-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 231
Net module
This module contains functions for configure and access the network. Lua RTOS has support for the following network interfaces, each of one identified by it's name:
- en: ethernet interface (SPI or RMII)
- wf: wifi interface
The functions of this module are organized in the following categories:
Currently only SPI ethernet based on the ENC424J600 chip is supported in Lua RTOS. This is a design decision due to that SPI ethernet only requires 2 dedicated GPIO (chip select, and interrupt) and 3 GPIO more that correspond to the SPI signals (clk, miso, mosi).
Please, keep in mind that SPI ethernet support is not enabled by default in KConfig. For enable it, follow the following steps:
-
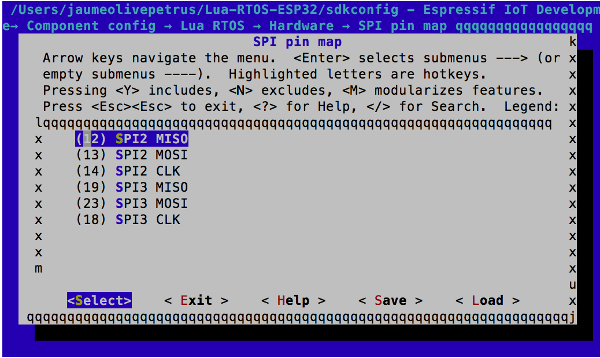
Check the SPI pin map, and adapt the map to your needs. This is done under the "Component config -> Lua RTOS -> Hardware -> SPI pin map" category in Kconfig.
-
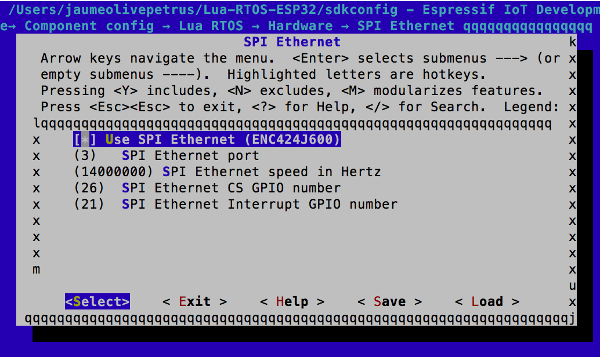
Enable SPI ethernet support, and adapt de default configuration to your needs. This is done under "Component config -> Lua RTOS -> Hardware -> SPI ethernet" category in Kconfig.
To use this module you must take into consideration the following:
-
Setup the interface.
-- Setup wifi net.wf.setup(...)
-
Start the interface.
-- Start wifi net.wf.start()
-
Interact with the network, for example, creating and MQTT client instance and publish some messages.
-
Stop the interface.
-- Stop wifi net.wf.stop()
Check if the network is available.
Arguments: nothing. Returns: true if the network is available, false if is not available, or an exception.
Get the network stats for all the available interfaces.
Arguments:
- table: if true, stats are return in a Lua table, if false stats are printed on the console.
Returns:
-
if table is false: nothing or an exception.
-
if table is true: a Lua table with the scan's result, or an exception. This table is an array of tables. Each entry corresponds to an interface. Each interface gives the following fields:
- interface: the interface name. In this version only wf interface are returned.
- ip: interface ip
- gw: interface gateway ip
- netmask: interface netmask
- mac: interface mac address
-- Get the network stats to the console
/ > net.stat()
wf: mac address 24:0a:c4:00:c9:5c
ip address 192.168.1.41 netmask 255.255.255.0
gw address 192.168.1.1-- Get the network stats to a table
net.stat(true)Returns packet representation of an IPv4 address that can be used with all net's module functions that require an IP address as argument. The IP address is provided from the 4 elements that make up an IPv4 address: ip1.ip2.ip3.ip4
Arguments:
- ip1: the first part of the ip address
- ip2: the second part of the ip address
- ip3: the third part of the ip address
- ip4: the fourth part of the ip address
Returns: an integer that encodes the IP address.
localhost = net.packip(127,0,0,1)
print(localhost)
16777343Returns a packet representation of an IPv4 address that can be used with all net's module functions that require an IP address as argument. The IP address is provided as the IPv4 canonical representation.
Arguments:
- ip: the IP addres string in IPv4 canonical representation
Returns: an integer that encodes the IP address.
localhost = net.packip("127.0.0.1")
print(localhost)
16777343Returns an unpacked representation of an IPv4 address packed by net.packip function. The unpacket representation is provided by the 4 elements that make up an IPv4 address.
Arguments:
- ip: the packet IP address
Returns:
- ip1: the first part of the ip address
- ip2: the second part of the ip address
- ip3: the third part of the ip address
- ip4: the fourth part of the ip address
localhost = net.packip("127.0.0.1")
ip1, ip2, ip3, ip4 = net.unpackip(localhost, '*n')
print(ip1.." "..ip2.." "..ip3.." "..ip4)
127 0 0 1Returns an unpacked representation of an IPv4 address packed by net.packip function. The IP unpacket representation is provided as the IPv4 canonical representation.
Arguments:
- ip: the packet IP address
Returns: the IP addres string in IPv4 canonical representation
localhost = net.packip("127.0.0.1")
ip = net.unpackip(localhost, '*s')
print(ip)
127.0.0.1Makes a DNS lookup.
Arguments:
- hostname: the hostname to make the lookup
Returns: the packet IP of the hostname.
ip = net.lookup("whitecatboard.org")
print(net.unpackip(ip, "*s"))
207.148.248.143Performs a wifi scan.
Arguments:
- table: if true, scan is return in a Lua table, if false scan is printed on the console.
Returns:
-
if table is false: nothing or an exception.
-
if table is true: a Lua table with the scan's result, or an exception. This table is an array of tables. Each entry corresponds to an station. Each station gives the following fields:
- ssid: station ssid.
- auth: authoritation type. Can be either net.wf.auth.OPEN, net.wf.auth.WEP, net.wf.auth.WPA_PSK, net.wf.auth.WPA2_PSK, or net.wf.auth.WPA_WPA2_PSK.
- rssi: signal rssi.
-- Scan wifi, and print to the console
/ > net.wf.scan()
SSID RSSI AUTH
---------------------------------------------------
MOVISTAR_B450 -46 WPA2_PSK
Xarxa Wi-Fi de JAUME -71 WPA_WPA2_PSK
MASMOVIL_TVsm -82 WPA_WPA2_PSK
Orange-3A24 -86 WPA_WPA2_PSK
MOVISTAR_8B90 -86 WPA2_PSK
vodafoneF6A7 -90 WPA_PSK
MOVISTAR_C461 -90 WPA2_PSK
MOVISTAR_91B0 -91 WPA2_PSK
MOVISTAR_C460 -91 WPA2_PSK
VodafoneG18F -94 WPA_PSK
Josema_Casa -94 WPA2_PSK-- Scan wifi, and get result into a table
scan = net.wf.scan(true)Setup wifi interface.
Arguments:
- mode: wifi mode. Can be either net.wf.mode.STA (station) or net.wf.mode.AP (access point).
- ssid: network's ssid to connect.
- password: network's password.
- power save (optional): power save. Can be either net.wf.powersave.NONE (don't set power save) or net.wf.powersave.MODEM. Default value is net.wf.powersave.NONE.
- channel (optional):
- When setup in AP is the channel number to use by the Soft-AP. It's a natural number between 1 and 13.
- When setup in STA is the starting channel number to use for connect the AP. It's a natural number between 1 and 13. Set to 0 if the AP's channel is unknown.
- Default value is 0.
- hidden (optional): only available when setup in AP mode. If true the SSID is hidden, if false it's visible.
Returns: nothing, or an exception.
Start the wifi interface.
Arguments: nothing. Returns: nothing, or an exception.
Stop the wifi interface.
Arguments: nothing. Returns: nothing, or an exception.