-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 554
Home
introduction(the new version download)
GDA is a Dalvik bytecode decompiler written entirely in c++. Unlike most app analysis tools, GDA does not need to rely on the Java platform, And as the use of The bytecode directly translated into Java code without Smali code translation. so it is more succinct, more portable and faster.In addition,it supports APK, DEX, ODEX and OAT files.
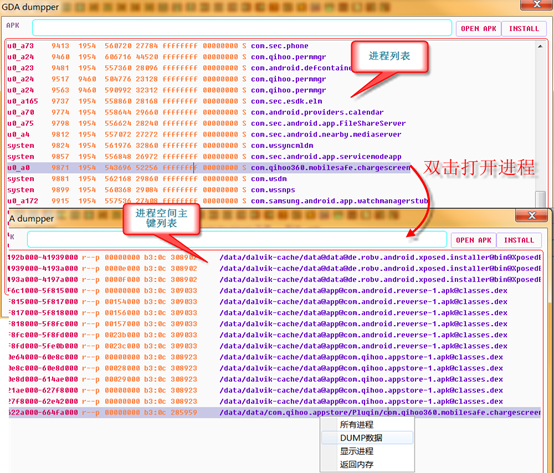
Open GDA and drag the apk file you want to analyze to the software interface:
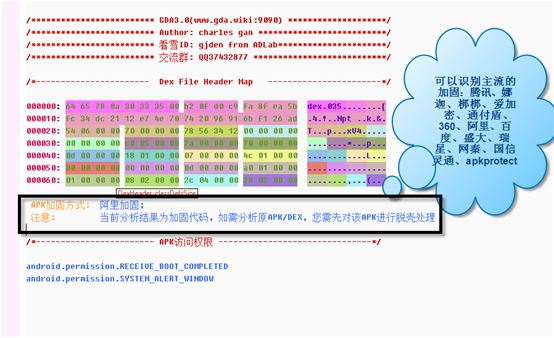
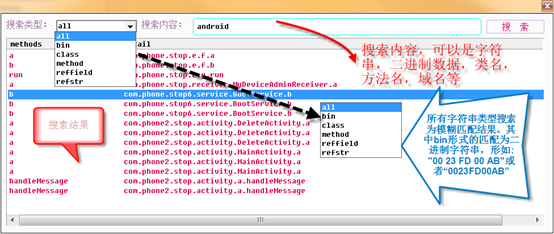
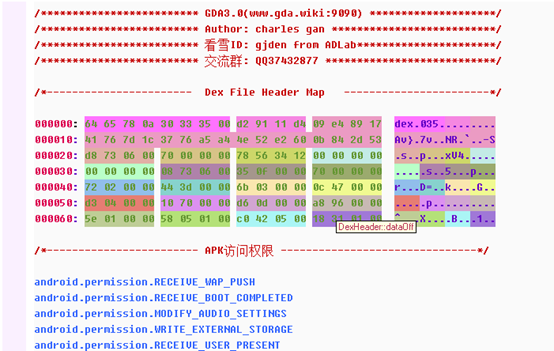
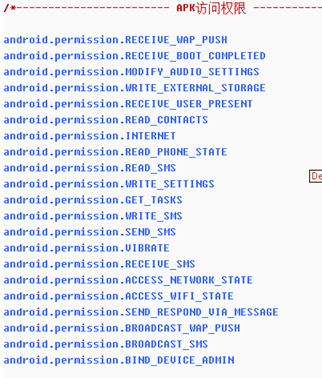
1. View all strings; 2. View all used strings; 3. view all APIs; 4. View AndroidManifest files; 5. Hexadecimal browsing data; 6. Suspicious (malicious behavior analysis); > 7. Vulnerability static scanning (to be implemented); 8. Expand permissions and view the module to which the permissions belong (method); 9. Classes and methods, if there are more DexClass*, indicates that apk uses mulitdex. 10, Dex head, did not click on DexClass to display the corresponding head, each color block represents a different area of the head, the mouse moves on it can see the prompt, each offset can right click to jump to the data area where the offset is located. 11. Overview of the permissions of the application; 12. Search/access records, double-click to view historical access; 13. Click to enter the entry function (method); 14. Connect the android device for memory dump.
If the APP is packed(protected), the GDA will automatically identify the packer and display between the Dex header and the APK permissions, as shown in fig:
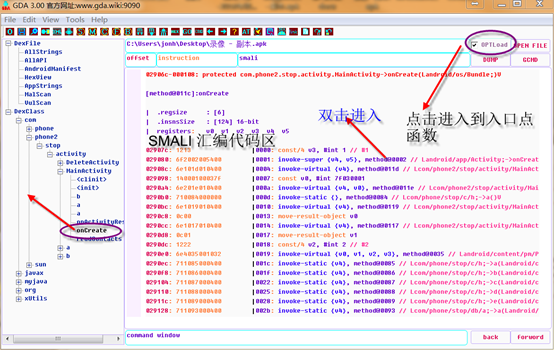
Click OPTLoad to enter the APK's entry function:
In assembly code area, you can decompile the current method by F5.
Double click into the called function, and X cross reference looks at the caller.
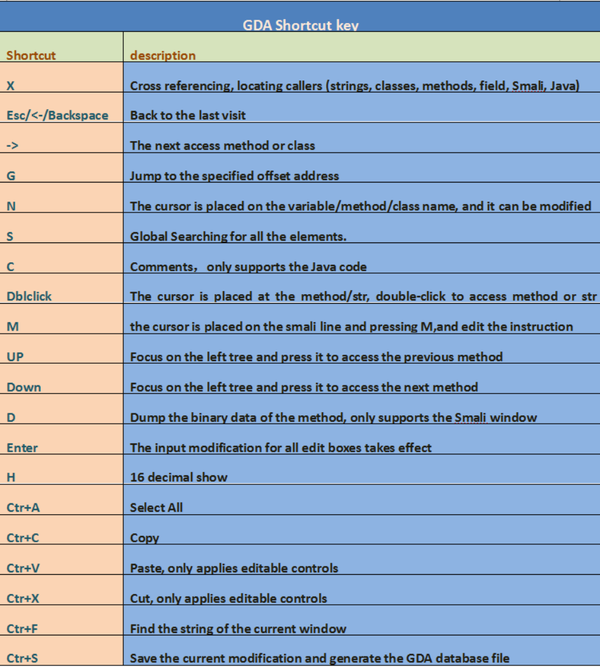
Shortcut key function description
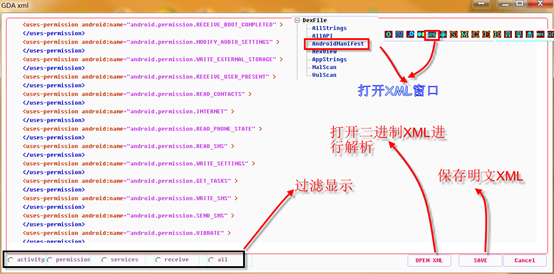
Fully autonomous decoding IS able to circumvent the decoding technique and successfully parse XML.
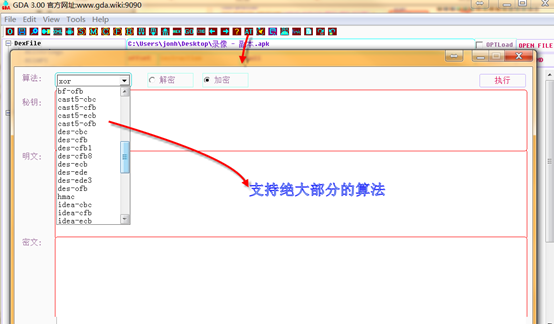
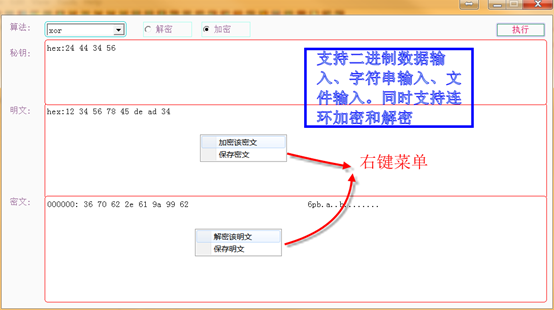
The tool implements encryption and decryption functions。the implemented algorithms is following:
Hash: md2 md4 md5 sha sha1 sha224 sha256 sha384 sha512
Symmetric:des idea rc2 rc4 rc4-40 rc2-40 rc2-64 bf cast5 aes(128 192 256)and which module such as:ecb cbc ofb cfb, others:cfb1 cfb8
Asymmetric:RSA
Coding:base62, base64
Specific use of reference to know: https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/26341224
This section introduces the basic usage of GDA through a Malware sample file.
The purpose of the brief analysis is to make a simple understanding and mastery of APK as a whole,Here's a Android malware as an example to introduce the use of GDA.
- First, you can drag the sample directly into GDA, and very quickly we can see the analysis results of the main interface. We judge whether there is reinforcement according to the brief results. if there is reinforcement, the main interface will show tip.if there is no indication, no reinforcement.
- Then you can check that the virus opens the scan sensitive permissions, from the main interface, we can see ta lot of sensitive permissions are enable .
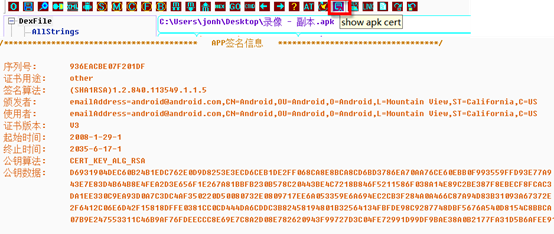
- We see the signature information of the APK through clicking the toolbar that follows the red markup.
4.Next, you can analyze the Activity, Service, receive and so on through the “AndroidManifest” in the tree frame.
5.Next, you can also understand the malware's roughly malicious behavior through the MalScan in the tree frame.
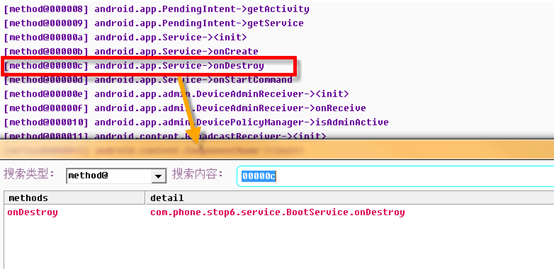
It can be seen that the malware has a lot of malicious manipulation. The list following Behavior description is the method of generating malicious behavior of this type. Double click method@ to access this method,For example, click enter the second description ” #读取联系人、短信等信息:” And [method@000067]: com.phone.stop.b.b.run
It's hard to see Smali. Check the decompile code by F5. Figure:
It can be seen that this method has realized the reading of the message box, and the analysis of the method is introduced later.
6.In addition, the analysis can also be done by looking at the string and API used by the APK. Where “AllStrings” gets all the strings of the APK, and “AllStrings” only gets all the strings that the Dex uses, and relatively AppStrings is a more useful string. The string@ region also supports cross referencing (X), editing (right-click menu), and double clicking.
The method@ region of AllAPI supports cross referencing functions
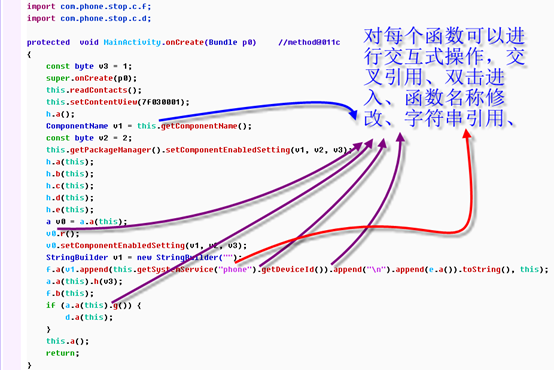
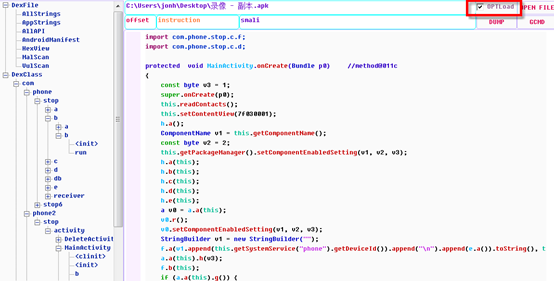
Detailed analysis is a comprehensive analysis for the malicious software execution logic and implementation process, the following brief introduction to the basic usage of GDA. click OPTLoad to enter the execution entry function of APK, and the onCreate function of MainActivity is the first execution function of the APK.
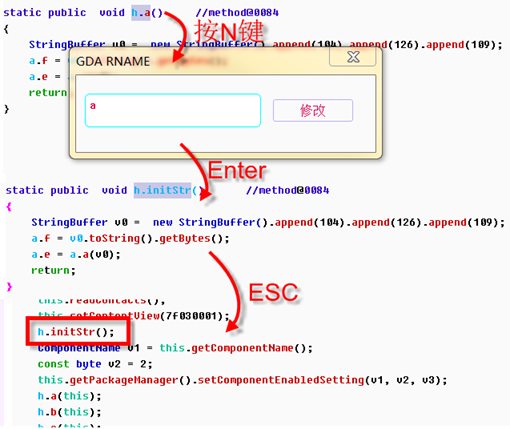
In order to efficiently analyze the entire APK, we need to identify the methods or classes that are identified, and GDA supports the modification of the method name and comments. double-clicking h.a();entering this method.
You can see that the method is just a initialization of the strings, so we modify the function name “initStr”.
By the same way, we can modify all the identified methods .
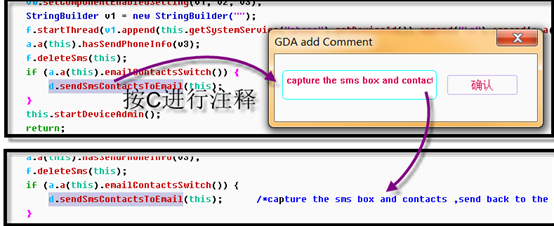
Sometimes you need to make a further description, so you can use the comment function (C).
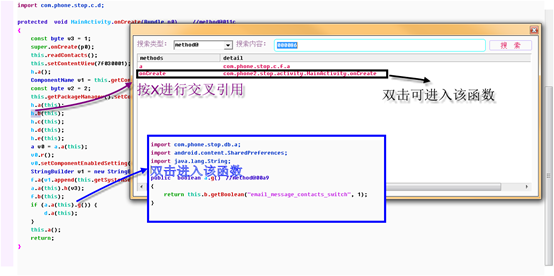
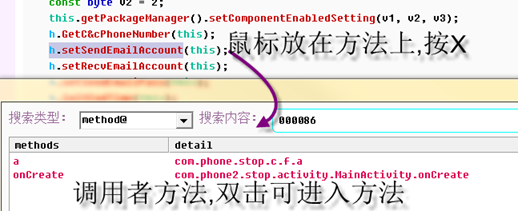
Many times you need to look at the caller of the current method, and you can see it by cross referencing.
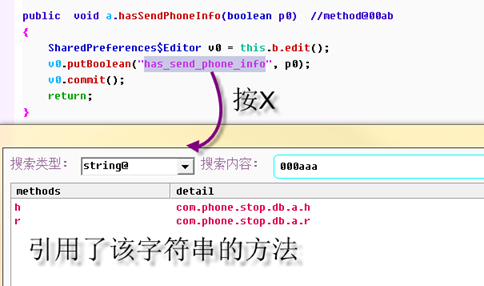
Sometimes you also need to know where the current string is being used. You can put the mouse between string double quotes, and press X to see the reference method.
Logic and flow analysis need to identify each method, as far as possible covering all the important methods for functional identification.