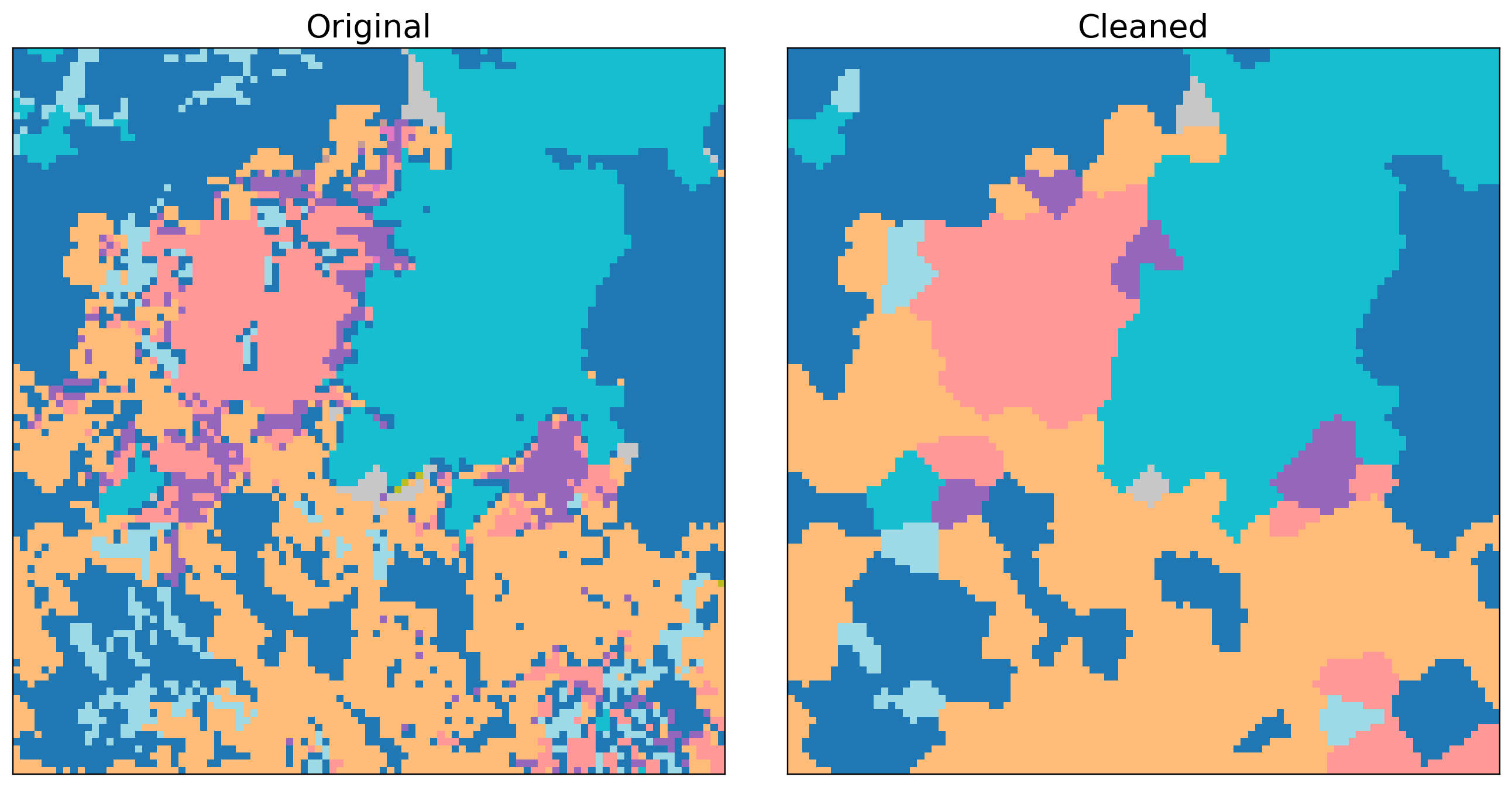
MultiClean is a Python library for morphological cleaning of multiclass 2D numpy arrays (segmentation masks and classification rasters). It provides efficient tools for edge smoothing and small-island removal across multiple classes, then fills gaps using the nearest valid class.
Below: Land Use before/after cleaning (smoothed edges, small-island removal, nearest-class gap fill).
pip install multicleanor
uv add multicleanimport numpy as np
from multiclean import clean_array
# Create a sample classification array with classes 0, 1, 2, 3
array = np.random.randint(0, 4, (1000, 1000), dtype=np.int32)
# Clean with default parameters
cleaned = clean_array(array)
# Custom parameters
cleaned = clean_array(
array,
class_values=[0, 1, 2, 3],
smooth_edge_size=2, # kernel width, larger value increases smoothness
min_island_size=100, # remove components with area < 100
connectivity=8, # 4 or 8
max_workers=4,
fill_nan=False # enable/disable the filling of nan values in input array
)MultiClean is designed for cleaning segmentation outputs from:
- Remote sensing: Land cover classification, crop mapping
- Computer vision: Semantic segmentation post-processing
- Geospatial analysis: Raster classification cleaning
- Machine learning: Neural network output refinement
- Multi-class processing: Clean all classes in one pass
- Edge smoothing: Morphological opening to reduce jagged boundaries
- Island removal: Remove small connected components per class
- Gap filling: Fill invalids via nearest valid class (distance transform)
- Fast: NumPy + OpenCV + SciPy with parallelism
MultiClean uses morphological operations to clean classification arrays:
- Edge smoothing (per class): Morphological opening with an elliptical kernel.
- Island removal (per class): Find connected components (OpenCV) and mark components with area
< min_island_sizeas invalid. - Gap filling: Compute a distance transform to copy the nearest valid class into invalid pixels.
Classes are processed together and the result maintains a valid label at every pixel.
from multiclean import clean_array
out = clean_array(
array: np.ndarray,
class_values: int | list[int] | None = None,
smooth_edge_size: int = 2,
min_island_size: int = 100,
connectivity: int = 4,
max_workers: int | None = None,
fill_nan: bool = False
)array: 2D numpy array of class labels (int or float). For float arrays,NaNis treated as nodata and will remainNaNunlessfill_nanis set toTrue.class_values: Classes to consider. IfNone, inferred fromarray(ignoresNaNfor floats). An int restricts cleaning to a single class.smooth_edge_size: Kernel size (pixels) for morphological opening. Use0to disable.min_island_size: Remove components with area strictly< min_island_size. Use1to keep single pixels.connectivity: Pixel connectivity for components,4or8.max_workers: Parallelism for per-class operations (None lets the executor choose).fill_nan: If True will fill NAN values from input array with nearest valid value.
Returns a numpy array matching the input shape. Integer inputs return integer outputs. Float arrays with NaN are supported and can be filled or remain as NAN.
from multiclean import clean_array
import rasterio
# Read land cover classification
with rasterio.open('landcover.tif') as src:
landcover = src.read(1)
# Clean with appropriate parameters for satellite data
cleaned = clean_array(
landcover,
class_values=[0, 1, 2, 3, 4], # forest, water, urban, crop, other
smooth_edge_size=1,
min_island_size=25,
connectivity=8,
fill_nan=False
)from multiclean import clean_array
# Model produces logits; convert to class predictions
np_pred = np_model_logits.argmax(axis=0) # shape: (H, W)
# Clean the segmentation
cleaned = clean_array(
np_pred,
smooth_edge_size=2,
min_island_size=100,
connectivity=4,
)See the notebooks folder for end-to-end examples:
- Land Use Example Notebook: land use classification cleaning
- Cloud Example Notebook: cloud/shadow classification cleaning
Contributions are welcome! Please feel free to submit a Pull Request.
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details.