|
| 1 | +# GraphCast |
| 2 | + |
| 3 | +=== "模型评估命令" |
| 4 | + |
| 5 | + ``` sh |
| 6 | + |
| 7 | + # linux |
| 8 | + wget -nc https://paddle-org.bj.bcebos.com/paddlescience/datasets/graphcast/dataset.zip |
| 9 | + wget -nc https://paddle-org.bj.bcebos.com/paddlescience/datasets/graphcast/dataset-step12.zip |
| 10 | + wget -nc https://paddle-org.bj.bcebos.com/paddlescience/models/graphcast/params.zip |
| 11 | + wget -nc https://paddle-org.bj.bcebos.com/paddlescience/models/graphcast/template_graph.zip |
| 12 | + wget -nc https://paddle-org.bj.bcebos.com/paddlescience/datasets/graphcast/stats.zip |
| 13 | + wget -nc https://paddle-org.bj.bcebos.com/paddlescience/datasets/graphcast/graphcast-jax2paddle.csv -P ./data/ |
| 14 | + |
| 15 | + # curl https://paddle-org.bj.bcebos.com/paddlescience/datasets/graphcast/dataset.zip -o dataset.zip |
| 16 | + # curl https://paddle-org.bj.bcebos.com/paddlescience/datasets/graphcast/dataset-step12.zip -o dataset-step12.zip |
| 17 | + # curl https://paddle-org.bj.bcebos.com/paddlescience/models/graphcast/template_graph.zip -o template_graph.zip |
| 18 | + # curl https://paddle-org.bj.bcebos.com/paddlescience/datasets/graphcast/stats.zip -o stats.zip |
| 19 | + # curl https://paddle-org.bj.bcebos.com/paddlescience/datasets/graphcast/graphcast-jax2paddle.csv --create-dirs -o ./data/graphcast-jax2paddle.csv |
| 20 | + |
| 21 | + unzip -q dataset.zip -d data/ |
| 22 | + unzip -q dataset-step12.zip -d data/ |
| 23 | + unzip -q params.zip -d data/ |
| 24 | + unzip -q stats.zip -d data/ |
| 25 | + unzip -q template_graph.zip -d data/ |
| 26 | + |
| 27 | + python graphcast.py mode=eval EVAL.pretrained_model_path="data/params/GraphCast_small---ERA5-1979-2015---resolution-1.0---pressure-levels-13---mesh-2to5---precipitation-input-and-output.pdparams" |
| 28 | + ``` |
| 29 | + |
| 30 | +## 1. 背景简介 |
| 31 | + |
| 32 | +全球中期天气预报往往是社会和经济领域相关决策的重要依据。传统的数值天气预报模型一般需要通过增加计算资源来提高预报的精度,而无法直接利用历史天气数据来提升基础模型的预测精度。基于机器学习的天气预报模型能够直接利用历史数据训练模型,提升精度,优化计算资源。同时,这种数据驱动的方法使得模型可从数据中的学习到那些不易用显式方程表示的数量关系,从而提高预测的准确性。 |
| 33 | + |
| 34 | +GraphCast 是一种基于机器学习的天气预报模型,该模型可以直接从再分析数据中进行训练,并且能够在一分钟内以 0.25° 的分辨率在全球范围内预测超过 10 天的数百个天气变量。论文表明,GraphCast 在 1380 个验证目标的实验中,有 90% 的预测结果显著优于最准确的操作确定性系统(operational deterministic systems),并且模型能很好地预测严重天气事件,包括热带气旋、大气河流和极端温度。 |
| 35 | + |
| 36 | +## 2. 模型原理 |
| 37 | + |
| 38 | +$X^t$ 表示 t 时刻的天气状态预测, |
| 39 | + |
| 40 | +$$ X^{t+1}=GraphCast(X^{t}, X^{t-1}) $$ |
| 41 | + |
| 42 | +GraphCast 通过自回归迭代,产生任意长度 T 的预测序列。 |
| 43 | + |
| 44 | +$$ X^{t+1:t+T}=(GraphCast(X^{t}, X^{t-1}), GraphCast(X^{t+1}, X^{t}), ... , GraphCast(X^{t+T-1}, X^{t+T-2}))$$ |
| 45 | + |
| 46 | +### 2.1 模型结构 |
| 47 | + |
| 48 | +GraphCast 的核心架构采用基于图神经网络(GNN)的“编码‑处理‑解码”结构。基于 GNN 的学习模拟器在学习流体和其他材料的复杂物理动力学方面非常有效,因为它们的表示和计算结构类似于学习型有限元求解器。 |
| 49 | + |
| 50 | +<figure markdown> |
| 51 | + 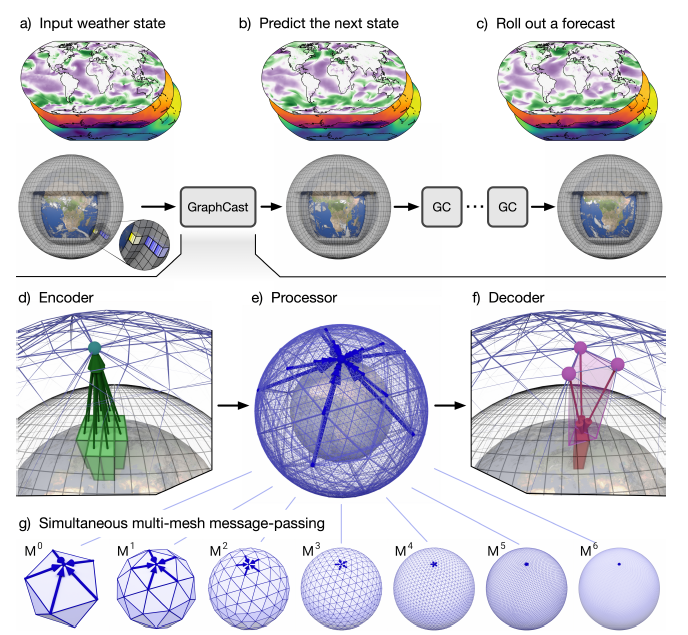{ loading=lazy style="margin:0 auto;"} |
| 52 | + <figcaption>GraphCast 的结构图</figcaption> |
| 53 | +</figure> |
| 54 | + |
| 55 | +由于经纬度网格密度是不均匀的,GraphCast 内部不使用经纬度网格,而是使用了“multi-mesh”表示。“multi-mesh”是通过将正二十面体进行 6 次迭代细化来构建的,如下图所示,每次迭代将多面体上的三角面分成 4 个更小的面。 |
| 56 | + |
| 57 | +GraphCast 模型运行在图 $\mathcal{G(V^\mathrm{G}, V^\mathrm{M}, E^\mathrm{M}, E^\mathrm{G2M}, E^\mathrm{M2G})}$ 上。 |
| 58 | + |
| 59 | +$\mathcal{V^\mathrm{G}}$ 是网格点的集合,每个网格节点代表对应经纬度点的大气垂直切片,节点 $v_𝑖^\mathrm{G}$ 的特征用 $\mathbf{v}_𝑖^\mathrm{G,features}$ 表示。 |
| 60 | + |
| 61 | +$V^\mathrm{M}$ 是 mesh 节点的集合,mesh 节点是通过将正二十面体迭代划分生成的,节点 $v_𝑖^\mathrm{M}$ 的特征用 $\mathbf{v}_𝑖^\mathrm{M,features}$ 表示。 |
| 62 | + |
| 63 | +$\mathcal{E^\mathrm{M}}$ 是一个无向边集合,其中的每条边连接一个发送mesh节点和接收mesh节点,用 $e^\mathrm{M}_{v^\mathrm{M}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{M}_r}$ 表示,对应的特征用 $\mathbf{e}^\mathrm{M,features}_{v^\mathrm{M}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{M}_r}$ 表示。 |
| 64 | + |
| 65 | +$\mathcal{E^\mathrm{G2M}}$ 是一个无向边集合,其中的每条边连接一个发送网格节点和一个接收 mesh 节点,用 $e^\mathrm{G2M}_{v^\mathrm{G}_s \rightarrow v^M_r}$ 表示,对应的特征用 $\mathbf{e}^\mathrm{G2M,features}_{v^\mathrm{G}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{M}_r}$ 表示。 |
| 66 | + |
| 67 | +$\mathcal{E^\mathrm{M2G}}$ 是一个无向边集合,其中的每条边连接一个发送mesh节点和一个接收网格节点,用 $e^\mathrm{M2G}_{v^M_s \rightarrow v^G_r}$ 表示,对应的特征用 $\mathbf{e}^\mathrm{M2G,features}_{v^\mathrm{M}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{G}_r}$ 表示。 |
| 68 | + |
| 69 | +### 2.2 编码器 |
| 70 | + |
| 71 | +编码器的作用是将数据转化为 GraphCast 内部的数据表示。首先利用五个多层感知机(MLP)将上述五个集合的特征嵌入至内部空间。 |
| 72 | + |
| 73 | +$$ |
| 74 | +\begin{aligned} |
| 75 | +\mathbf{v}^\mathrm{G}_i = \mathbf{MLP}^\mathrm{embedder}_\mathcal{V^\mathrm{G}}(\mathbf{v}^\mathrm{G,features}_i) \\ |
| 76 | +\mathbf{v}^\mathrm{M}_i = \mathbf{MLP}^\mathrm{embedder}_\mathcal{V^\mathrm{M}}(\mathbf{v}^\mathrm{M,features}_i) \\ |
| 77 | +\mathbf{e}^\mathrm{M}_{v^\mathrm{M}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{M}_r} = \mathbf{MLP}^\mathrm{embedder}_\mathcal{E^\mathrm{M}}(\mathbf{e}^{\mathrm{M,features}}_{v^\mathrm{M}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{M}_r}) \\ |
| 78 | +\mathbf{e}^\mathrm{G2M}_{v^\mathrm{G}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{M}_r} = \mathbf{MLP}^\mathrm{embedder}_\mathcal{E^\mathrm{G2M}}(\mathbf{e}^{\mathrm{G2M,features}}_{v^\mathrm{G}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{M}_r}) \\ |
| 79 | +\mathbf{e}^\mathrm{M2G}_{v^\mathrm{M}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{G}_r} = \mathbf{MLP}^\mathrm{embedder}_\mathcal{E^\mathrm{M2G}}(\mathbf{e}^{\mathrm{M2G,features}}_{v^\mathrm{M}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{G}_r}) \\ |
| 80 | +\end{aligned} |
| 81 | +$$ |
| 82 | + |
| 83 | +之后通过一个 Grid2Mesh GNN 层,将信息从网格节点传递到 mesh 节点。$\mathcal{E^\mathrm{G2M}}$ 中的边通过关联的节点更新信息。 |
| 84 | + |
| 85 | +$$ |
| 86 | +\mathbf{e}^\mathrm{G2M}_{v^\mathrm{G}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{M}_r} {'} = \mathbf{MLP}^\mathrm{Grid2Mesh}_\mathcal{E^\mathrm{G2M}}([\mathbf{e}^\mathrm{G2M}_{v^\mathrm{G}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{M}_r}, \mathbf{v}_r^\mathrm{G}, \mathbf{v}_s^\mathrm{M}]) |
| 87 | +$$ |
| 88 | + |
| 89 | +mesh 节点通过其关联的边更新信息。 |
| 90 | + |
| 91 | +$$ |
| 92 | +\mathbf{v}^\mathrm{M}_i {'} = \mathbf{MLP}^\mathrm{Grid2Mesh}_\mathcal{V^\mathrm{M}}([\mathbf{v}^\mathrm{M}_i, \sum_{\mathbf{e}^\mathrm{G2M}_{v^\mathrm{G}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{M}_r} : v^\mathrm{M}_r=v^\mathrm{M}_i} \mathbf{e}^\mathrm{G2M}_{v^\mathrm{G}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{M}_r} {'}]) |
| 93 | +$$ |
| 94 | + |
| 95 | +同样网格节点也进行信息更新。 |
| 96 | + |
| 97 | +$$ |
| 98 | +\mathbf{v}^\mathrm{G}_i {'} = \mathbf{MLP}^\mathrm{Grid2Mesh}_\mathcal{V^\mathrm{G}}(\mathbf{v}^\mathrm{G}_i) |
| 99 | +$$ |
| 100 | + |
| 101 | +最后通过残差连接更新三个元素。 |
| 102 | + |
| 103 | +$$ |
| 104 | +\begin{aligned} |
| 105 | +\mathbf{v}^\mathrm{G}_i \leftarrow \mathbf{v}^\mathrm{G}_i + \mathbf{v}^\mathrm{G}_i {'} \\ |
| 106 | +\mathbf{v}^\mathrm{M}_i \leftarrow \mathbf{v}^\mathrm{M}_i + \mathbf{v}^\mathrm{M}_i {'} \\ |
| 107 | +\mathbf{e}^\mathrm{G2M}_{v^\mathrm{G}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{M}_r} = \mathbf{e}^\mathrm{G2M}_{v^\mathrm{G}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{M}_r} + \mathbf{e}^\mathrm{G2M}_{v^\mathrm{G}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{M}_r} {'} |
| 108 | +\end{aligned} |
| 109 | +$$ |
| 110 | + |
| 111 | +### 2.3 处理器 |
| 112 | + |
| 113 | +处理器包含一个Multi-mesh GNN 层,$\mathcal{E^\mathrm{M}}$ 中的边通过关联的节点更新信息。 |
| 114 | + |
| 115 | +$$ |
| 116 | +\mathbf{e}^\mathrm{M}_{v^\mathrm{M}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{M}_r} {'} = \mathbf{MLP}^\mathrm{Mesh}_\mathcal{E^\mathrm{M}}([\mathbf{e}^\mathrm{M}_{v^\mathrm{M}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{M}_r}, \mathbf{v}^\mathrm{M}_s, \mathbf{v}^\mathrm{M}_r]) |
| 117 | +$$ |
| 118 | + |
| 119 | +mesh 节点通过其关联的边更新信息。 |
| 120 | + |
| 121 | +$$ |
| 122 | +\mathbf{v}^\mathrm{M}_i {'} = \mathbf{MLP}^\mathrm{Mesh}_\mathcal{V^\mathrm{M}}([\mathbf{v}^\mathrm{M}_i, \sum_{\mathbf{e}^\mathrm{G2M}_{v^\mathrm{G}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{M}_r} : v^\mathrm{M}_r=v^\mathrm{M}_i} \mathbf{e}^\mathrm{M}_{v^\mathrm{G}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{M}_r} {'}]) |
| 123 | +$$ |
| 124 | + |
| 125 | +最后通过残差连接更新元素。 |
| 126 | + |
| 127 | +$$ |
| 128 | +\begin{aligned} |
| 129 | +\mathbf{v}^\mathrm{M}_i \leftarrow \mathbf{v}^\mathrm{M}_i + \mathbf{v}^\mathrm{M}_i {'} \\ |
| 130 | +\mathbf{e}^\mathrm{M}_{v^\mathrm{M}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{M}_r} \leftarrow \mathbf{e}^\mathrm{M}_{v^\mathrm{M}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{M}_r} + \mathbf{e}^\mathrm{M}_{v^\mathrm{M}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{M}_r} {'}\\ |
| 131 | +\end{aligned} |
| 132 | +$$ |
| 133 | + |
| 134 | +### 2.4 解码器 |
| 135 | + |
| 136 | +解码器的作用是将 mesh 内的信息取回网格中,并进行预测。解码器包含一个Mesh2Grid GNN 层。 |
| 137 | + |
| 138 | +$\mathcal{E^\mathrm{M2G}}$ 中的边通过关联的节点的更新信息。 |
| 139 | + |
| 140 | +$$ |
| 141 | +\mathbf{e}^\mathrm{M2G}_{v^\mathrm{M}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{G}_r} {'} = \mathbf{MLP}^\mathrm{Mesh2Grid}_\mathcal{E^\mathrm{M2G}}([\mathbf{e}^\mathrm{M2G}_{v^\mathrm{M}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{G}_r},\mathbf{v}^\mathrm{M}_s, \mathbf{v}^\mathrm{M}_r]) |
| 142 | +$$ |
| 143 | + |
| 144 | +网格节点通过其关联的边更新信息。 |
| 145 | + |
| 146 | +$$ |
| 147 | +\mathbf{v}^\mathrm{G}_i {'} = \mathbf{MLP}^\mathrm{Mesh2Grid}_\mathcal{V^\mathrm{G}}([\mathbf{v}^\mathrm{G}_i, \sum_{\mathbf{e}^\mathrm{G2M}_{v^\mathrm{M}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{G}_r} : v^\mathrm{G}_r=v^\mathrm{G}_i} \mathbf{e}^\mathrm{M2G}_{v^\mathrm{M}_s \rightarrow v^\mathrm{G}_r} {'}]) |
| 148 | +$$ |
| 149 | + |
| 150 | +通过残差连接对网格节点进行更新。 |
| 151 | + |
| 152 | +$$ |
| 153 | +\mathbf{v}^\mathrm{G}_i \leftarrow \mathbf{v}^\mathrm{G}_i + \mathbf{v}^\mathrm{G}_i {'} |
| 154 | +$$ |
| 155 | + |
| 156 | +接着利用另一个 MLP 对网格信息进行处理,得到预测值。 |
| 157 | + |
| 158 | +$$ |
| 159 | +\mathbf{\hat{y}}^\mathrm{G}_i= \mathbf{MLP}^\mathrm{Output}_\mathcal{V^\mathrm{G}}(\mathbf{v}^\mathrm{G}_i) |
| 160 | +$$ |
| 161 | + |
| 162 | +将输入状态 $X^{t}$ 与预测值 $\hat{Y}^{t}$ 相加得到下一个天气状态 $\hat{X}^{t+1}$ |
| 163 | + |
| 164 | +$$ \hat{X}^{t+1} = GraphCast(X^{t}, X^{t-1}) = X^{t} + \hat{Y}^{t} $$ |
| 165 | + |
| 166 | +## 3. 模型构建 |
| 167 | + |
| 168 | +接下来开始讲解如何基于 PaddleScience 代码,实现 GraphCast。关于该案例中的其余细节请参考 [API文档](../api/arch.md)。 |
| 169 | + |
| 170 | +### 3.1 数据集介绍 |
| 171 | + |
| 172 | +数据集采用了 ECMWF 的 ERA5 数据集 的 [2020年再分析存档子集](https://paddle-org.bj.bcebos.com/paddlescience/datasets/graphcast/dataset.zip),数据时间段为1979-2018 年,时间间隔为6小时(对应每天的00z、06z、12z和18z),水平分辨率为0.25°,包含 37 个垂直大气压力层。 |
| 173 | + |
| 174 | +模型预测总共227个目标变量,其中包括5个地面变量,以及在13个压力层中的每个层次的6个大气变量。 |
| 175 | + |
| 176 | +### 3.2 加载预训练模型 |
| 177 | + |
| 178 | +在执行命令中设定预训练模型的文件路径,如下。 |
| 179 | + |
| 180 | +``` sh |
| 181 | +python graphcast.py mode=eval EVAL.pretrained_model_path="data/params/GraphCast_small---ERA5-1979-2015---resolution-1.0---pressure-levels-13---mesh-2to5---precipitation-input-and-output.pdparams" |
| 182 | +``` |
| 183 | + |
| 184 | +### 3.3 模型构建 |
| 185 | + |
| 186 | +我们使用神经网络 `GraphCastNet` 作为模型,其接收天气数据,输出预测结果。 |
| 187 | + |
| 188 | +``` py linenums="28" |
| 189 | +--8<-- |
| 190 | +examples/graphcast/graphcast.py:28:29 |
| 191 | +--8<-- |
| 192 | +``` |
| 193 | + |
| 194 | +### 3.4 评估器构建 |
| 195 | + |
| 196 | +我们使用 `ppsci.validate.SupervisedValidator` 构建评估器。首先定义数据加载器的配置,然后创建评估器。 |
| 197 | + |
| 198 | +``` py linenums="31" |
| 199 | +--8<-- |
| 200 | +examples/graphcast/graphcast.py:31:39 |
| 201 | +--8<-- |
| 202 | +``` |
| 203 | + |
| 204 | +我们需要定义训练损失函数的计算过程。 |
| 205 | + |
| 206 | +``` py linenums="50" |
| 207 | +--8<-- |
| 208 | +examples/graphcast/graphcast.py:50:67 |
| 209 | +--8<-- |
| 210 | +``` |
| 211 | + |
| 212 | +接着我们还需要定义 metric 指标。 |
| 213 | + |
| 214 | +``` py linenums="69" |
| 215 | +--8<-- |
| 216 | +examples/graphcast/graphcast.py:69:86 |
| 217 | +--8<-- |
| 218 | +``` |
| 219 | + |
| 220 | +最后完成评估器的构建。 |
| 221 | + |
| 222 | +``` py linenums="88" |
| 223 | +--8<-- |
| 224 | +examples/graphcast/graphcast.py:88:92 |
| 225 | +--8<-- |
| 226 | +``` |
| 227 | + |
| 228 | +### 3.5 模型评估 |
| 229 | + |
| 230 | +完成上述设置之后,只需要将上述实例化的对象按顺序传递给 `ppsci.solver.Solver`,然后启动评估。 |
| 231 | + |
| 232 | +``` py linenums="94" |
| 233 | +--8<-- |
| 234 | +examples/graphcast/graphcast.py:94:104 |
| 235 | +--8<-- |
| 236 | +``` |
| 237 | + |
| 238 | +### 3.6 结果可视化 |
| 239 | + |
| 240 | +评估完成后,我们以图片的形式对结果进行可视化,如下所示。 |
| 241 | + |
| 242 | +``` py linenums="106" |
| 243 | +--8<-- |
| 244 | +examples/graphcast/graphcast.py:106:118 |
| 245 | +--8<-- |
| 246 | +``` |
| 247 | + |
| 248 | +## 4. 完整代码 |
| 249 | + |
| 250 | +``` py linenums="1" title="graphcast.py" |
| 251 | +--8<-- |
| 252 | +examples/graphcast/graphcast.py |
| 253 | +--8<-- |
| 254 | +``` |
| 255 | + |
| 256 | +## 5. 结果展示 |
| 257 | + |
| 258 | +下图展示了温度的真值结果、预测结果和误差。 |
| 259 | + |
| 260 | +<figure markdown> |
| 261 | + 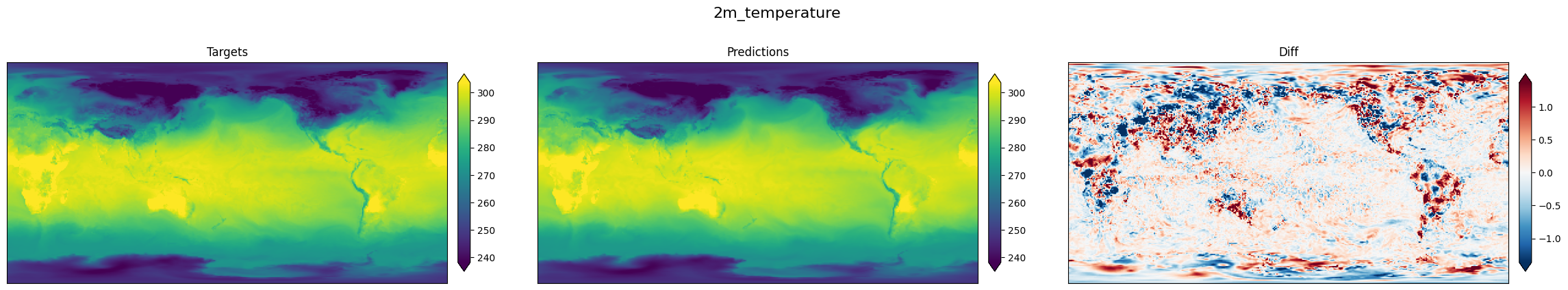{ loading=lazy style="margin:0 auto;"} |
| 262 | + <figcaption>真值结果("targets")、预测结果("prediction")和误差("diff")</figcaption> |
| 263 | +</figure> |
| 264 | + |
| 265 | +可以看到模型预测结果与真实结果基本一致。 |
| 266 | + |
| 267 | +## 6. 参考文献 |
| 268 | + |
| 269 | +- [GraphCast: Learning skillful medium-range global weather forecasting](https://doi.org/10.1080/09540091.2022.2131737) |
0 commit comments