-
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 365
HAA Infra Red
Since version 1.5.0 HAA has been able to control infra-red (IR) devices. In order to do this the HAA accessory must have an infra-red transmitter.
Examples of devices that have infra-red transmitters are:
Put some examples here
Alternatively look at some examples of the Web of how to add an IR transmitter to an accessory.
Put some web links here
To understand more about infra-red transmissions and how they are used to control devices around the home refer to the following sites for more information:
IR commands consist of groups of infra-red light pulses sent sequentially.
These pulses are split into marks and spaces. With marks being the period
where infra-red light is transmitted and spaces being the period where no
infra-red light is transmitted.
A mark consists of an alternating burst of infra-red light where the
light is pulsed on & off at a particular frequency.
The most common frequency used by IR transmitters is 38KHz.
Manufacturers often define an IR protocol for their equipment.
This protocol defines what a mark consists of and the duration of
marks & spaces. Sony TV remotes use the Sony Control-S protocol for instance.
For more details on IR data formats checkout this
Vishay document or this
IR Remote Control Theory
document.
HAA supports IR control by enabling the specification of either RAW
or Protocol formats for the data to be transmitted.
A RAW format defines the code to send as an exact replica of a captured
signal. An HAA IR Capture Tool is provided for enabling the capture
of remote control codes using an IR receiver hooked up to an HAA accessory.
A Protocol format defines the infra-red sequence exactly how the manufacturer
intended the codes to be sent.
In RAW mode the IR codes are sent exactly as captured using the
HAA IR Capture Tool.
Transmitting the raw captured data is not recommended because you are using a
copy of the signal and the quality of the captured signal may be degraded. Use
it only if you are unable to decipher the protocol being used by the equipment.
RAW mode also uses a lot more flash storage to hold the definition of the
codes, requiring 2 characters for each mark or space sequence.
Below is a sample output from using the HAA IR Capture Tool.
The table shows the sequential codes that have been captured by the tool.
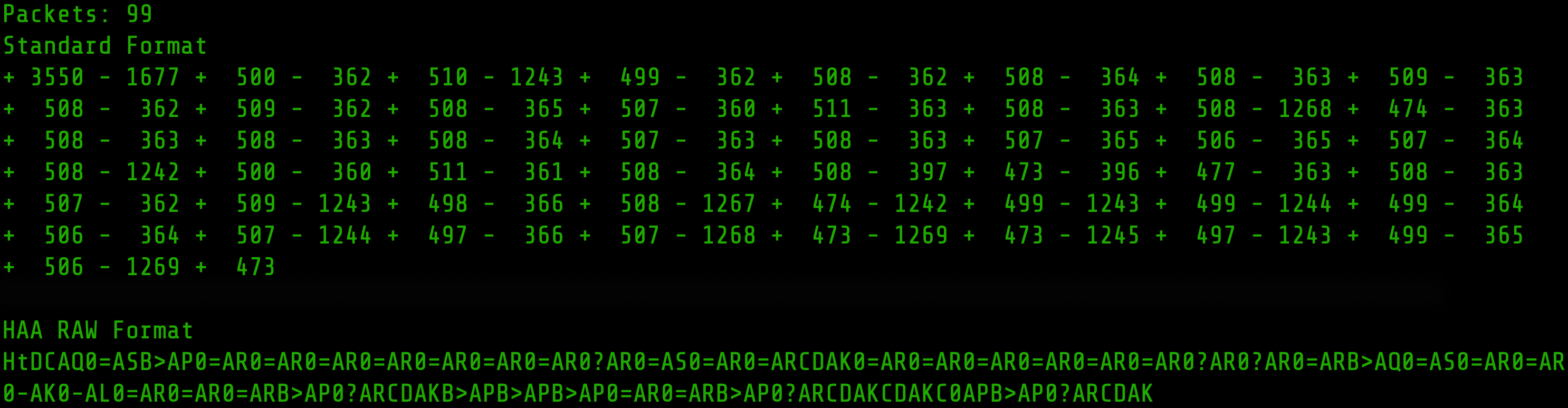
In order to re-transmit these codes using RAW mode the numeric values need to
be translated into a RAW code string.
This can be done using the IR Encoder Table.
From the table you can convert the integer code stream into a series of HAA
RAW codes.
Round the integers output by the IR Capture Tool to the nearest 0 or 5 and
then find the value in the N column of the IR Encoder Table.
The corresponding value in the C column can then be used to create a RAW
code sequence to be transmitted by your HAA accessory.
In the above table the RAW code string can be constructed as follows:
- The integer
+ 3550is represented by the codeHt - The integer
-1677, rounded down to1675, is represented by the codeDC - The integer
+ 500is represented by the codeAQ - The integer
- 362, rounded down to- 360is represented by the code0=etc...
The RAW code string can then be constructed as
"w" : "HtDCAQ0=A5B>AP0=AR0=AR0=AR0=AR0=AR0=AR0=AR0?AR0A50=AR0ARCDAK0=AR0=AR0=AR0=AR0=AR0=AR0?AR0?AR0=ARB>AQ0=A50=AR0=AR0-AK0-AL0=AR0=AR0=AR0>AP0?ARCDAKB>APB>APB>AP0=AR0=ARB>AP0?ARCDAKCDAKC0APB>AP0?ARCDAK"
Note: see how long the string becomes when using RAW codes.
TBD
Home Accessory Architect
Home Accessory
Installation
Setup Mode
HAA Home App
Configuration
About
General
| GPIOs Configuration
Accessory
| Actions
Service Types
Air Quality
Battery
Data History
Fan
Free Monitor
Garage Door
HAA iAirZoning
Heater Cooler
Humidifier
Light Sensor
Lightbulb
Lock Mechanism
Sensors
Power Monitor
Security System
Stateless Button & Doorbell
Switch & Outlet
Temperature & Humidity
TV
Water Valve
Window Covering