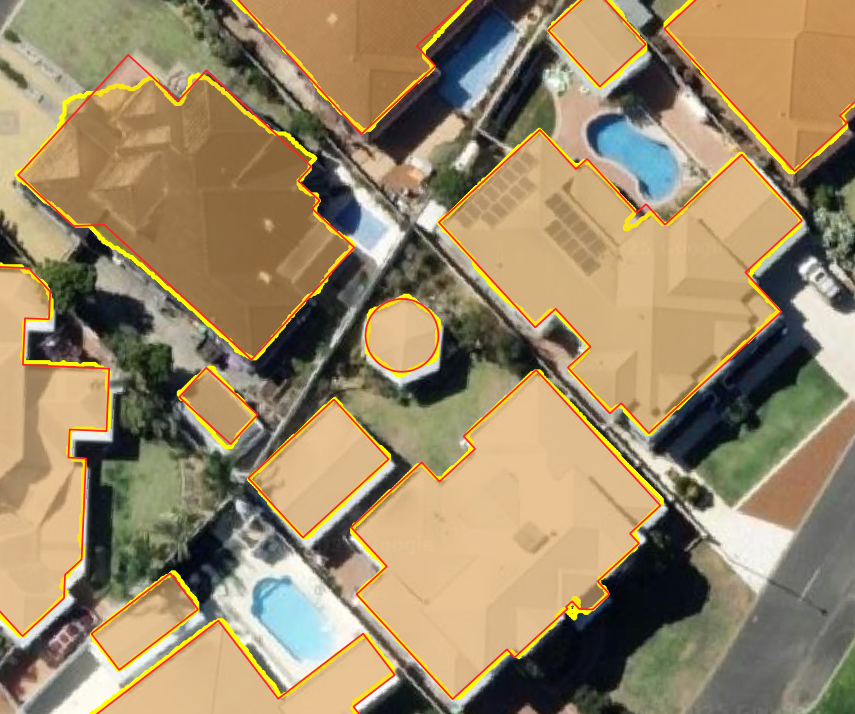
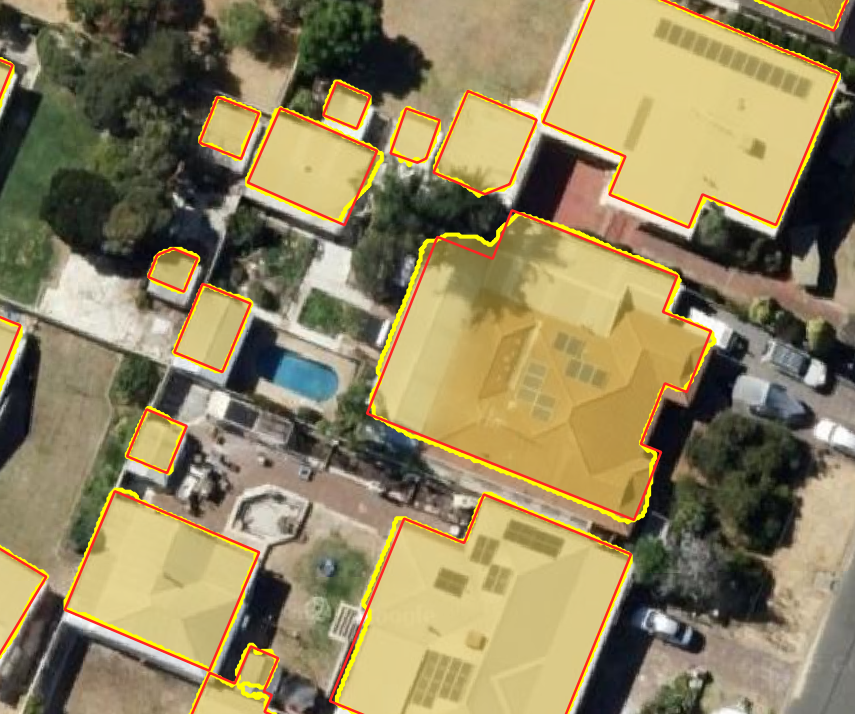
A Python library for regularizing building footprints in geospatial data. This library helps clean up and standardize building polygon geometries by aligning edges to principal directions. Built as an open source alternative to the ArcGIS Regularize Building Footprint (3D Analyst) tool.
Before and after regularization:
Building footprints extracted from remote sensing imagery often contain noise, irregular edges, and geometric inconsistencies. This library provides tools to regularize these footprints by:
- Aligning edges to principal directions (orthogonal and optional 45-degree angles)
- Converting near-rectangular buildings to perfect rectangles
- Converting near-circular buildings to perfect circles
- Simplifying complex polygons while maintaining their essential shape
- Supporting parallel processing for efficient computation with large datasets
- Fine-tune building alignment with neighboring buildings
Inspired by RS-building-regularization, this library takes a geometric approach to building regularization with improvements for usability and integration with the GeoPandas ecosystem.
pip install buildingregulariseror
conda install conda-forge::buildingregulariseror
uv add buildingregulariserimport geopandas as gpd
from buildingregulariser import regularize_geodataframe
# Load your building footprints
buildings = gpd.read_file("buildings.gpkg")
# Regularize the building footprints
regularized_buildings = regularize_geodataframe(
buildings,
)
# Save the results
regularized_buildings.to_file("regularized_buildings.gpkg")- GeoDataFrame Integration: Works seamlessly with GeoPandas GeoDataFrames
- Polygon Regularization: Aligns edges to principal directions
- 45-Degree Support: Optional alignment to 45-degree angles
- Align with neighboring buildings: Align each building with neighboring buildings
- Circle Detection: Identifies and converts near-circular shapes to perfect circles
- Edge Simplification: Reduces the number of vertices while preserving shape
- Parallel Processing: Utilizes multiple CPU cores for faster processing of large datasets
from buildingregulariser import regularize_geodataframe
import geopandas as gpd
buildings = gpd.read_file("buildings.gpkg")
regularized = regularize_geodataframe(buildings)regularized = regularize_geodataframe(
buildings,
parallel_threshold=2.0, # Higher values allow less edge alignment
simplify_tolerance=0.5, # Controls simplification level, should be 2-3 x the raster pixel size
allow_45_degree=True, # Enable 45-degree angles
allow_circles=True, # Enable circle detection
circle_threshold=0.9 # IOU threshold for circle detection
neighbor_alignment=True, # After regularization try to align each building with neighboring buildings
neighbor_search_distance: float = 100.0, # The search distance around each building to find neighbors
neighbor_max_rotation: float = 10, # The maximum rotation allowed to align with neighbors
)- geodataframe: Input GeoDataFrame with polygon geometries
- parallel_threshold: Distance threshold for handling parallel lines (default: 1.0)
- simplify: If True, applies simplification to the geometry (default: True)
- simplify_tolerance: Tolerance for simplification (default: 0.5)
- allow_45_degree: If True, allows edges to be oriented at 45-degree angles (default: True)
- diagonal_threshold_reduction: Used to reduce the chance of diagonal edges being generated, can be from 0 to 22.5 (default: 15.0)
- allow_circles: If True, detects and converts near-circular shapes to perfect circles (default: True)
- circle_threshold: Intersection over Union (IoU) threshold for circle detection (default: 0.9)
- num_cores: Number of CPU cores to use for parallel processing (default: 1)
- include_metadata: Include the main direction, IOU, perimeter and aligned_direction (if used) in output gdf
- neighbor_alignment: If True, try to align each building with neighboring buildings (default: False)
- neighbor_search_distance: The distance to find neighboring buildings (default: 350.0)
- neighbor_max_rotation: The maximum allowable rotation to align with neighbors (default: 10)
- A new GeoDataFrame with regularized polygon geometries
- Edge Analysis: Analyzes each polygon to identify principal directions
- Edge Orientation: Aligns edges to be parallel, perpendicular, or at 45 degrees to the main direction
- Circle Detection: Optionally identifies shapes that are nearly circular and converts them to perfect circles
- Edge Connection: Ensures proper connectivity between oriented edges
- Angle Enforcement: Post-processing to ensure target angles are precisely maintained
- Neighbor Alignment: Optionally align each building with neighboring buildings, via rotation around centroid.
This project is licensed under the MIT License
This library was inspired by the RS-building-regularization project, with improvements for integration with the GeoPandas ecosystem and enhanced regularization algorithms.