-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 22
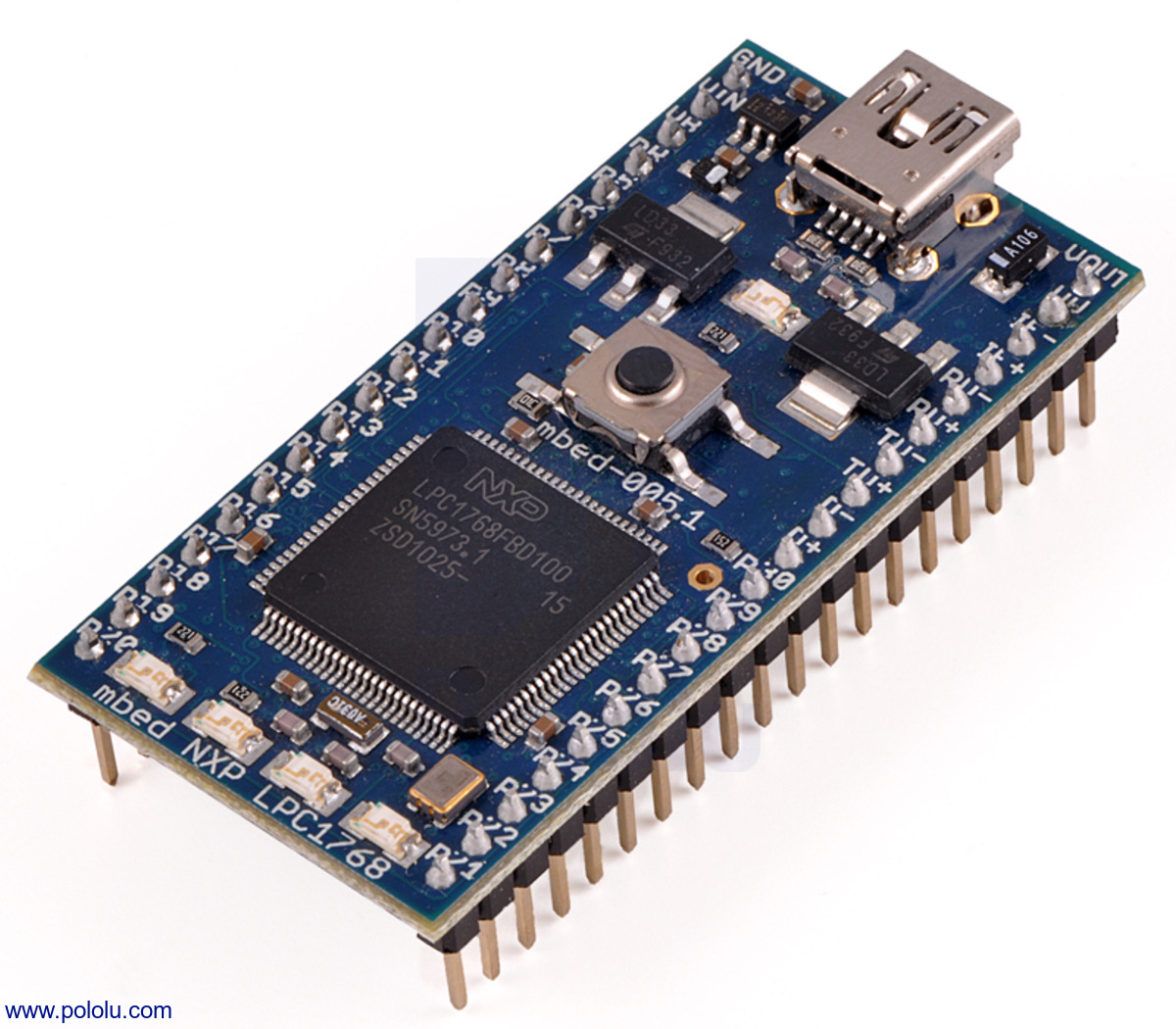
MCU Info Page: LPC1768
The LPC1768 is one of the very first MCUs to be supported by Mbed, and one of the only original MCUs that's still supported today. While it's getting a little long in the tooth, as its highish power consumption and small RAM differentiate it from most modern MCUs, it's still a capable chip with a large array of peripherals. Not to mention, it has a huge
| CPU | Flash/Code Memory | RAM | Communication Peripherals | Other Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cortex-M4F, clocked at up to 80 MHz |
Total: 512 kiB Available to user:* 481.5 kiB |
Total: 32 kiB (SRAM) + 16 kiB (AHBSRAM0) + 16 kiB (AHBSRAM1) Available to user:* 20.1kiB See note about memory banks below |
|
|
*"Available to user" subtracts both regions of memory unusable by Mbed OS projects and the baseline memory used by a minimal build of Mbed OS.
The LPC1768 divides its RAM into three banks: main SRAM, AHBSRAM0, and AHBSRAM1. The AHBSRAM banks are optimized for use with DMA, but are also usable as standard RAM. However, they are not contiguous with the first one, so the GNU linker is not able to automatically place items in these memory banks. Thus, only the first 32k bank is available to naive code.
To make use of these memory banks, you need to manually place items in them using an attribute declaration. If you have code like this:
SomeLargeObject obj;change it to:
SomeLargeObject obj __attribute__((section("AHBSRAM0")));This will move the object into the ABHSRAM0 bank.