-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 48
Scipion HPC clusters on AWS
The following diagram shows a basic HPC cluster architecture on AWS:

There are two options to deploy elastic HPC clusters on AWS:
StarCluster is a utility developed by MIT for creating and managing distributed computing clusters hosted on Amazon’s Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2).
Detailed information about StarCluster can be found on its web site but the following step-by-step guide shows how to deploy ScipionCloud on Amazon’s EC2.
-
First you need to install StarCluster client on your machine, which is used to create and manage the clusters. Follow instructions on the StarCluster installation page
The fastest way is to use Python PIP:
sudo easy_install StarCluster
It is recommended to update it to the latest version from git:
git clone https://github.com/jtriley/StarCluster.git cd StarCluster sudo python setup.py install
You might need to install the following packages: python-dev, libffi-dev, libssl-dev.
Execute StarCluster help and choose second option to create the configuration file:
starcluster help StarCluster - (http://star.mit.edu/cluster) Software Tools for Academics and Researchers (STAR) Please submit bug reports to starcluster@mit.edu cli.py:87 - ERROR - config file /home/user/.starcluster/config does not exist` Options: -------- [1] Show the StarCluster config template [2] Write config template to /home/user/.starcluster/config [q] Quit Please enter your selection:
-
Then you need to edit StarCluster configuration file and customize it for your needs. StarCluster provides a quick installation guide that is good enough to start, although extensive documentation can be found at its site.
The following example shows how to customize it for a ScipionCloud cluster with two t2.medium nodes (only some parameters are shown, the rest can be left with their default value).
Add a scipioncluster template (or other name you like) that will be used as default template. Also, enable experimental features (load balancer for elastic clusters, explained later).
#################################### ## StarCluster Configuration File ## #################################### [global] DEFAULT_TEMPLATE=scipioncluster # enable experimental features for this release ENABLE_EXPERIMENTAL=True
-
Replace AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID, AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY and AWS_USER_ID with yours, managed on Security Credentials/Access keys and Account settings.
-
Select AWS region (ScipionCloud AMI currently exists only on AWS EU Ireland region).
############################################# ## AWS Credentials and Connection Settings ## ############################################# [aws info] # replace these with your AWS keys AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID = XXXXXXXXXXXX AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY = XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX # replace this with your account number (found on account settings) AWS_USER_ID= XXXXXXXXX AWS_REGION_NAME = eu-west-1 AWS_REGION_HOST = ec2.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com
Specify the key pair to use (managed on EC2 / Security Groups / Key pairs)
########################### ## Defining EC2 Keypairs ## ########################### [key scipion-key] KEY_LOCATION=~/scipion-key.rsa
Define the scipioncluster template:
Set the cluster size and the instance image and type (although starcluster allows different images and types for master and node, current Scipion AMI is unique for both).
The list of instance types might not be updated on the config file, you can check them here.
You might also want to choose a prefix for the machine names.
Although not necessary it is recommended to attach an external EBS storage. Just uncomment the VOLUMES parameter and create a volume section as explained here.
[cluster scipioncluster] KEYNAME = scipion-key # number of ec2 instances to launch CLUSTER_SIZE = 2 # Uncomment to prepent the cluster tag to the dns name of all nodes created # using this cluster config. ie: mycluster-master and mycluster-node001 # If you choose to enable this option, it's recommended that you enable it in # the DEFAULT_TEMPLATE so all nodes will automatically have the prefix DNS_PREFIX = True # image id correspoding to ScipionCloud-1.2-beta AMI NODE_IMAGE_ID = ami-811e79f8 NODE_INSTANCE_TYPE = t2.medium PERMISSIONS = http, https #VOLUMES = scipion_data
Configure Security Group permissions.
############################################ ## Configuring Security Group Permissions ## ############################################ # open port 80 on the cluster to the world [permission http] IP_PROTOCOL = tcp FROM_PORT = 80 TO_PORT = 80 # open https on the cluster to the world [permission https] IP_PROTOCOL = tcp FROM_PORT = 443 TO_PORT = 443
-
Start the cluster:
starcluster start my-scipion-cluster
-
Log in to the cluster using ubuntu account Your URL and VNC password will be printed on the terminal.
starcluster sshmaster -u ubuntu my-scipion-cluster
-
As explained for a single Scipion instance, you can now go to your browser and access the virtual machine through a remote desktop:
where master-ip can be seen either on the EC2 console or executing the following command:
starcluster listclusters
Look for your cluster and get the master IP address from the list of cluster nodes (in this example 54-229-188-230).
my-scipion-cluster (security group: @sc-my-scipion-cluster)
-----------------------------------------------------------
Launch time: 2016-06-15 14:16:49
Uptime: 0 days, 00:19:47
VPC: vpc-8f99f4ea
Subnet: subnet-36480d41
Zone: eu-west-1a
Keypair: scipion-key
EBS volumes: N/A
Cluster nodes:
my-scipion-cluster-master running i-98351812 ec2-54-229-188-230.eu-west-1.compute.amazonaws.com
my-scipion-cluster-node001 running i-99351813 ec2-54-229-182-132.eu-west-1.compute.amazonaws.com
Total nodes: 2
-
To stop the cluster (and stop being charged) use starcluster too (if you do it through the EC2 console you mess up starcluster own record!).
starcluster stop my-scipion-cluster
-
To restart the cluster you just need to type:
starcluster start -x my-scipion-cluster
-
To terminate the cluster (and delete VMs but not EBS external volumes)
starcluster terminate my-scipion-cluster
StarCluster provides a experimental feature, called Elastic Load Balancer, that can be used to balance clusters dynamically depending on the batch system workload (Sun Grid Engine). To use it you need a cluster running as explained above. Detailed documentation can be found here but the basic usage is as follows:
To start balancing:
starcluster loadbalance my-scipion-cluster
This will keep the cluster size between 1 and CLUSTER_SIZE limits depending on the batch system workload. This limits can be changed by passing them as parameters to the loadbalance command, for instance:
starcluster loadbalance -m 20 -n 2 my-scipion-cluster
This will create up to 20 nodes if the load requires it and will keep a minimum of 2 nodes.
To see a list of all the parameters that can be passed to the loadbalance just type:
starcluster loadbalance --help
The following image, extracted from Starcluster documentation, shows the workflow for each loadbalance loop.
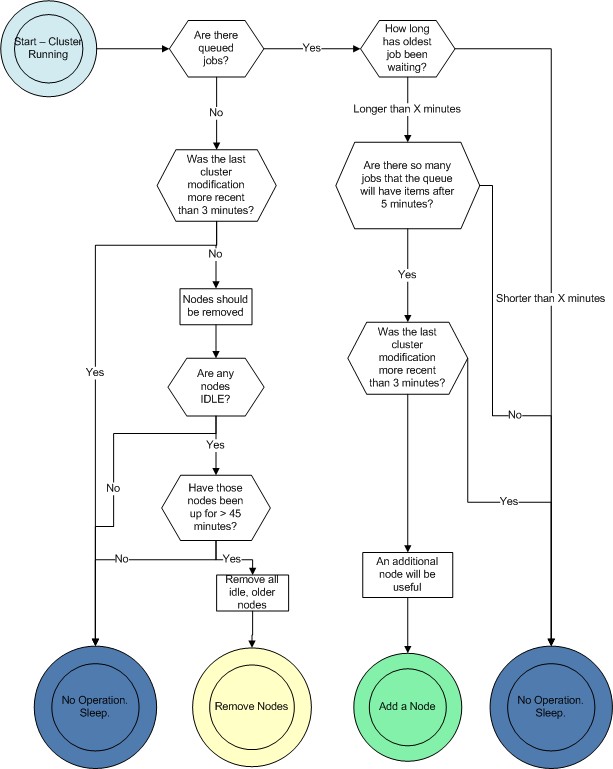
Another interesting parameter to tun up is the maximum time to wait until a node is added (-w option). The default value is 900 seconds (15 minutes) which might be too long.
It is and open-source tool developed by AWS that allows to create and configure an elastic HPC cluster on AWS EC2.
We have not yet tested it with ScipionCloud but an easy How-to can be found here.