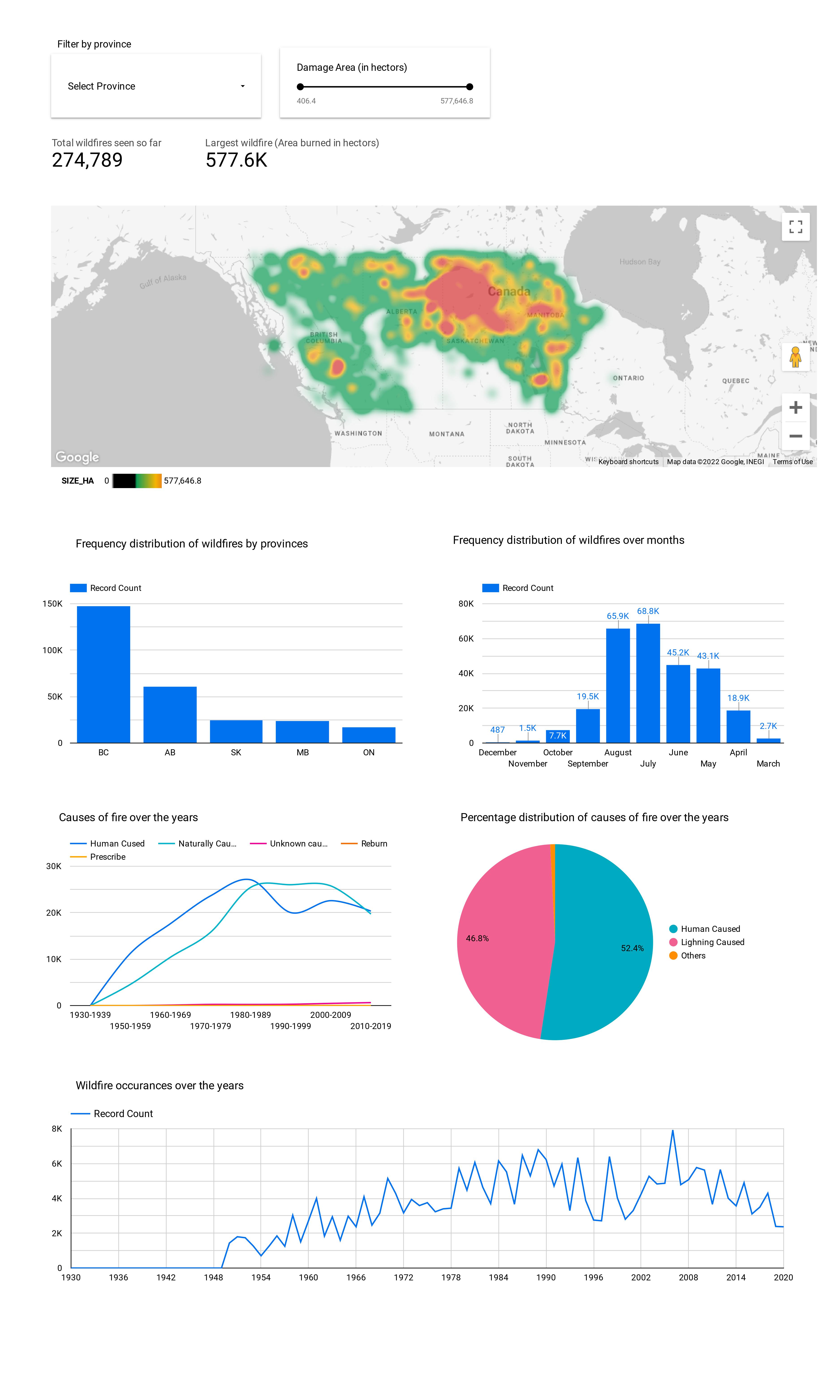
To perform exploratory analysis Bigquery project is then connected to DataStudio platform to perform visualization
Next based on the exploratory analysis we drill down on fire activity in alberta and perform predictive analysis to estimate fire sizes in future using various ML models.
| Regression Model | Mean Absolute Error |
|---|---|
| SVM | 0.1552 |
| Random Forest | 0.1374 |
| Gradient Boosting | 0.0110 |
| K-Means | 0.1998 |