A Spring Cloud Gateway Server WebFlux application that routes API requests to the Base Payments Service.
- Overview
- Tech Stack
- Configuration
- Running Locally
- Testing
- Monitoring and Management
- Service Integration
- Logging
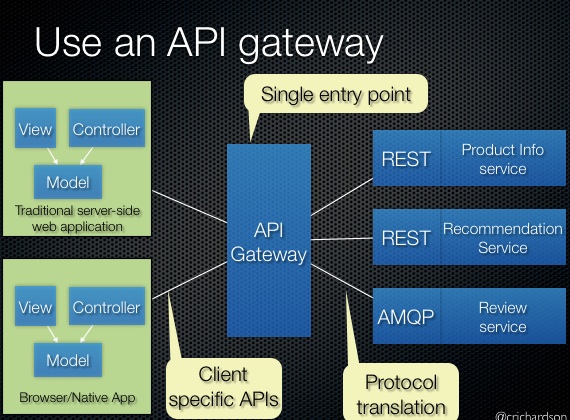
This gateway serves as an API gateway for the Base Payments microservice architecture. It handles routing, load balancing, and provides a single entry point for client applications to interact with the underlying services.
💡 API Gateway Pattern: Acts as a single entry point for all clients, providing a unified interface to the microservices.
| Technology | Version | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Java | 21 | Programming Language |
| Spring Boot | 3.5.0 | Application Framework |
| Spring Cloud | 2025.0.0 | Cloud Native Development |
| Spring Cloud Gateway Server WebFlux | - | API Gateway |
| Spring Cloud Netflix Eureka Client | - | Service Discovery |
| Spring Cloud LoadBalancer | - | Load Balancing |
| Spring Boot Actuator | - | Monitoring & Management |
| Spring Boot WebFlux | - | Reactive Programming |
| Redis | - | Rate Limiting & Caching |
| Docker Compose | - | Container Orchestration |
The application runs on port 9090
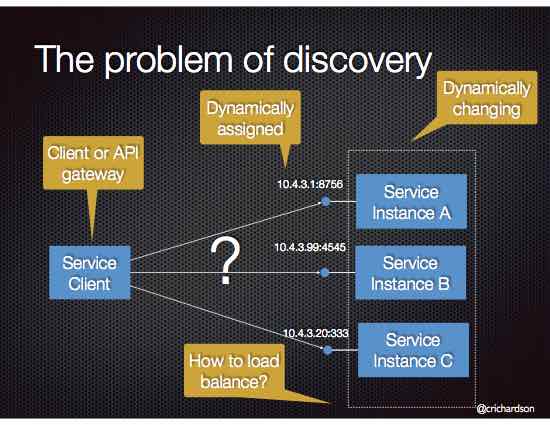
Uses Eureka for service discovery
| Path | Target Service | Additional Headers | Rate Limiting |
|---|---|---|---|
/orders/** |
BASE-PAYMENTS | version: 1.0.0 |
10 req/sec, burst: 20 |
/products/** |
BASE-PAYMENTS | version: 1.0.0 |
10 req/sec, burst: 20 |
The application uses Redis-based rate limiting to protect the API from excessive requests:
- Rate: 10 requests per second
- Burst Capacity: 20 requests
- Key Resolver: Client IP address (each IP has its own rate limit)
- Redis: Required for storing rate limit counters
- Response: Returns HTTP 429 (Too Many Requests) status code when rate limit is exceeded
- Empty Response: Configured to return a response body with the status code
The project includes Docker Compose integration for easy setup of required services:
- Redis: Automatically starts a Redis container for rate limiting
- Spring Boot Docker Compose: Automatically manages container lifecycle
- Volume Persistence: Redis data is persisted across restarts
💡 How it works: When you run the application with
./gradlew bootRun, Spring Boot automatically detects thedocker-compose.ymlfile and starts the defined services before the application starts.
✅ Java 21 or higher
✅ Gradle
✅ Eureka Server running on port 8761
✅ Docker and Docker Compose (optional, for automatic Redis setup)
💡 Note: If you don't have Docker installed, you'll need Redis Server running on port 6379 for rate limiting.
1️⃣ Clone the repository:
git clone [repository-url]
cd base-payments-gateway2️⃣ Build the application:
./gradlew build3️⃣ Run the application:
./gradlew bootRun💡 Alternatively, you can run the JAR file directly:
java -jar build/libs/base-payments-gateway-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
4️⃣ The application will be available at http://localhost:9090
⚠️ Note: The automated tests for this project may encounter issues due to the complexity of testing Spring Cloud Gateway with Redis rate limiting in a test environment. Some tests are commented out because they require Redis to be running. To run these tests, uncomment them and ensure Redis is running. The manual testing procedures below provide a reliable way to verify the functionality.
The project includes automated tests organized by feature to verify the functionality of the gateway:
-
Orders Feature Tests:
- OrdersRouteTest: Verifies that the orders route is correctly configured with the proper path predicate
- OrdersVersionHeaderTest: Ensures that the version header is correctly added to requests to the orders endpoint
- OrdersRateLimitTest: Tests the rate limiting functionality for the orders endpoint, including verification of the 429 status code when the rate limit is exceeded
-
Products Feature Tests:
- ProductsRouteTest: Verifies that the products route is correctly configured with the proper path predicate
- ProductsVersionHeaderTest: Ensures that the version header is correctly added to requests to the products endpoint
- ProductsRateLimitTest: Tests the rate limiting functionality for the products endpoint, including verification of the 429 status code when the rate limit is exceeded
The tests use WireMock to simulate the backend services, allowing for comprehensive testing of the gateway's routing, header manipulation, and rate limiting capabilities without requiring external services.
You can also test the gateway routes manually using tools like cURL, Postman, or any HTTP client:
-
Start the Gateway and Dependencies:
- Start Redis (automatically handled by Docker Compose)
- Start Eureka Server (if available)
- Start the Base Payments Service (or a mock service on the same port)
- Start the Gateway application
-
Test the Orders Route:
# Send a request to the orders endpoint curl -v http://localhost:9090/orders # Check that the request is routed to the BASE-PAYMENTS service # Verify that the 'version: 1.0.0' header is added
-
Test the Products Route:
# Send a request to the products endpoint curl -v http://localhost:9090/products # Check that the request is routed to the BASE-PAYMENTS service # Verify that the 'version: 1.0.0' header is added
You can test the rate limiting functionality by sending multiple requests in quick succession:
-
Test Rate Limiting:
# Send multiple requests to the orders endpoint for i in {1..25}; do curl -v http://localhost:9090/orders echo "Request $i completed" # No delay between requests to trigger rate limiting done
-
Expected Behavior:
- The first 20 requests should succeed (due to burst capacity of 20)
- Subsequent requests should receive a 429 Too Many Requests response
- After waiting a few seconds, new requests should succeed again
-
Verify Rate Limit Reset:
# Wait for rate limit to reset (about 2 seconds) sleep 2 # Send another request, which should now succeed curl -v http://localhost:9090/orders
Postman provides a more user-friendly interface for testing:
- Create a Collection for gateway tests
- Add Requests for each endpoint (/orders, /products)
- Use the Runner to send multiple requests to test rate limiting
- Check Response Headers to verify routing and rate limiting behavior
You can monitor rate limiting through the application logs:
# Tail the logs to see rate limiting in action
tail -f logs/application.log
# Look for entries like:
# "Requesting tokens from Redis rate limiter: 1"
# "Received token response: [true/false]"💡 Tip: Set the logging level to DEBUG or TRACE in application.yml for more detailed rate limiting logs.
Spring Boot Actuator provides endpoints to monitor the application, including rate limiting:
-
Gateway Routes: View all configured routes
http://localhost:9090/actuator/gateway/routes -
Gateway Global Filters: View all global filters, including rate limiting
http://localhost:9090/actuator/gateway/globalfilters -
Gateway Route Filters: View filters for specific routes
http://localhost:9090/actuator/gateway/routefilters -
Redis Health: Check Redis connection status
http://localhost:9090/actuator/health/redis -
Metrics: Monitor rate limiter metrics
http://localhost:9090/actuator/metrics/spring.cloud.gateway.requests
💡 Tip: You can use these endpoints to verify that the rate limiter is properly configured and functioning.
If you encounter issues when testing:
- Verify that Eureka Server is running and the BASE-PAYMENTS service is registered
- Check the gateway logs for routing errors
- Ensure the BASE-PAYMENTS service is accessible directly
- Verify that the route configuration in application.yml is correct
- Verify that Redis is running (
docker psshould show the Redis container) - Check Redis connection in the logs
- Try restarting Redis (
docker-compose restart redis) - Ensure the rate limiter configuration in application.yml is correct
- Try with a different client IP to reset the rate limit counter
- 404 Not Found: The route may be incorrect or the downstream service is not available
- 503 Service Unavailable: The downstream service might be registered with Eureka but not actually running
- 429 Too Many Requests: Rate limit exceeded (this is expected when testing rate limiting)
- Connection Refused: Redis or Eureka might not be running
The application exposes various Spring Boot Actuator endpoints for monitoring and management:
| Endpoint | URL | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Health Check | http://localhost:9090/actuator/health | Shows application health information |
| Info | http://localhost:9090/actuator/info | Displays application information |
| All Actuator Endpoints | http://localhost:9090/actuator | Lists all available actuator endpoints |
This gateway routes requests to the Base Payments Service using:
- ✅ Eureka for service discovery
- ✅ Load Balancing for distributing traffic
The application has detailed logging enabled for:
- 📋 Spring Cloud Gateway Server WebFlux
- 📋 Spring Web
- 📋 Netflix Discovery
- 📋 Spring Cloud Client Discovery
⚠️ Note: Detailed logging helps in debugging and monitoring the gateway's behavior, but may impact performance in production environments.
- Spring Cloud Gateway Server WebFlux Documentation
- Spring Boot Documentation
- Microservices.io - API Gateway Pattern
- Microservices.io - Service Discovery Pattern
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details.