diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
index 384414bc..9da3aece 100644
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
- +
+ # `hepstats` package: statistics tools and utilities
@@ -6,15 +6,16 @@
[![Scikit-HEP][sk-badge]](https://scikit-hep.org/)
[](https://pypi.org/project/hepstats/)
-[](https://pypi.org/project/hepstats/)
[](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/hepstats)
+[](https://pypi.org/project/hepstats/)
[](https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3519200)
+[](https://github.com/scikit-hep/hepstats/actions)

-[](https://codecov.io/gh/scikit-hep/hepstats)
+[](https://codecov.io/gh/scikit-hep/hepstats?branch=main)
[](https://github.com/psf/black)
-[](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/scikit-hep/hepstats/master)
+[](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/scikit-hep/hepstats/main)
hepstats is a library for statistical inference aiming to cover the needs High Energy Physics.
It is part of the [Scikit-HEP project](https://scikit-hep.org/).
@@ -33,11 +34,11 @@ pip install hepstats
or similar (use e.g. `virtualenv` if you wish).
## Changelog
-See the [changelog](https://github.com/scikit-hep/hepstats/blob/master/CHANGELOG.md) for a history of notable changes.
+See the [changelog](https://github.com/scikit-hep/hepstats/blob/main/CHANGELOG.md) for a history of notable changes.
## Getting Started
-The `hepstats` module includes `modeling`, `hypotests` and `splot` submodules. This a quick user guide to each submodule. The [binder](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/scikit-hep/hepstats/master) examples are also a good way to get started.
+The `hepstats` module includes `modeling`, `hypotests` and `splot` submodules. This a quick user guide to each submodule. The [binder](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/scikit-hep/hepstats/main) examples are also a good way to get started.
### modeling
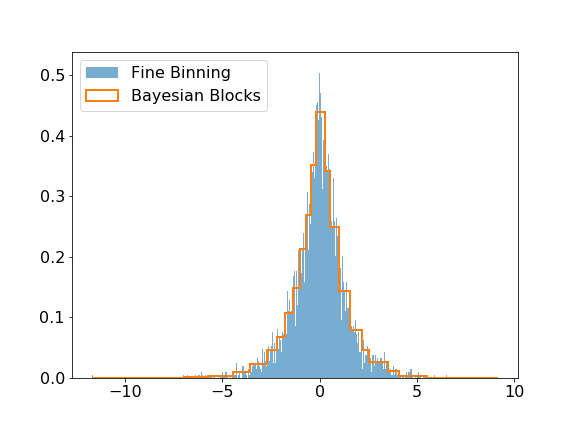
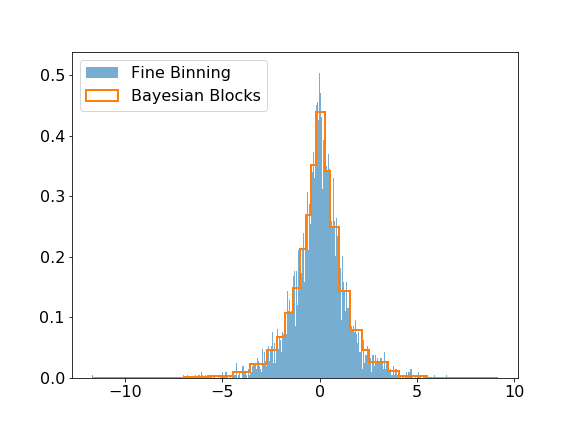
@@ -56,13 +57,13 @@ The modeling submodule includes the [Bayesian Block algorithm](https://arxiv.org
>>> plt.legend(loc=2)
```
-
+
### hypotests
-This submodule provides tools to do hypothesis tests such as discovery test and computations of upper limits or confidence intervals. hepstats needs a fitting backend to perform computations such as [zfit](https://github.com/zfit/zfit). Any fitting library can be used if their API is compatible with hepstats (see [api checks](https://github.com/scikit-hep/hepstats/blob/master/hepstats/hypotests/utils/fit/api_check.py)).
+This submodule provides tools to do hypothesis tests such as discovery test and computations of upper limits or confidence intervals. hepstats needs a fitting backend to perform computations such as [zfit](https://github.com/zfit/zfit). Any fitting library can be used if their API is compatible with hepstats (see [api checks](https://github.com/scikit-hep/hepstats/blob/main/hepstats/hypotests/utils/fit/api_check.py)).
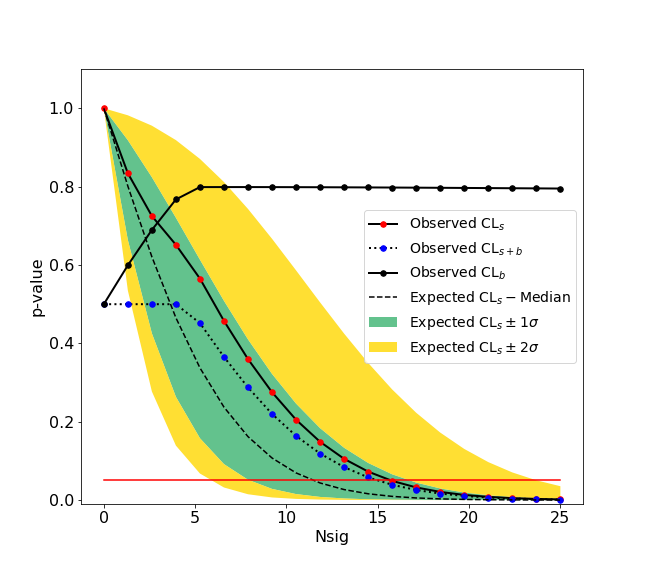
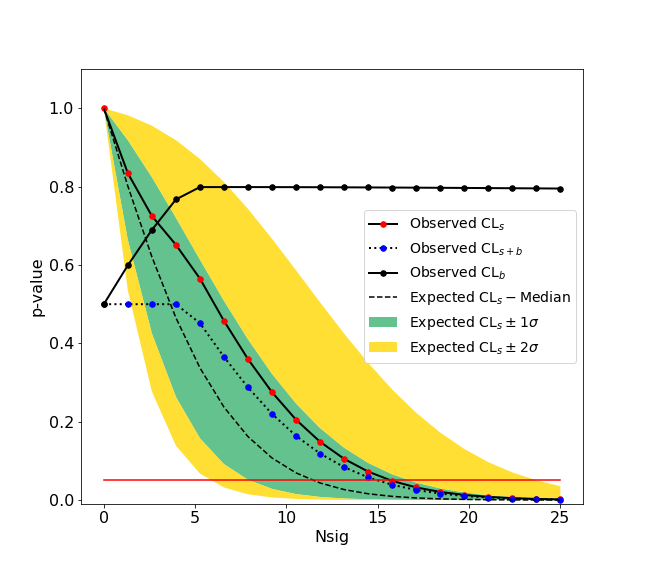
-We give here a simple example of an upper limit calculation of the yield of a Gaussian signal with known mean and sigma over an exponential background. The fitting backend used is the [zfit](https://github.com/zfit/zfit) package. An example with a **counting experiment** analysis is also given in the [binder](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/scikit-hep/hepstats/master) examples.
+We give here a simple example of an upper limit calculation of the yield of a Gaussian signal with known mean and sigma over an exponential background. The fitting backend used is the [zfit](https://github.com/zfit/zfit) package. An example with a **counting experiment** analysis is also given in the [binder](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/scikit-hep/hepstats/main) examples.
```python
>>> import zfit
@@ -105,11 +106,11 @@ Expected upper limit +2 sigma: Nsig = 22.24864429383046
Expected upper limit -2 sigma: Nsig = 6.400549971360598
```
-
+
### splots
-A full example using the **sPlot** algorithm can be found [here](https://github.com/scikit-hep/hepstats/tree/master/notebooks/splots/splot_example.ipynb). **sWeights** for different components in a data sample, modeled with a sum of extended probability density functions, are derived using the `compute_sweights` function:
+A full example using the **sPlot** algorithm can be found [here](https://github.com/scikit-hep/hepstats/tree/main/notebooks/splots/splot_example.ipynb). **sWeights** for different components in a data sample, modeled with a sum of extended probability density functions, are derived using the `compute_sweights` function:
```python
>>> from hepstats.splot import compute_sweights
# `hepstats` package: statistics tools and utilities
@@ -6,15 +6,16 @@
[![Scikit-HEP][sk-badge]](https://scikit-hep.org/)
[](https://pypi.org/project/hepstats/)
-[](https://pypi.org/project/hepstats/)
[](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/hepstats)
+[](https://pypi.org/project/hepstats/)
[](https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3519200)
+[](https://github.com/scikit-hep/hepstats/actions)

-[](https://codecov.io/gh/scikit-hep/hepstats)
+[](https://codecov.io/gh/scikit-hep/hepstats?branch=main)
[](https://github.com/psf/black)
-[](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/scikit-hep/hepstats/master)
+[](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/scikit-hep/hepstats/main)
hepstats is a library for statistical inference aiming to cover the needs High Energy Physics.
It is part of the [Scikit-HEP project](https://scikit-hep.org/).
@@ -33,11 +34,11 @@ pip install hepstats
or similar (use e.g. `virtualenv` if you wish).
## Changelog
-See the [changelog](https://github.com/scikit-hep/hepstats/blob/master/CHANGELOG.md) for a history of notable changes.
+See the [changelog](https://github.com/scikit-hep/hepstats/blob/main/CHANGELOG.md) for a history of notable changes.
## Getting Started
-The `hepstats` module includes `modeling`, `hypotests` and `splot` submodules. This a quick user guide to each submodule. The [binder](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/scikit-hep/hepstats/master) examples are also a good way to get started.
+The `hepstats` module includes `modeling`, `hypotests` and `splot` submodules. This a quick user guide to each submodule. The [binder](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/scikit-hep/hepstats/main) examples are also a good way to get started.
### modeling
@@ -56,13 +57,13 @@ The modeling submodule includes the [Bayesian Block algorithm](https://arxiv.org
>>> plt.legend(loc=2)
```
-
+
### hypotests
-This submodule provides tools to do hypothesis tests such as discovery test and computations of upper limits or confidence intervals. hepstats needs a fitting backend to perform computations such as [zfit](https://github.com/zfit/zfit). Any fitting library can be used if their API is compatible with hepstats (see [api checks](https://github.com/scikit-hep/hepstats/blob/master/hepstats/hypotests/utils/fit/api_check.py)).
+This submodule provides tools to do hypothesis tests such as discovery test and computations of upper limits or confidence intervals. hepstats needs a fitting backend to perform computations such as [zfit](https://github.com/zfit/zfit). Any fitting library can be used if their API is compatible with hepstats (see [api checks](https://github.com/scikit-hep/hepstats/blob/main/hepstats/hypotests/utils/fit/api_check.py)).
-We give here a simple example of an upper limit calculation of the yield of a Gaussian signal with known mean and sigma over an exponential background. The fitting backend used is the [zfit](https://github.com/zfit/zfit) package. An example with a **counting experiment** analysis is also given in the [binder](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/scikit-hep/hepstats/master) examples.
+We give here a simple example of an upper limit calculation of the yield of a Gaussian signal with known mean and sigma over an exponential background. The fitting backend used is the [zfit](https://github.com/zfit/zfit) package. An example with a **counting experiment** analysis is also given in the [binder](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/scikit-hep/hepstats/main) examples.
```python
>>> import zfit
@@ -105,11 +106,11 @@ Expected upper limit +2 sigma: Nsig = 22.24864429383046
Expected upper limit -2 sigma: Nsig = 6.400549971360598
```
-
+
### splots
-A full example using the **sPlot** algorithm can be found [here](https://github.com/scikit-hep/hepstats/tree/master/notebooks/splots/splot_example.ipynb). **sWeights** for different components in a data sample, modeled with a sum of extended probability density functions, are derived using the `compute_sweights` function:
+A full example using the **sPlot** algorithm can be found [here](https://github.com/scikit-hep/hepstats/tree/main/notebooks/splots/splot_example.ipynb). **sWeights** for different components in a data sample, modeled with a sum of extended probability density functions, are derived using the `compute_sweights` function:
```python
>>> from hepstats.splot import compute_sweights
 +
+ # `hepstats` package: statistics tools and utilities
@@ -6,15 +6,16 @@
[![Scikit-HEP][sk-badge]](https://scikit-hep.org/)
[](https://pypi.org/project/hepstats/)
-[](https://pypi.org/project/hepstats/)
[](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/hepstats)
+[](https://pypi.org/project/hepstats/)
[](https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3519200)
+[](https://github.com/scikit-hep/hepstats/actions)

-[](https://codecov.io/gh/scikit-hep/hepstats)
+[](https://codecov.io/gh/scikit-hep/hepstats?branch=main)
[](https://github.com/psf/black)
-[](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/scikit-hep/hepstats/master)
+[](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/scikit-hep/hepstats/main)
hepstats is a library for statistical inference aiming to cover the needs High Energy Physics.
It is part of the [Scikit-HEP project](https://scikit-hep.org/).
@@ -33,11 +34,11 @@ pip install hepstats
or similar (use e.g. `virtualenv` if you wish).
## Changelog
-See the [changelog](https://github.com/scikit-hep/hepstats/blob/master/CHANGELOG.md) for a history of notable changes.
+See the [changelog](https://github.com/scikit-hep/hepstats/blob/main/CHANGELOG.md) for a history of notable changes.
## Getting Started
-The `hepstats` module includes `modeling`, `hypotests` and `splot` submodules. This a quick user guide to each submodule. The [binder](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/scikit-hep/hepstats/master) examples are also a good way to get started.
+The `hepstats` module includes `modeling`, `hypotests` and `splot` submodules. This a quick user guide to each submodule. The [binder](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/scikit-hep/hepstats/main) examples are also a good way to get started.
### modeling
@@ -56,13 +57,13 @@ The modeling submodule includes the [Bayesian Block algorithm](https://arxiv.org
>>> plt.legend(loc=2)
```
-
+
### hypotests
-This submodule provides tools to do hypothesis tests such as discovery test and computations of upper limits or confidence intervals. hepstats needs a fitting backend to perform computations such as [zfit](https://github.com/zfit/zfit). Any fitting library can be used if their API is compatible with hepstats (see [api checks](https://github.com/scikit-hep/hepstats/blob/master/hepstats/hypotests/utils/fit/api_check.py)).
+This submodule provides tools to do hypothesis tests such as discovery test and computations of upper limits or confidence intervals. hepstats needs a fitting backend to perform computations such as [zfit](https://github.com/zfit/zfit). Any fitting library can be used if their API is compatible with hepstats (see [api checks](https://github.com/scikit-hep/hepstats/blob/main/hepstats/hypotests/utils/fit/api_check.py)).
-We give here a simple example of an upper limit calculation of the yield of a Gaussian signal with known mean and sigma over an exponential background. The fitting backend used is the [zfit](https://github.com/zfit/zfit) package. An example with a **counting experiment** analysis is also given in the [binder](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/scikit-hep/hepstats/master) examples.
+We give here a simple example of an upper limit calculation of the yield of a Gaussian signal with known mean and sigma over an exponential background. The fitting backend used is the [zfit](https://github.com/zfit/zfit) package. An example with a **counting experiment** analysis is also given in the [binder](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/scikit-hep/hepstats/main) examples.
```python
>>> import zfit
@@ -105,11 +106,11 @@ Expected upper limit +2 sigma: Nsig = 22.24864429383046
Expected upper limit -2 sigma: Nsig = 6.400549971360598
```
-
+
### splots
-A full example using the **sPlot** algorithm can be found [here](https://github.com/scikit-hep/hepstats/tree/master/notebooks/splots/splot_example.ipynb). **sWeights** for different components in a data sample, modeled with a sum of extended probability density functions, are derived using the `compute_sweights` function:
+A full example using the **sPlot** algorithm can be found [here](https://github.com/scikit-hep/hepstats/tree/main/notebooks/splots/splot_example.ipynb). **sWeights** for different components in a data sample, modeled with a sum of extended probability density functions, are derived using the `compute_sweights` function:
```python
>>> from hepstats.splot import compute_sweights
# `hepstats` package: statistics tools and utilities
@@ -6,15 +6,16 @@
[![Scikit-HEP][sk-badge]](https://scikit-hep.org/)
[](https://pypi.org/project/hepstats/)
-[](https://pypi.org/project/hepstats/)
[](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/hepstats)
+[](https://pypi.org/project/hepstats/)
[](https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3519200)
+[](https://github.com/scikit-hep/hepstats/actions)

-[](https://codecov.io/gh/scikit-hep/hepstats)
+[](https://codecov.io/gh/scikit-hep/hepstats?branch=main)
[](https://github.com/psf/black)
-[](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/scikit-hep/hepstats/master)
+[](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/scikit-hep/hepstats/main)
hepstats is a library for statistical inference aiming to cover the needs High Energy Physics.
It is part of the [Scikit-HEP project](https://scikit-hep.org/).
@@ -33,11 +34,11 @@ pip install hepstats
or similar (use e.g. `virtualenv` if you wish).
## Changelog
-See the [changelog](https://github.com/scikit-hep/hepstats/blob/master/CHANGELOG.md) for a history of notable changes.
+See the [changelog](https://github.com/scikit-hep/hepstats/blob/main/CHANGELOG.md) for a history of notable changes.
## Getting Started
-The `hepstats` module includes `modeling`, `hypotests` and `splot` submodules. This a quick user guide to each submodule. The [binder](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/scikit-hep/hepstats/master) examples are also a good way to get started.
+The `hepstats` module includes `modeling`, `hypotests` and `splot` submodules. This a quick user guide to each submodule. The [binder](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/scikit-hep/hepstats/main) examples are also a good way to get started.
### modeling
@@ -56,13 +57,13 @@ The modeling submodule includes the [Bayesian Block algorithm](https://arxiv.org
>>> plt.legend(loc=2)
```
-
+
### hypotests
-This submodule provides tools to do hypothesis tests such as discovery test and computations of upper limits or confidence intervals. hepstats needs a fitting backend to perform computations such as [zfit](https://github.com/zfit/zfit). Any fitting library can be used if their API is compatible with hepstats (see [api checks](https://github.com/scikit-hep/hepstats/blob/master/hepstats/hypotests/utils/fit/api_check.py)).
+This submodule provides tools to do hypothesis tests such as discovery test and computations of upper limits or confidence intervals. hepstats needs a fitting backend to perform computations such as [zfit](https://github.com/zfit/zfit). Any fitting library can be used if their API is compatible with hepstats (see [api checks](https://github.com/scikit-hep/hepstats/blob/main/hepstats/hypotests/utils/fit/api_check.py)).
-We give here a simple example of an upper limit calculation of the yield of a Gaussian signal with known mean and sigma over an exponential background. The fitting backend used is the [zfit](https://github.com/zfit/zfit) package. An example with a **counting experiment** analysis is also given in the [binder](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/scikit-hep/hepstats/master) examples.
+We give here a simple example of an upper limit calculation of the yield of a Gaussian signal with known mean and sigma over an exponential background. The fitting backend used is the [zfit](https://github.com/zfit/zfit) package. An example with a **counting experiment** analysis is also given in the [binder](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/scikit-hep/hepstats/main) examples.
```python
>>> import zfit
@@ -105,11 +106,11 @@ Expected upper limit +2 sigma: Nsig = 22.24864429383046
Expected upper limit -2 sigma: Nsig = 6.400549971360598
```
-
+
### splots
-A full example using the **sPlot** algorithm can be found [here](https://github.com/scikit-hep/hepstats/tree/master/notebooks/splots/splot_example.ipynb). **sWeights** for different components in a data sample, modeled with a sum of extended probability density functions, are derived using the `compute_sweights` function:
+A full example using the **sPlot** algorithm can be found [here](https://github.com/scikit-hep/hepstats/tree/main/notebooks/splots/splot_example.ipynb). **sWeights** for different components in a data sample, modeled with a sum of extended probability density functions, are derived using the `compute_sweights` function:
```python
>>> from hepstats.splot import compute_sweights