You signed in with another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You signed out in another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You switched accounts on another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.Dismiss alert
Copy file name to clipboardExpand all lines: README.md
+37-43Lines changed: 37 additions & 43 deletions
Original file line number
Diff line number
Diff line change
@@ -16,65 +16,59 @@ _GitHub Copilot can help you code by offering autocomplete-style suggestions rig
16
16
</header>
17
17
18
18
<!--
19
-
<<< Author notes: Step 1 >>>
20
-
Choose 3-5 steps for your course.
21
-
The first step is always the hardest, so pick something easy!
22
-
Link to docs.github.com for further explanations.
23
-
Encourage users to open new tabs for steps!
19
+
<<< Author notes: Step 2 >>>
20
+
Start this step by acknowledging the previous step.
21
+
Define terms and link to docs.github.com.
24
22
-->
25
23
26
-
## Step 1: Leverage Codespaces with VS Code for Copilot
24
+
## Step 2: Seeing AI code suggestions in a Javascript file!
27
25
28
-
_Welcome to "Develop With AI Powered Code Suggestions Using GitHub Copilot and VS Code"! :wave:_
26
+
_Nice work! :tada: You created a Codespace using a devcontainer file that installed Copilot!_
29
27
30
-
GitHub Copilot is an AI pair programmer that helps you write code faster and with less work. It draws context from comments and code to suggest individual lines and whole functions instantly. GitHub Copilot is powered by OpenAI Codex, a generative pretrained language model created by OpenAI.
28
+
GitHub Copilot provides suggestions for numerous languages and a wide variety of frameworks, but works especially well for Python, JavaScript, TypeScript, Ruby, Go, C# and C++. The following samples are in JavaScript, but other languages will work similarly.
31
29
32
-
**Copilot works with many code editors including VS Code, Visual Studio, JetBrains IDE, and Neovim.**
30
+
Let's try this out utilizing Javascript for Copilot.
33
31
34
-
Additionally, GitHub Copilot is trained on all languages that appear in public repositories. For each language, the quality of suggestions you receive may depend on the volume and diversity of training data for that language.
32
+
### :keyboard: Activity: Add a Javascript file and start writing code
35
33
36
-
Using Copilot inside a Codespace shows just how easy it is to get up and running with GitHub's suite of [Collaborative Coding](https://github.com/features#features-collaboration) tools.
34
+
1. From inside the codespace in the VS Code explorer window, create a new file.
37
35
38
-
> **Note**
39
-
> This skills exercise will focus on leveraging GitHub Codespace. It is recommended that you complete the GitHub skill, [Codespaces](https://github.com/skills/code-with-codespaces), before moving forward with this exercise.
36
+
> **Note**:
37
+
> If you closed the Codespace from above, please open it back up or create a new Codespace.
40
38
41
-
### :keyboard: Activity: Enable Copilot inside a Codespace
39
+
2. Name the file `skills.js`
40
+
3. Verify your new file looks like:
41
+
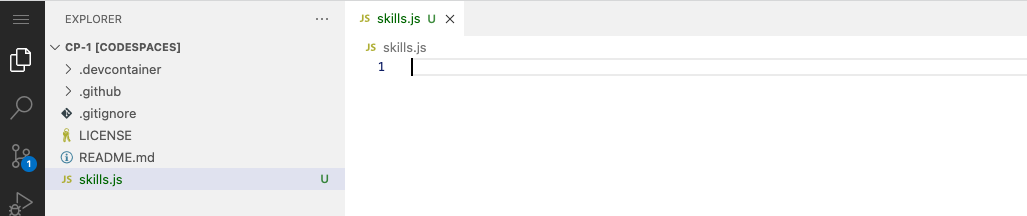
42
+
4. In the `skills.js` file, type the following function header.
42
43
43
-
**We recommend opening another browser tab to work through the following activities so you can keep these instructions open for reference.**
44
+
```
45
+
function calculateNumbers(var1, var2)
46
+
```
47
+
48
+
GitHub Copilot will automatically suggest an entire function body in grayed text. Below is an example of what you'll most likely see, but the exact suggestion may vary.
49
+
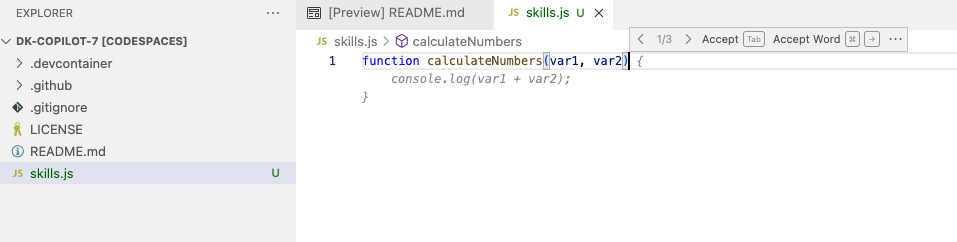
44
50
45
-
Before you open up a codespace on a repository, you can create a development container and define specific extensions or configurations that will be used or installed in your codespace. Let's create this development container and add copilot to the list of extensions.
51
+
5. Press `Tab` to accept the suggestion.
52
+
53
+
### :keyboard: Activity: Push code to your repository from the codespace
54
+
55
+
1. Use the VS Code terminal to add the `skills.js` file to the repository:
46
56
47
-
1. Navigating back to your **Code** tab of your repository, click the **Add file** drop-down button, and then click `Create new file`.
48
-
1. Type or paste the following in the empty text field prompt to name your file.
49
57
```
50
-
.devcontainer/devcontainer.json
58
+
git add skills.js
51
59
```
52
-
1. In the body of the new **.devcontainer/devcontainer.json** file, add the following content:
60
+
61
+
2. Next from the VS Code terminal stage and commit the changes to the repository:
62
+
63
+
```
64
+
git commit -m "Copilot first commit"
65
+
```
66
+
67
+
3. Finally from the VS Code terminal push to code to the repository:
68
+
53
69
```
54
-
{
55
-
// Name this configuration
56
-
"name": "Codespace for Skills!",
57
-
"customizations": {
58
-
"vscode": {
59
-
"extensions": [
60
-
"GitHub.copilot"
61
-
]
62
-
}
63
-
}
64
-
}
70
+
git push
65
71
```
66
-
1. Select the option to **Commit directly to the `main` branch**, and then click the **Commit new file** button.
67
-
1. Navigate back to the home page of your repository by clicking the **Code** tab located at the top left of the screen.
68
-
1. Click the **Code** button located in the middle of the page.
69
-
1. Click the **Codespaces** tab on the box that pops up.
70
-
1. Click the **Create codespace on main** button.
71
-
72
-
**Wait about 2 minutes for the codespace to spin itself up.**
73
-
74
-
1. Verify your codespace is running. The browser should contain a VS Code web-based editor and a terminal should be present such as the below:
75
-
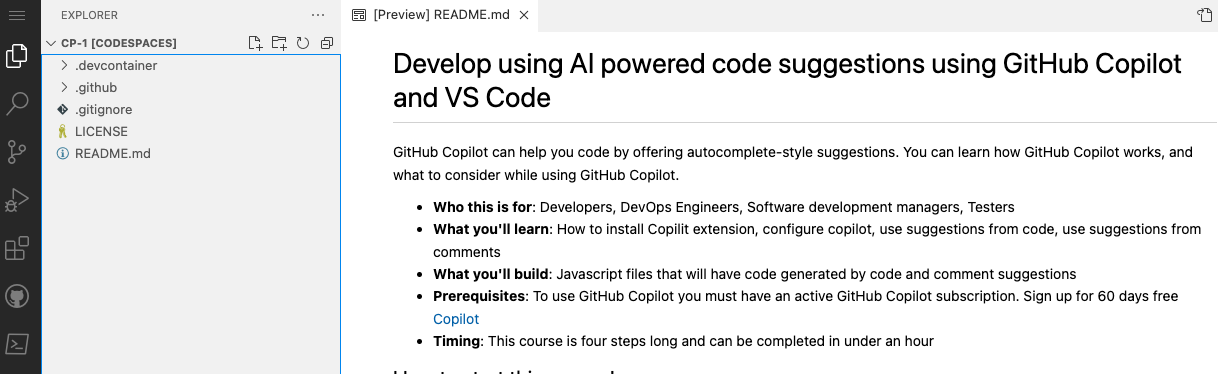
76
-
1. The `copilot` extension should show up in the VS Code extension list. Click the extensions sidebar tab. You should see the following:
77
-
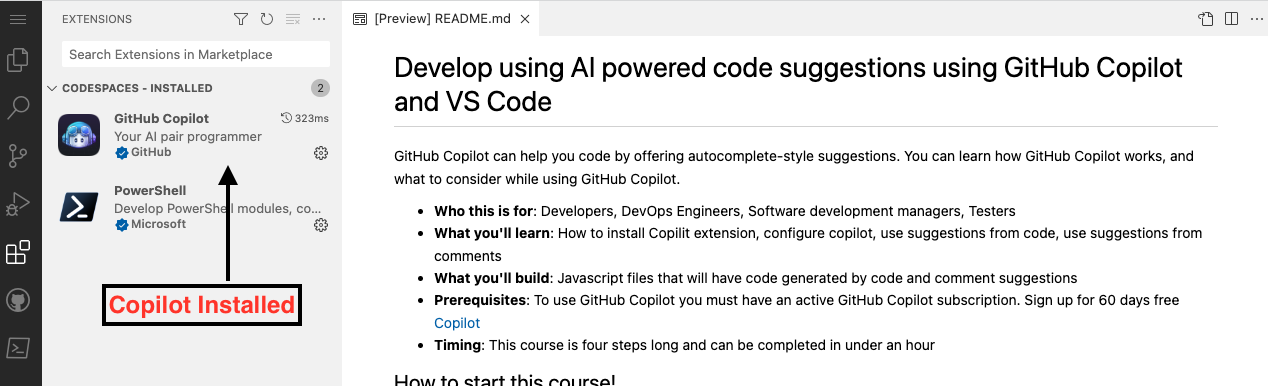
78
72
79
73
**Wait about 60 seconds then refresh your repository landing page for the next step.**
0 commit comments