-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 85
Description
Description
Using a configuration template, such as this example.cfg.yml, to create environments within Elastic Beanstalk by running eb create example --cfg example --sample, they are always created with an application load balancer.
OptionSettings:
aws:autoscaling:launchconfiguration:
IamInstanceProfile: aws-elasticbeanstalk-ec2-role
aws:elasticbeanstalk:environment:
LoadBalancerType: classic
aws:ec2:instances:
InstanceTypes: t2.micro
EnvironmentTier:
Type: Standard
Name: WebServer
AWSConfigurationTemplateVersion: 1.1.0.0
In order to use this template, you'll need to specify the aws:ec2:vpc namespace if you do not have a default VPC within your AWS account
The LoadBalancerType has been set for transparency, but the documentation states that it should default to classic anyway: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/elasticbeanstalk/latest/dg/command-options-general.html#command-options-general-elasticbeanstalkenvironment.
With this in mind, it appears that the above template successfully creates an environment with a classic load balancer when running an earlier version of the ebcli.
Steps to reproduce
Assuming a folder structure as defined here: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/elasticbeanstalk/latest/dg/environment-configuration-methods-during.html#configuration-options-during-ebcli-savedconfig
With EB CLI 3.16.0 installed
- Run
eb create example-v-3-16-0 --cfg example --sample. - On the AWS console, check the configuration of the created environment. It will have a classic load balancer.
With EB CLI 3.18.2 installed
- Run
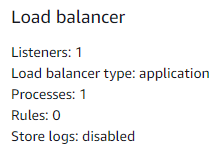
eb create example-v-3-18-2 --cfg example --sample. - On the AWS console, check the configuration of the created environment. It will have an application load balancer.
Observed result
Expected result
Additional environment details (Ex: Windows, Mac, Amazon Linux etc)
- OS: Microsoft Windows 10 Pro - Version 10.0.18363 Build 18363
- EBCLI version: EB CLI 3.18.2 (Python 3.8.0)